Abstract
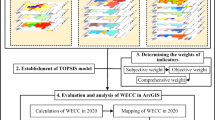
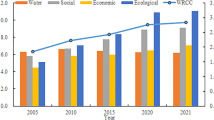
This study aims to investigate the water resource carrying capacity (WRCC) of Henan Province, identify its main obstacles, and provide suggestions for optimizing its WRCC. The article constructs a WRCC evaluation system with 20 indicators for the four subsystems of water resources, economy, society, and ecology based on literature and the actual situation of Henan Province. The entropy weighted TOPSIS method is used to calculate the WRCC of Henan Province from 2005 to 2021. The coupling coordination model is used to explore the degree of coupling coordination among internal systems, while the obstacle model is used to study its restrictive influencing factors. The study found that (1) the WRCC fluctuated in a U-shaped pattern around 0.5 during the study period; (2) the coupling and coordination degree of each subsystem is generally good, except for 2012 and 2013, which showed basic coordination; (3) currently, the main obstacles to the WRCC are ecosystems and water resources. The main indicators are afforestation area, proportion of the tertiary industry, fertilizer usage, and urban sewage treatment rate. Therefore, Henan Province should take measures such as reducing fertilizer usage, standardizing urban sewage treatment, improving water efficiency, and optimizing industrial structure to optimize its WRCC and promote comprehensive utilization of water resources.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyses during the current study are not publicly available due to [REASON(S) WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arrow K, Bolin B, Costanza R et al (1996) Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment[J]. Environ Dev Econ 1(1):104–110. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355770X00000413
Bardram JE (2000) Temporal coordination –on time and coordination of collaborative activities at a surgical department. Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW) 9:157–187
Broten N (2017) An essay on the principle of population[M]. Macat Library; Taylor and Francis
Chang-Ming L, Hong-Rui W (2003) An analysis of the relationship between water resources and population-economy-society environment[J]. J Nat Resour. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.2003.05.017
Cheng C, Liu Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Shen S, Yang R, Xu Z, Hong Y (2019) Diagnosing cropland’s allowable range and spatial allocation in China’s typical mountainous plateau area: An evaluation framework based on ecological carrying capacity. Sci Total Environ 1(685):1255–1268
Chi Y, Xue L, Zhang H (2018) Comprehensive benefit analysis of regional water resources based on multi-objective evaluation. IOP Con. Ser : Earth Environ Sci 108:032040. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/108/3/032040
Chunyang LU, Feng W, Qingyuan Y et al (2011) An evaluation of urban land use performance based on the improved TOPSIS method and diagnosis of its obstacle indicators: A case study of Chongqing[J]. Resour Sci
Dai J, Khan YA (2023) Ecological environment pressure state and response system for coupling coordinate development: an application on china data. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 30(10):25682–25690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23900-1
Duan C, Liu C, Chen X et al (2010) Preliminary research on regional water resources carrying capacity conception and method[J]. Acta Geogr Sin 65(1):82–90
Fan S, Yang X, Feifei W (2020) Catastrophe progression method based on M-K test and correlation analysis for assessing water resources carrying capacity in Hubei province[J]. J Water Clim Chang 11(2)
Feng L-H, Zhang X-C, Luo G-Y (2007) Application of system dynamics in analyzing the carrying capacity of water resources in Yiwu City, China[J]. Math Comput Simul 79(3)
Gao Y, Liu C (1997) Limit analysis on the development and utilization of regional water resources[J]. J Hydraul Eng 8(8):73–79
Heisey P (1996) The conditions of agricultural growth: the economics of agrarian change under population pressure: Ester Boserup. London, Earthscan Publications Ltd, 1993 (first published in 1965). 124 pp. Price: £10.95 (paperback). ISBN 1 85383 159 X[J] 50(3):329–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-521x(96)90017-7
Ji J, Qu X, Zhang Q, Tao J (2022) Predictive analysis of water resource carrying capacity based on system dynamics and improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in Henan Province. Environ Monit Assess 194(7):500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10131-7
Jian C, Liang-Song Z, Yan-Ni H et al (2011) Analysis of harmony degree between urbanization and eco-environment in Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science)
Lei X, Qiu G (2016) Empirical study about the carrying capacity evaluation of regional resources and environment based on entropy-weight TOPSIS model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0580
Lei X, Qiu R, Liu Y (2016) Evaluation of regional land use performance based on entropy TOPSIS model and diagnosis of its obstacle factors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (TCSAE). https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.13.035
Li R, Jiachen G, Shu** S et al (2021) Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in Guiyang City[J]. Water 13(16)
Li Y, Yuyi Y, Wenge Z (2023) Water footprint assessment of major crops in Henan Province and reduction suggestions[J]. Water 15(6)
Li-Hua K, Ying-Cong YE, ** H, Fuqiang W, Lei T (2022) Comprehensive evaluation on water resources carrying capacity based on water-economy-ecology concept framework and EFAST-cloud model: A case study of Henan Province, China[J]. Ecol Indic 143
Lu L, Lei Y, Wu T, Kunyao C (2022) Evaluating water resources carrying capacity: The empirical analysis of Hubei Province, China 2008–2020[J]. Ecol Indic 144
Lu-Feng G, Yan-Tao W, Wei-Bo J et al (2018) Empirical study about the carrying capacity evaluation of marine resources and environment based on the entropy-weight TOPSIS model[J]. Mar Environ Sci
Lv B, Changrong L, Tianxiao L, Meng Fanxiang F, Qiang JY, Renjie H (2023) Evaluation of the water resource carrying capacity in Heilongjiang, eastern China, based on the improved TOPSIS model[J]. Ecol Indic 150
Malakar K, Lu C (2021) Measuring sustainability as distance to ideal position of economy, society and environment: Application to China's provincial water resources (2004-17). J Environ Manage 15(292):112742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112742
Nan G, Yaofeng MA, Tianshun LI et al (2013) Study on the coordinative development between tourism industry and urbanization based on coupling model: a case study of **'an[J]. Tourism Tribune. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2013.01.007
Pang W, Ma YF, Tang ZX (2011) The coupling relationship and coordinated development between tourism economy and ecological environment: A case study of **′an City[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition)
Sun H, Guo H, Li L et al (2000) System analysis on water resources supporting alternatives for Chaidamu Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Enviromentalence
Sun W, Zhang Y, Chen H et al (2022) Trend analysis and obstacle factor of inter provincial water resources carrying capacity in China: from the perspective of decoupling pressure and support capacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:31551–31566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18255-y
Sun X, Zhou Z, Wang Y (2023) Water resource carrying capacity and obstacle factors in the Yellow River basin based on the RBF neural network model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:22743–22759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23712-3
Tong J, ** G (2015) Study on water resources carrying capacity in Nan**g based on principal component analysis[J]. J Water Resour Water Eng 26(01):122–125
Veldkamp TIE, Wada Y, Aerts JCJH, Döll P, Gosling SN, Liu J, Masaki Y, Oki T, Ostberg S, Pokhrel Y, Satoh Y, Kim H, Ward PJ (2017) Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century. Nat Commun 15(8):15697. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15697
Wang S, Xu L, Yang F, Wang H (2014) Assessment of water ecological carrying capacity under the two policies in Tieling City on the basis of the integrated system dynamics model. Sci Total Environ 15(472):1070–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.115
Wang X, Shen D (2019) Impact of high quality development on water resources carrying capacity in the Yellow River Basin[J]. J Environ Econ 4(04):47–62
Wei F, Zhou F, Wang Y (2022a) Evaluation and countermeasures of water resources carrying capacity in Ningbo City [J]. Yellow River 44(S2):97–99
Wei J, Liu L, Ma Y et al (2022b) Spatial temporal pattern of coupling coordination degree between high quality development and ecological environment in Henan Province in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River [J]. J Henan Normal Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 50(02):48–57. https://doi.org/10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2022.02.006
Wetzel KR et al (1995) Sizing the earth: Recognition of economic carrying capacity[J]. Ecol Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-8009(94)00019-R
Wu M, Wu J, Zang C (2020) A comprehensive evaluation of the eco-carrying capacity and green economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China[J]. J Clean Prod 281(1):124945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124945
**aojun L, Hanliang FU, Management SO (2015) Evaluation on water resources carrying capacity based on variable-weight and entropy-weight methods with improved TOPSIS——A case study of prefecture cities in Shaanxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation
**aonan C (2019) Expression and mathematical property of coupling model, and its misuse in geographical science[J]. Econ Geogr
**e N (2020) Coupling of urbanization and the development of the marine tourism industry: an exploratory study[J]. J Coastal Res 106(sp1):213
**ng C, Qin X, **g C (2023) Research on the urban water resources carrying capacity by using system dynamics simulation[J]. Hydrol Res 54(3)
**nqing L, Lixiao Z, Yan H et al (2022) System dynamics modeling of food-energy-water resource security in a megacity of China: Insights from the case of Bei**g[J]. J Clean Prod 355
**n-**n WU (2016) Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity based on combination weight TOPSIS Model[J]. Yunnan Water Power
**nxin F, **gdong LI, Lei LI et al (2019) Evaluation and driving force of water resources carrying capacity in Dianchi Basin[J]. J Irrig Drain
Xu Z, Cao Y (2022) Application of TOPSIS method based on entropy weight evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in Changchun City[J]. J Saf Environ 22(05):2900–2907. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2021.1448
Xuepeng JI, Yong** B, Haibo DU et al (2017) Research on the spatial quantitative evaluation and coupling coordination degree of ecological carrying capacity in Gansu Province[J]. Acta Ecol Sin. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201606071096
Ya-Ru S, Zeng-Chuan D, Miao L (2018) Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity based on improved TOPSIS method and diagnosis of obstacle factors in Yancheng City[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower
Yaqing L, **g Z, Yongyu S (2022) Comprehensive comparison and assessment of three models evaluating water resource carrying capacity in Bei**g, China[J]. Ecol Indic 143
Yifan WU, Guo** L, Chang LU et al (2015) Evaluation of urban land use performance based on the improved TOPSIS model and diagnosis of its obstacle degree in Daqing[J]. Res Soil Water Conserv
Yu Z, Yunfeng C, Pengyan Z et al (2019) Spatial-temporal evolution and coupling analysis of farm land multi-functions in Henan Province[J]. Journal of Henan University(Natural Science)
Zhang J, Dong Z (2022) Assessment of coupling coordination degree and water resources carrying capacity of Hebei Province (China) based on WRESP2D2P framework and GTWR approach[J]. Sustain Cities Soc 82:103862
Zhang J, Guo Z (2016) Comprehensive evaluation on the agricultural drought risk in Henan Province based on Projection Pursuit Model[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment
Zhang Y, Yun G, Yan Z, Zhijie L, Zulin Z, Yulong Z, ** L (2023) Assessment of agricultural water resources carrying capacity and analysis of its spatio-temporal variation in Henan Province, China[J]. J Clean Prod:403
Zhao Y, Rongkun D, Ying Y, Fan L, Yue Z, **nyi W (2022) Integrated evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity during the transformation of resource-exhausted cities based on Euclidean distance and a Gray-TOPSIS model: A case study of Jiaozuo City, China[J]. Ecol Indica 142
Zhong ZY, Jun X, Ge T (2002) A primary study on the theories and process of water resources carrying capacity[J]. Prog Geogr. https://doi.org/10.11820/dlkxjz.2002.02.011
Zhou C, Feng XG, Tang R (2016) Analysis and forecast of coupling coordination development among the regional economy-ecological environment-tourism industry—a case study of provinces along the Yangtze Economic Zone[J]. Econ Geogr
Zuo Q (2017) Review of research methods of water resources carrying capacity[J]. Adv Sci Technol Water Resour 37(3):1–6. https://doi.org/10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2017.03.001
Zuo Q, Zhang X (2015) Dynamic carrying capacity of water resources under climate change[J]. Shuili Xuebao/J Hydraul Eng 46(4):387–395
Zou T, Guo P, Wu Q (2023) Applying an entropy-weighted TOPSIS method to evaluate energy green consumption revolution progressing of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30(14):42267–42281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25175-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“Comprehensive Evaluation of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in Henan Province Based on Entropy Weight TOPSIS -Coupling Coordination—Obstacle Model” is the result of the joint efforts of the three of us, so after discussion, we decided to publish this article as the co first author.
The following is the contribution of each member:
Zhengqi Wei: Develop overall objectives and select appropriate research methods; Write first draft; Supervise; Article management.
Dandan Ji: Data collection; Review and editing; Project implementation and coordination; Revision of the paper.
Le Yang: Data processing; Write first draft; Data comparison and analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not involve human participants or animal research. There is no behavior that does not conform to the ethical standards.
Consent to participate
All authors agree with the contributions of each author in this article, and there is no dispute.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Ji, D. & Yang, L. Comprehensive evaluation of water resources carrying capacity in Henan Province based on entropy weight TOPSIS — coupling coordination — obstacle model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 115820–115838 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30456-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30456-1