Abstract
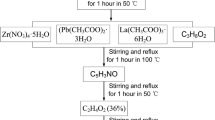
In order to avoid the deterioration of the electrical properties of the lead zirconate titanate (PZT) coating due to the poor bonding performance between the PZT coating and the metal substrate, an Al2O3 layer is introduced as a transition layer between the PZT coating and the metal substrate. It is found that the failure of the PZT/Al2O3 structure depends on the size of the transition layer. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) results show that as the transition layer thickness increases beyond 90 μm, cracks appear in the coating, and the crack direction is perpendicular to the PZT/Al2O3 interface. With the increase in thickness, in addition to the cracks perpendicular to the PZT/Al2O3 interface, cracks parallel to the interface also appeared in the coating. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show that the PZT coating samples have a typical perovskite structure, and their crystallinity is negatively correlated with Al2O3 thickness. With the increase of the transition layer thickness, the electrical properties of PZT/Al2O3 gradually decrease. Piezoelectric force microscope (PFM) results show that the amplitude response decreases with increasing Al2O3 thickness. When the Al2O3 thickness is 110 μm, the energy loss during the polarization process is the most significant. The residual stress results show that different sizes of Al2O3 transition layers provide different initial stress conditions for the PZT/Al2O3 structure. The initial compressive residual stress increases with increasing Al2O3 layer thickness. It changes the stress distribution at the interface and provides a driving force for crack growth, and the structural integrity of the PZT coating is damaged. The phase results show that the domain size of the PZT coating increases with the increase of the Al2O3 layer size, which may be due to the peeling between PZT and Al2O3, which makes the PZT layer not completely constrained by the matrix, and the domain size of the PZT coating increases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.F. Janas and A. Safari, Overview of Fine-Scale Piezoelectric Ceramic/Polymer Composite Processing, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1995, 78(11), p 2945-2955.
Z. Xue, C. Wang, and H. Tan, Controlled Surface Wrinkling as a Novel Strategy for the Compressibility-Tunable PZT Film-Based Energy Harvesting System, Extreme Mech. Lett., 2021, 42(10), p 101102.
J. He, J. Zhang, S. Qian, X. Chen, and X. Chou, Flexible Heterogeneous Integration of PZT Film by Controlled Spalling Technology, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 807, p 151696.
N.A. Strnad, B.M. Hanrahan, D.M. Potrepka, J.S. Pulskamp, R.J. Phaneuf, and R.G. Polcawich, Growth of Thin Film Ferroelectric PZT, PHT, and Antiferroelectric PHO From Atomic Layer Deposition Precursors, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 104(13), p 1216-1228.
Y. Luo, T. Qu, Y. Cui, Y. Pan, and B. Zhang, Cylindrical Fused Silica Resonators Driven by PZT Thin Film Electrodes with Q Factor Achieving 2.89 Million After Coating, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), p 9461.
K.K. Sappati and S. Bhadra, Flexible Piezoelectric 0-3 PZT–PDMS Thin Film for Tactile Sensing, IEEE Sens. J., 2020, 20(9), p 4610-4617.
T. Ito, T. Nishi, T. Umegaki, H. Hida, and I. Kanno, Iop, The piezoelectric PZT thin films deposited on metal substrates, in 17th International Conference on Micro and Nanotechnology for Power Generation and Energy Conversion Applications (PowerMEMS), 2017 (Kanazawa, JAPAN).
A. Sharma, Z.G. Ban, S.P. Alpay, and J.V. Mantese, Pyroelectric Response of Ferroelectric Thin Films, J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 95(7), p 3618-3625.
G.S. Wang, D. Remiens, E. Dogheche, and X.L. Dong, Effect of Thermal Strain on Structure and Polarization Fatigue of CSD-Derived PbZr0.53Ti0.47O3/LaNiO3 Hetero-structures, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process., 2007, 88(4), p 657-660.
L.G. Meiners, Electrical Properties of Al2O3 and AlPxOy Dielectric Layers on InP, Thin Solid Films, 1984, 113(2), p 85-92.
Q. Wan, N. Zhang, L. Wang, Q. Shen, and C. Lin, Preparation of PZT on Diamond by Pulsed Laser Deposition with Al2O3 Buffer Layer, Thin Solid Films, 2002, 415(1), p 64-67.
S.W. Bae, H.H. Park, and T.S. Kim, Ferroelectric Properties of Direct-Patterned Half-Micron Thick PZT Film, Sens. Actuators A, 2006, 125(2), p 548-552.
V.P. Afanas’ev, G.N. Mosina, A.A. Petrov, I.P. Pronin, L.M. Sorokin, and E.A. Tarakanov, Specific Properties of the PZT-Based Thin-Film Capacitor Structures with Excess Lead Oxide, Tech. Phys. Lett., 2001, 27(6), p 467-469.
K. Sreenivas and M. Sayer, Characterization of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Thin Films Deposited From Multielement Metal Targets, J. Appl. Phys., 1988, 64(3), p 1484-1493.
S.B. Krupanidhi, Recent Advances in the Deposition of Ferroelectric Thin Films, Integr. Ferroelectr., 1992, 1(2-4), p 161-180.
J. Akedo, Aerosol Deposition of Ceramic Thick Films at Room Temperature: Densification Mechanism of Ceramic Layers, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(6), p 1834-1839.
J.-J. Choi, J. Ryu, B.-D. Hahn, W.-H. Yoon, and D.-S. Park, Effects of a Conducting LaNiO3 Thick Film as a Buffer Layer of a Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Film on Titanium Substrates, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2009, 6(6), p 687-691.
M.-R. Huang, C.-J. Peng, and H.-Y. Lu, Aerosol Deposition of Dense Lead Zirconate Titanate Thin Films at Room Temperature, Ceram. Int., 2004, 30(8), p 2163-2169.
L. Zhou, Z.G. **ng, H.D. Wang, P.F. He, and X.Y. Zhu, Interfacial Microstructure and Bonding Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Multilayer Ceramic Coating (Al2O3/BaTiO3/Al2O3-40 wt.% TiO2), J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2020, 29(8), p 1-14.
T. Yamada, J. Yasumoto, D. Ito, O. Sakata, Y. Imai, T. Kiguchi, T. Shiraishi, T. Shimizu, H. Funakubo, and M. Yoshino, Negligible Substrate Clam** Effect on Piezoelectric Response in (111)-Epitaxial Tetragonal Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Films, J. Appl. Phys., 2015, 99(7), p 225.
T. Fujisawa, Y. Ehara, S. Yasui, T. Kamo, T. Yamada, O. Sakata, and H. Funakubo, Direct Observation of Intrinsic Piezoelectricity of Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 by Time-Resolved X-Ray Diffraction Measurement Using Single-Crystalline Films, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105, p 012905.
J.W. Lee, C.S. Park, J.H. Jo, and H.E. Kim, Thick Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Film Without Substrate, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91(7), p 072903.
M. Schwanninger, J.C. Rodrigues, H. Pereira, and B. Hinterstoisser, Effects of Short-Time Vibratory Ball Milling on the Shape of FT-IR Spectra of Wood and Cellulose, Vib. Spectrosc., 2004, 36(1), p 23-40.
L. Zhou, C. Meng, Y. Dong, and Z. Yuan, Enhanced Dielectric and Microwave Absorption Properties of Cr/Al2O3 Coatings Deposited by Low-Power Plasma Spraying, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2016, 100(2), p 620-626.
E. Klyatskin, L. Espinosa-Fernández, G. Darut, F. Segovia, M.D. Salvador, G. Montavon, and H. Agorges, Sliding Wear Behavior of Al2O3-TiO2 COATINGS FABRICATED by the Suspension Plasma Spraying Technique, Tribol. Lett., 2015, 59(1), p 85.
S. Goel, S. Bjrklund, N. Curry, S. Govindarajan, and S. Joshi, Axial Plasma Spraying of Mixed Suspensions: A Case Study on Processing, Characteristics, and Tribological Behavior of Al2O3-YSZ Coatings, Appl. Sci., 2020, 10(15), p 5140.
G. Bolelli, J. Rauch, V. Cannillo, A. Killinger, L. Lusvarghi, and R. Gadow, Microstructural and Tribological Investigation of High-Velocity Suspension Flame Sprayed (HVSFS) Al2O3 Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(1), p 35-49.
A. Guignard, G. Mauer, R. Vaen, and D. Stver, Deposition and Characteristics of Submicrometer-Structured Thermal Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2012, 21(3-4), p 416-424.
Ki. Tajima, H.J. Hwang, M. Sando, and K. Niihara, Electric-Field-Induced Crack Growth Behavior in PZT/Al2O3 Composites, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 83(3), p 65-653.
K.I. Kim, H.C. Ju, D.M. Kim, W.G. Kim, and T.W. Hong, Evaluation of Hydrogen Permeation on Al2O3-PZT Composite Membrane, Solid State Ion., 2012, 225, p 712-715.
C.C. Chou, C.S. Hou, and T.H. Yeh, Domain Pinning Behavior of Ferroelectric Pb1-xSrxTiO3 Ceramics, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 25(12), p 2505-2508.
B. Satish, A.R. James, and M.K. Jayaraj, Structural and Electrical Properties of Pulsed Laser Deposited BaPbO3 Conductive Thin Films and its Effect on the Ferroelectric Properties of PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3/BaPbO3 Heterostructures, Ferroelectrics, 2017, 510(1), p 71-79.
E. Obelode and J. Gibmeier, Residual Stress Analysis on Thick Film Systems by the Incremental Hole-Drilling Method—Simulation and Experimental Results, Exp. Mech., 2013, 53(6), p 965-976.
T. Liu, M.L. Wallace, S.E. Trolier-Mckinstry, and T.N. Jackson, High-Temperature Crystallized Thin-Film PZT on Thin Polyimide Substrates, J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 122(16), 164103.
T. Ohno, K. Fukumitsu, T. Honda, A. Sakamoto, S. Tanaka, S. Hirai, T. Matsuda, N. Sakamoto, and H. Suzuki, Piezoelectric Properties of a Near Strain-Free Lead Zirconate Titanate Thin Films Deposited on a Si Substrate, Mater. Lett., 2019, 239(MAR 15), p 71-74.
X. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Shi, J. Jian, and H. Yang, Heteroepitaxy of Flexible Piezoelectric Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)O3 Sensor on Inorganic Mica Substrate for Lamb Wave-Based Structural Health Monitoring, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, p 13156.
M.G. Kang, M.S. Noh, J.J. Pyeon, W.S. Jung, and C.Y. Kang, Direct Growth of Ferroelectric Oxide Thin Films on Polymers Through Laser-Induced Low-Temperature Liquid-Phase Crystallization, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32(15), p 6483-6493.
L. Pintilie, I. Vrejoiu, D. Hesse, G. Lerhun, and M. Alexe, Extrinsic Contributions to the Apparent Thickness Dependence of the Dielectric Constant in Epitaxial Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Thin Films, Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 75(22), p 224113.
B.A. Tuttle, J.A. Voigt, T.J. Garino, D.C. Goodnow, R.W. Schwartz, D.L. Lamppa, T.J. Headley, and M.O. Eatough, Chemically prepared Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 thin films: The effects of orientation and stress, in Eighth IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, 1992 (Greenville), p. 344.
Acknowledgment
The author thanks for the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China. And the author also thanks Microscopic Technology & Analysis Center, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences in SEM measurements.
Funding
The paper was financially supported by the General program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52130509) and Key basic research project of the Foundation Strengthening Plan (Grant No. 2019-JCJQ-JJ-034, 2019-JCJQ-ZD-302); And the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [HEUCF].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, Q., Guo, W., Huang, Y. et al. Effect of Al2O3 Transition Layer Thickness on the Microstructure and Ferroelectric Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate. J Therm Spray Tech 32, 1667–1677 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-023-01578-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-023-01578-2