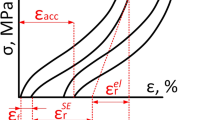
Abstract
In order to develop biomedical shape memory alloys with high biocompatibility, novel (Ti-xZr)-2Mn-2Mo (TZMM) alloys were designed, and their microstructure, shape memory effect and martensitic transformation behavior were investigated. In this study, Ti/Zr atomic ratio of the TZMM alloys was varied between 1, 2 and 5. The experimental results revealed that the TZMM alloys were all composed of single β phase before plastic deformation. A certain amount of stress-induced α″ phase appeared after 2% strain loading. Primary β twin-bands and secondary stress-induced martensite (SIM) α″ twins were activated simultaneously in the β matrix of the TZMM alloys. (TZ)5:1MM alloy with a favorable {001}β<110>β recrystallization texture showed relatively optimal shape memory effect within the TZMM alloys, with a recoverable strain of 2.9%. The increase of Zr content in the alloy increased the β phase stability of metastable TZMM alloys, thereby requiring for higher stress to induce the martensitic transformation and ultimately impairing the shape memory effect of the alloys.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these finds cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
G.F. Andreasen and T.B. Hilleman, An Evaluation of 55 Cobalt Substituted Nitinol Wire for use in Orthodontics, J. Am. Dent. Assoc., 1971, 82, p 1373–1375.
J. Mohd Jani, M. Leary, A. Subic, and M.A. Gibson, A Review of Shape Memory Alloy Research, Applications and Opportunities, Mater. Design, 2014, 56, p 1078–1113.
N.B. Morgan, Medical Shape Memory Alloy Applications-The Market and its Products, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 378, p 16–23.
M. Pocek, F. Maspes, S. Masala, E. Squillaci, and G. Simonetti, Palliative Treatment of Neoplastic Strictures by Self-Expanding Nitinol Strecker Stent, Eur. Radiol., 1996, 6, p 230–235.
A. Biesiekierski, J. Wang, M.A.H. Gepreel, and C. Wen, A New Look at Biomedical Ti-Based Shape Memory Alloys, Acta. Biomater., 2012, 8, p 1661–1669.
D. Beyersmann and A. Hartwig, Carcinogenic Metal Compounds: Recent Insight into Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms, Arch. Toxicol., 2008, 82, p 493–512.
H.Y. Kim, T. Sasaki, K. Okutsu, J.I. Kim, T. Inamura, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, Texture and Shape Memory Behavior of Ti-22Nb-6Ta Alloy, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, p 423–433.
Y. Al-Zain, H.Y. Kim, H. Hosoda, T.H. Nam, and S. Miyazaki, Shape Memory Properties of Ti-Nb-Mo Biomedical Alloys, Acta. Mater., 2010, 58, p 4212–4223.
T. Maeshima, S. Ushimaru, K. Yamauchi, and M. Nishida, Effect of Heat Treatment on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity in Ti-Mo-Sn Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 25, p 844–847.
H.Y. Kim, S. Hashimoto, J.I. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, Mechanical Properties and Shape Memory Behavior of Ti-Mo-Ga Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 25, p 438–440.
Y. Cui and L.K.H.B. YanLuoXu, Microstructure and Shape Memory Effect of Ti-20Zr-10Nb Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 652–656.
W. Qu, X. Sun, B. Yuan, C. **ong, Y. Li, and Y. Nie, Phase Transformation and Microstructure Evolution of the Deformed Ti-30Zr-5Nb Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2017, 126, p 81–85.
Y. Li, Y. Cui, F. Zhang, and H. Xu, Shape Memory Behavior in Ti-Zr Alloys, Scripta. Mater., 2011, 64, p 584–587.
J. Wang, Q. Li, C. **ong, L. Yan, and B. Sun, Effect of Zr on the Martensitic Transformation and the Shape Memory Effect in Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2017, 737, p 672–677.
Q. Li, X. Ma, C. **ong, W. Qu, and Y. Li, Effects of Annealing Temperature on Microstructures and Shape Memory Effect of Ti-19Zr-11Nb-2Ta Alloy Sheets, J. Alloy Compd., 2021, 897, p 162728.
J. Zhang, S. Fan, Y. Hao, N. Gozdecki, E. Lebrun, P. Vermaut, R. Portier, T. Gloriant, P. Laheurte, and F. Prima, Influence of Equiatomic Zr/Nb Substitution on Superelastic Behavior of Ti-Nb-Zr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 563, p 78–85.
S. Li and T.H. Nam, Superelasticity and Tensile Strength of Ti-Zr-Nb-Sn Alloys with High Zr Content for Biomedical Applications, Intermetallics, 2019, 112, 106545.
H.Y. Kim, Y. Ikehara, J.I. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, Martensitic Transformation, Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of Ti-Nb Binary Alloys, Acta. Mater., 2006, 54, p 2419–2429.
P. Xue, Y. Li, F. Zhang, and C. Zhou, Shape Memory Effect and Phase Transformations of Ti-19.5Zr-10Nb-0.5Fe Alloy, Scripta. Mater., 2015, 101, p 99–102.
S. Li, I.U. Rehman, J.H. Lim, W.T. Lee, J.B. Seol, J.G. Kim, and T.H. Nam, Effect of Sn Content on Microstructure, Texture Evolution, Transformation Behavior and Superelastic Properties of Ti–20Zr–9Nb–(2–5)Sn (at.%) Shape Memory Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 827, p 141994.
H.Y. Kim, J. Fu, H. Tobe, J. Kim, and S. Miyazaki, Crystal Structure, Transformation Strain, and Superelastic Property of Ti-Nb-Zr and Ti-Nb-Ta Alloys, Shap. Mem. Superelasticity, 2015, 1, p 107–116.
A. Konopatsky, V. Sheremetyev, S. Dubinskiy, Y. Zhukova, K. Firestein and D. Golberg, Structure and Superelasticity of Novel Zr-Rich Ti-Zr-Nb Shape Memory Alloys, Shap. Mem. Superelasticity, 2021, 7(2), p 304–313.
A. Kudryashova, V. Sheremetyev, K. Lukashevich, V. Cheverikin, and V. Brailovski, Effect of a Combined Thermomechanical Treatment on the Microstructure, Texture and Superelastic Properties of Ti-18Zr-14Nb Alloy for Orthopedic Implants, J. Alloy Compd., 2020, 843, p 156066.
G.N. Dayananda and M.S. Rao, Effect of Strain rate on Properties of Superelastic Niti Thin Wires, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 486, p 96–103.
S. Li, Y.W. Kim, M.S. Choi, and T.H. Nam, Achieving High Porosity and Large Recovery Strain in Ni-Free High Zr-Containing Ti-Zr-Based Shape Memory Alloy Scaffolds by Fiber Metallurgy, Intermetallics, 2021, 128, 107015.
J.Y. Zhang, F. Sun, Z. Chen, Y. Yang, B.L. Shen, J. Li, and F. Prima, Strong and Ductile Beta Ti-18Zr-13Mo Alloy with Multimodal Twinning, Mater. Res. Lett., 2019, 7, p 251–257.
X. Song, C. **ong, F. Zhang, Y. Nie, and Y. Li, Strain Induced Martensite Stabilization in β Ti-Zr-Nb Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2019, 259, 126914.
A. Konopatsky, T.O. Teplyakova, D.V. Popova, K.Y. Vlasova, S.D. Prokoshkin, and D.V. Shtansky, Surface Modification and Antibacterial Properties of Superelastic Ti-Zr-Based Alloys for Medical Application, Coll. Surf. Biointerfaces, 2021, 209, 112183.
M.F. Ijaz, H.Y. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, Superelastic Properties of Biomedical (Ti-Zr)-Mo-Sn Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2015, 48, p 11–20.
A. Biesiekierski, D. **, Y. Li, J. Lin, K.S. Munir, Y. Yamabe-Mitarai, and C. Wen, Extraordinary High Strength Ti-Zr-Ta Alloys Through Nanoscaled, Dual-Cubic Spinodal Reinforcement, Acta. Biomater., 2017, 53, p 549–558.
S. Li, M.S. Choi, and T.H. Nam, Effect of Thermo-Mechanical Treatment on Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Superelastic Ti-Zr-Based Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 789, p 139664.
J.Y. Zhang, J.S. Li, G.F. Chen, L. Liu, Z. Chen, Q.K. Meng, B.L. Shen, F. Sun, and F. Prima, Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel β Metastable Ti-Mo-Zr Alloy with Large Ductility and Improved Yield Strength, Mater. Charact., 2018, 139, p 421–427.
S. Miyazaki, My Experience with Ti-Ni-Based and Ti-Based shape memory alloys, Shap. Mem. Superelasticity, 2017, 3, p 279–314.
C.H. Wang, M. Liu, P.F. Hu, J.C. Peng, J.A. Wang, Z.M. Ren, and G.H. Cao, The Effects of α″ and ω Phases on the Superelasticity and Shape Memory Effect of Binary Ti-Mo Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2017, 720, p 488–496.
T. Inamura, R. Shimizu, H.Y. Kim, S. Miyazaki, and H. Hosoda, Optimum Rolling ratio for Obtaining 001 Recrystallization Texture in Ti-Nb-Al Biomedical Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 61, p 499–505.
T. Inamura, Y. Kinoshita, J.I. Kim, H.Y. Kim, and S. Miyazaki, Effect of 001 <110> Texture on Superelastic Strain of Ti-Nb-Al Biomedical Shape Memory Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 438, p 865–869.
T. Inamura, H.Y. Kim, and H. Tobe, Origin of 332 Twinning in Metastable β-Ti Alloys, Acta Mater., 2014, 64, p 345–355.
F. Sun, J.Y. Zhang, M. Marteleur, T. Gloriant, P. Vermaut, D. Laille, P. Castany, C. Curfs, P.J. Jacques, and F. Prima, Investigation of Early Stage Deformation Mechanisms in a Metastable β Titanium Alloy Showing Combined Twinning-Induced Plasticity and Transformation-Induced Plasticity Effects, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 6406–6417.
P.J. Buenconsejo, H.Y. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki, Shape Memory Behavior of Ti-Ta and its Potential as a High-Temperature Shape Memory Alloy, Acta Mater., 2009, 57, p 1068–1077.
S. Miyazaki, H.Y. Kim, and H. Hosoda, Development and Characterization of Ni-Free Ti-Base Shape Memory and Superelastic Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 25, p 438–440.
M. Abdel-Hady, H. Fuwa, K. Hinoshita, H. Kimura, Y. Shinzato, and M. Morinaga, Phase Stability Change with Zr Content in β-Type Ti-Nb Alloys, Scripta Mater., 2007, 57, p 1000–1003.
Y.L. Hao, S.J. Li, S.Y. Sun, and R. Yang, Effect of Zr and Sn on Young’s Modulus and Superelasticity of Ti-Nb-Based Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 441, p 112–118.
J.J. Gao, I. Thibon, D. Laillé, P. Castany, and T. Gloriant, Influence of Texture and Transformation Strain on the Superelastic Performance of a New Ti-20Zr-3Mo-3Sn Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 762, 138075.
S. Hanada, M. Ozeki, and O. Izumi, Deformation Characteristics in β Phase Ti-Nb Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1985, 16, p 789–795.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0304700, 2017YFB0304704), the science and technology planning project of Guangdong province (No. 2017B090903005) and the Education Department of Guangdong Province No. 2020ZDZX2024. XJW acknowledges the financial support from **an University (No. 21620110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL performed investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. JL did validation and investigation. WL and XZ contributed to validation and data curation. WL was involved in validation and supervision. XW was involved in writing—review & editing, funding acquisition, conceptualization, and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Li, J., Lai, W. et al. Effect of Equiatomic Ti/Zr Substitution on the Shape Memory Effect of Biomedical Ti-Zr-Mn-Mo Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 8721–8730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06963-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06963-6