Abstract
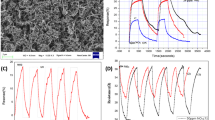
A carbon monoxide gas sensor based on single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) has been developed for detection of carbon monoxide (CO) at room temperature. Copper chloride (CuCl) was mixed with SWNT by mechanical blending. The thin film was deposited on interdigitated electrodes by using airbrush technology. This paper described the fabrication of the sensor for detecting carbon monoxide with concentrations from 20 ppm to 100 ppm. The performance of CO gas sensor was measured by using relevant apparatus to obtain the continuous sensor electric resistance change on exposure to CO and air atmosphere at room temperature, respectively. The results exhibited that the senor presented a larger sensitivity and a good recoverability. The experimental results suggested the potential use of CuCl doped SWCNT for CO detecting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryan M A, Homer M L, Buehler M G, et al. Monitoring the air quality in a closed chamber using an electronic nose. J SAE Transaction, 1997, 106: 1014–1019
Valentini L, Lozzi L, Cantalini C, et al. Effects of oxygen annealing on gas sensing properties of carbon nanotube thin films. J Thin Solid Films, 2003, 436: 95–100
Khan H Z, Salah A N, Habib S S, et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes film sensor for carbon mono-oxide gas. J Current Nanoscience, 2012, 8: 274–279
Mubeen S, Lai M, Zhang T, et al. Hybrid tin oxide-SWNT nanostructures based gas sensor. J Electrochim Acta, 2013, 92: 484–490
Kim H, Hong M H, Jang H W, et al. CO gas sensing properties of direct-patternable TiO2 thin films containing multi-wall carbon nanotubes. J Thin Solid Films, 2012, 529: 89–93
Jeong H Y, Lee D S, Choi H K, et al. Flexible room-temperature NO gas sensors based on carbon nanotubes/reduced graphene hybrid films. J Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 213105
Shang S, Li L, Yang X, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate-carbon nanotubes composites prepared by microemulsion polymerization for gas sensor. J Compos Sci Technol, 2009, 69: 1156–1159
Kong J, Franklin N R, Zhou C, et al. Nanotube molecular wires as chemical sensors. Science, 2000, 287: 622–625
Collins P G, Bradley K, Ishigami M, et al. Extreme oxygen sensitivity of electronic properties of carbon nanotubes. Science, 2000, 287: 1801–1804
Lucas F O, McNally P J, Daniels S, et al. Electrical properties of γ-CuCl thin films. J Mater Sci-Mater El, 2009, 20: 144–148
Dutta P K, Rao R R, Swartz S L, et al. Sensing of carbon monoxide gas in reducing environments. Sensor Actuat B-Chem, 2002, 84: 189–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Tai, H., **e, G. et al. A carbon monoxide sensor based on single-walled carbon nanotubes doped with copper chloride. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56, 2576–2580 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5337-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5337-8