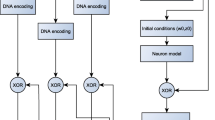
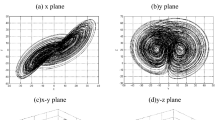
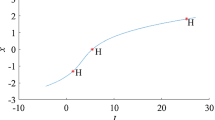
Abstract
Bursting is a diverse and common phenomenon in neuronal activation patterns and it indicates that fast action voltage spiking periods are followed by resting periods. The interspike interval (ISI) is the time between successive action voltage spikes of neuron and it is a key indicator used to characterize the bursting. Recently, a three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh-Rose (mHR) neuron model was constructed to generate hidden chaotic bursting. However, the properties of the discrete mHR neuron model have not been investigated, yet. In this article, we first construct a discrete mHR neuron model and then acquire different hidden chaotic bursting sequences under four typical sets of parameters. To make these sequences more suitable for the application, we further encode these hidden chaotic sequences using their ISIs and the performance comparative results show that the ISI-encoded chaotic sequences have much more complex chaos properties than the original sequences. In addition, we apply these ISI-encoded chaotic sequences to the application of image encryption. The image encryption scheme has a symmetric key structure and contains plain-text permutation and bidirectional diffusion processes. Experimental results and security analyses prove that it has excellent robustness against various possible attacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, Mao S, Liu Y. Big data: A survey. Mobile Netw Appl, 2014, 19: 171–209
Yang C, Huang Q, Li Z, et al. Big data and cloud computing: Innovation opportunities and challenges. Int J Digit Earth, 2017, 10: 13–53
Yu S D, Liu L L, Wang Z Y, et al. Transferring deep neural networks for the differentiation of mammographic breast lesions. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 441–447
Su L, Wang L Y, Li K, et al. Automated X-ray recognition of solder bump defects based on ensemble-ELM. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 1512–1519
Tawalbeh L, Muheidat F, Tawalbeh M, et al. IoT privacy and security: Challenges and solutions. Appl Sci, 2020, 10: 4102
Baptista M S. Cryptography with chaos. Phys Lett A, 1998, 240: 50–54
Kocarev L. Chaos-based cryptography: A brief overview. IEEE Circ Syst Mag, 2001, 1: 6–21
Fadhel S, Shafry M, Farook O. Chaos image encryption methods: A survey study. Bull EEI, 2017, 6: 99–104
Hua Z, Zhu Z, Chen Y, et al. Color image encryption using orthogonal Latin squares and a new 2D chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn, 2021, 104: 4505–4522
Bao B C, Zhu Y X, Ma J, et al. Memristive neuron model with an adapting synapse and its hardware experiments. Sci China Tech Sci, 2021, 64: 1107–1117
Rajamani V, Kim H, Chua L. Morris-Lecar model of third-order barnacle muscle fiber is made of volatile memristors. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 060426
Chen M, Qi J W, Wu H G, et al. Bifurcation analyses and hardware experiments for bursting dynamics in non-autonomous memristive FitzHugh-Nagumo circuit. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 1035–1044
Lu L L, Jia Y, Xu Y, et al. Energy dependence on modes of electric activities of neuron driven by different external mixed signals under electromagnetic induction. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 427–440
Du L, Cao Z L, Lei Y M, et al. Electrical activities of neural systems exposed to sinusoidal induced electric field with random phase. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 1141–1150
Lv M, Ma J, Yao Y G, et al. Synchronization and wave propagation in neuronal network under field coupling. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 448–457
Aihara K, Takabe T, Toyoda M. Chaotic neural networks. Phys Lett A, 1990, 144: 333–340
Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol, 1952, 117: 500–544
Bao H, Liu W, Chen M. Hidden extreme multistability and dimensionality reduction analysis for an improved non-autonomous memristive FitzHugh-Nagumo circuit. Nonlinear Dyn, 2019, 96: 1879–1894
Xu Q, Tan X, Zhu D, et al. Bifurcations to bursting and spiking in the Chay neuron and their validation in a digital circuit. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2020, 141: 110353
Bao H, Zhu D, Liu W, et al. Memristor synapse-based Morris-Lecar model: Bifurcation analyses and FPGA-based validations for periodic and chaotic bursting/spiking firings. Int J Bifurcat Chaos, 2020, 30: 2050045
Lin H, Wang C, Sun Y, et al. Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn, 2020, 100: 3667–3683
Hindmarsh J L, Rose R M. A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature, 1982, 296: 162–164
Rose R M, Hindmarsh J L. The assembly of ionic currents in a thalamic neuron I. The three-dimensional model. Proc Royal Soc Lond B, 1989, 237: 267–288
Tlelo-Cuautle E, Díaz-Muñoz J D, González-Zapata A M, et al. Chaotic image encryption using hopfield and Hindmarsh-Rose neurons implemented on FPGA. Sensors, 2020, 20: 1326
Yang Y, Wang L, Duan S, et al. Dynamical analysis and image encryption application of a novel memristive hyperchaotic system. Optics Laser Tech, 2021, 133: 106553
Hu G, Li B. Coupling chaotic system based on unit transform and its applications in image encryption. Signal Process, 2021, 178: 107790
Khan M, Masood F. A novel chaotic image encryption technique based on multiple discrete dynamical maps. Multimed Tools Appl, 2019, 78: 26203–26222
Wang S C, Wang C H, Xu C. An image encryption algorithm based on a hidden attractor chaos system and the Knuth-Durstenfeld algorithm. Optics Lasers Eng, 2020, 128: 105995
Hua Z Y, Zhou B H, Zhang Y X, et al. Modular chaotification model with FPGA implementation. Sci China Tech Sci, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1717-1
Hua Z, Zhou Y, Huang H. Cosine-transform-based chaotic system for image encryption. Inf Sci, 2019, 480: 403–419
Wang X, Guan N, Zhao H, et al. A new image encryption scheme based on coupling map lattices with mixed multi-chaos. Sci Rep, 2020, 10: 9784
Zhang Y, Tang Y. A plaintext-related image encryption algorithm based on chaos. Multimed Tools Appl, 2018, 77: 6647–6669
Li H, Hua Z, Bao H, et al. Two-dimensional memristive hyperchaotic maps and application in secure communication. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3022539
Bao H, Hu A, Liu W, et al. Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2020, 31: 502–511
Yang Y, Liao X. Filippov Hindmarsh-Rose neuronal model with threshold policy control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2019, 30: 306–311
Bao B, Hu A, Bao H, et al. Three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with hidden coexisting asymmetric behaviors. Complexity, 2018, 2018: 1–11
Djeundam S R D, Yamapi R, Kofane T C, et al. Deterministic and stochastic bifurcations in the Hindmarsh-Rose neuronal model. Chaos, 2013, 23: 033125
Lakshmanan S, Lim C P, Nahavandi S, et al. Dynamical analysis of the Hindmarsh-Rose neuron with time delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2017, 28: 1953–1958
Li B, He Z. Bifurcations and chaos in a two-dimensional discrete Hindmarsh-Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn, 2014, 76: 697–715
Jafari S, Sprott J C, Golpayegani S M R H. Elementary quadratic chaotic flows with no equilibria. Phys Lett A, 2013, 377: 699–702
Gu H, Pan B, Chen G, et al. Biological experimental demonstration of bifurcations from bursting to spiking predicted by theoretical models. Nonlinear Dyn, 2014, 78: 391–407
Bao H, Chen M, Wu H G, et al. Memristor initial-boosted coexisting plane bifurcations and its extreme multi-stability reconstitution in two-memristor-based dynamical system. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 603–613
Bandt C, Pompe B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 88: 174102
Richman J S, Moorman J R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2000, 278: 2039–2049
Lorenz E N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J Atmos Sci, 1963, 20: 130–141
Chen G, Ueta T. Yet another chaotic attractor. Int J Bifurcat Chaos, 1999, 09: 1465–1466
Xu C, Sun J, Wang C. A novel image encryption algorithm based on bit-plane matrix rotation and hyper chaotic systems. Multimed Tools Appl, 2020, 79: 5573–5593
Wang B, Zhang B F, Liu X W. An image encryption approach on the basis of a time delay chaotic system. Optik, 2021, 225: 165737
Hua Z, Zhu Z, Yi S, et al. Cross-plane colour image encryption using a two-dimensional logistic tent modular map. Inf Sci, 2021, 546: 1063–1083
Ye G, Huang X. Spatial image encryption algorithm based on chaotic map and pixel frequency. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 058104
Pak C, Huang L. A new color image encryption using combination of the 1D chaotic map. Signal Process, 2017, 138: 129–137
Preishuber M, Hutter T, Katzenbeisser S, et al. Depreciating motivation and empirical security analysis of chaos-based image and video encryption. IEEE Trans Inform Forensic Secur, 2018, 13: 2137–2150
Gan Z, Chai X, Han D, et al. A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on 3-D bit-plane permutation. Neural Comput Applic, 2019, 31: 7111–7130
Alvarez G, Li S. Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems. Int J Bifurcat Chaos, 2006, 16: 2129–2151
Luo Y, Du M, Liu J. A symmetrical image encryption scheme in wavelet and time domain. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul, 2015, 20: 447–460
Wang N, Li C, Bao H, et al. Generating multi-scroll Chua’s attractors via simplified piecewise-linear Chua’s diode. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2019, 66: 4767–4779
Wu Y, Noonan J P, Agaian S. NPCR and UACI randomness tests for image encryption. Cyber J Multidiscip J Sci Tech, 2011, 1: 31–38
Yuan J, Wu Y, Lu X, et al. Recent advances in deep learning based sentiment analysis. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 1947–1970
** H, Cao Y, Wang T, et al. Recent advances of neural text generation: Core tasks, datasets, models and challenges. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 1990–2010
Zhang J, Zong C. Neural machine translation: Challenges, progress and future. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 2028–2050
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51777016, 51607013 and 62071142).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, H., Hua, Z., Liu, W. et al. Discrete memristive neuron model and its interspike interval-encoded application in image encryption. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64, 2281–2291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-021-1845-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-021-1845-x