Abstract
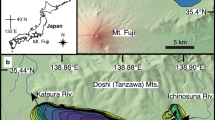
Atmospheric dust has wide-reaching effects, not only influencing climate conditions, but also ecosystems. The eastern region of the Asian continent is one of the largest emitters of dust in the world, and recent economic growth in the region has been accompanied by an increase in anthropogenic emissions. However, the effects of increased Asian dusts on aquatic ecosystems are not well understood. We examined fossil pigments and zooplankton remains from 210Pb-dated sediments taken from high mountain lakes of Hourai-Numa and Hachiman-Numa, located in the Towada-Hachimantai National Park of Japan Islands, to uncover historical changes in the phyto- and zooplankton community over the past 100 years. Simultaneously, we measured the geochemical variables of TOC, TN, TP, δ13C, δ15N, and lead isotopes (207Pb/206Pb, 208Pb/206Pb) in the sediments to identify environmental factors causing such changes. As a result, despite few anthropogenic activities in the watersheds, alpine lakes in Japan had increased algal and herbivore plankton biomasses by 3–6 fold for recent years depending on the surrounding terrestrial vegetation and landscape conditions. Biological and biogeochemical proxies recorded from the lake sediments showed that this eutrophication occurred after the 1990s when P deposition increased as a result of atmospheric loading of dust transported from the Asian continent. The continued increase of anthropogenically produced dust may therefore impart damaging impacts on mountain ecosystems even if they are protected from direct anthropogenic disturbances.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg G, Satake K (2009) Sources of dissolved mine drainage and atmospheric transported lead: a comparative case study in Japan and Sweden. Sci Total Environ 408:117–121
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1983) The assessment of 210Pb data from sites with varying sediment accumulation rates. Hydrobiologia 103:29–35
Bellis DJ, Satake K, Inagaki M, Zeng J, Oizumi T (2005) Seasonal and long-term change in lead deposition in central Japan: evidence for atmospheric transport from continental Asia. Sci Total Environ 341:149–158
Chan CK, Yao X (2008) Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos Environ 42:1–42
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Elser JJ, Andersen T, Baron JS, Bergström AK, Jansson M, Kyle M, Nydick KR, Steger L, Hessen DO (2009) Shifts in lake N: P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 326:835–837
Farmer JG, Lovell MA (1986) Natural enrichment of arsenic in Loch Lomond sediments. Geo et Cosmo Acta 50:2059–2067
Frey DG (1986) Cladocera analysis. In: Berglund BE (ed) Handbook of Holocene palaeo-ecology and palaeohydrology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 667–692
Furutani H, Meguro A, Iguchi H, Uematsu M (2010) Geographical distribution and sources of phosphorus in atmospheric aerosol over the North Pacific Ocean. Geophys Res Lett 37:L03805
Guibaud G, Gauthier C (2003) Study of aluminium concentration and speciation of surface water in four catchments in the Limousin region (France). J Inorg Biochem 97:16–25
Hirao Y, Mabuchi H, Fukuda E, Tanaka H, Imamura T, Todoroki H, Kimura K, Matsumoto E (1986) Lead isotope ratios in Tokyo Bay sediments and their implications in the lead consumption of Japanese industries. Geochem J 20:1–15
Hofmann W (1978) Analysis of animal microfossils from the Grosser Segeberger See (FRG). Arch Hydrobiol 82:316–346
Inoue M, Tanimizu M (2008) Anthropogenic lead inputs to the western Pacific during the 20th century. Sci Total Environ 406:123–130
Itoh N, Tani Y, Nagatani T, Soma M (2003) Phototrophic activity and redox condition in Lake Hamana, Japan, indicated by sedimentary photosynthetic pigments and molybdenum over the last ~250 years. J Paleolimnol 29:403–422
Kang J, Choi MS, Lee CB (2009) Atmospheric metal and phosphorus concentrations, inputs, and their biogeochemical significances in the Japan/East Sea. Sci Total Environ 407:2270–2284
McConnell JR, Aristarain AJ, Banta JR, Edwards PR, Simões JC (2007) 20th-Century doubling in dust archived in an Antarctic Peninsula ice core parallels climate change and desertification in South America. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5743–5748
Ministry of the Environment (1979, 1987, 1993) Government of Japan National Survey on the Natural Environment, Tohoku region. In: Ministry of the Environment
Morales-Baquero R, Pulido-Villena E, Reche I (2006) Atmospheric inputs of phosphorus and nitrogen to the southwest Mediterranean region: biogeochemical responses of high mountain lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 51:830–837
Mukai H, Furuta N, Fujli T, Ambe Y, Sakamoto K, Hashkmoto Y (1993) Characterization of sources of lead in the urban air of Asia using ratios of stable lead isotopes. Environ Sci Technol 27:1347–1356
Mukai H, Tanaka A, Fujii T, Nakao M (1994) Lead isotope ratios of airborne particulate matter as tracers of long-range transport of air pollutants around Japan. J Geophys Res 99:3717–3726
Müller B, Granina L, Schaller T, Ulrich A, Wehrli B (2002) P, As, Sb, Mo, and other elements in sedimentary Fe/Mn layers of Lake Baikal. Environ Sci Technol 36:411–420
Murozumi M, Nakamura S, Yoshida K (1982) Impacts of aerosol lead to natural ecosystems. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 9:1479–1484
Murphy J, Riley J (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nagafuchi O, Rose NL, Hoshika A, Satake K (2009) The temporal record and sources of atmospherically deposited fly-ash particles in Lake Akagi-konuma, a Japanese mountain lake. J Paleolimnol 42:359–371
Nakano T, Morohashi S, Yasuda H, Sakai M, Aizawa S, Shichi K, Morisawa T, Takahashi M, Sanada M, Matsuura Y, Sakai H, Akama A, Okada N (2006) Determination of seasonal and regional variation in the provenance of dissolved cations in rain in Japan based on Sr and Pb isotopes. Atmos Environ 40:7409–7420
Neff JC, Ballantyne AP, Farmer GL, Mahowald NM, Conroy JL, Landry CC, Overpeck JT, Painter TH, Lawrence CR, Reynolds RL (2008) Increasing eolian dust deposition in the western United States linked to human activity. Nature Geosci 1:189–195
Oide K, Nakagawa H, Kanisawa S (1989) Nihon No Chishitu 2 Tohoku District. Kyoritsu-shuppan, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Richardson CJ (1985) Mechanisms controlling phosphorus retention capacity in freshwater wetlands. Science 228:1424–1427
Richardson CJ, Qian SS (1999) Long-term phosphorus assimilative capacity in freshwater wetlands: a new paradigm for sustaining ecosystem structure and function. Environ Sci Technol 33:1545–1551
Richter A, Burrows JP, Nüß H, Granier C, Niemeier U (2005) Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from space. Nature 437:129–132
Roberts N (1998) The impact of modern times. In: Roberts N (ed) The holocene: an environmental history, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 155–181
Schelske CL, Hodell DA (1995) Using carbon isotopes of bulk sedimentary organic matter to reconstruct the history of nutrient loading and eutrophication in Lake Erie. Limnol Oceanogr 40:918–929
Smol JP, Wolfe AP, Birks HJB, Douglas MSV, Jones VJ, Korhola A, Pienitz R, Rühland K, Sorvari S, Antoniades D (2005) Climate-driven regime shifts in the biological communities of arctic lakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4397–4402
Spencer KL, Cundy AB, Croudace IW (2003) Heavy metal distribution and early-diagenesis in salt marsh sediments from the Medway Estuary, Kent, UK. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 57:43–54
Takahashi H (2005) Improvement of vegetation in wetland around Hachiman-Numa. In: Study Club on regional environment planning in Touhoku (ed) Research report of study club on regional environment planning in Touhoku. Study Club on regional environment planning in Touhoku, vol 11, pp 1–38 (in Japanese)
Tan SC, Shi GY, Shi JH, Gao HW, Yao X (2011) Correlation of Asian dust with chlorophyll and primary productivity in the coastal seas of China during the period from 1998 to 2008. J Geophys Res 116:G02029
Tani Y, Matsumoto GI, Soma M, Soma Y, Hashimoto S, Kawai T (2009) Photosynthetic pigments in sediment core HDP-04 from Lake Hovsgol, Mongolia, and their implication for changes in algal productivity and lake environment for the last 1 Ma. Quat Int 205:74–83
Toyoda K, Masuda A (1991) Chemical leaching of pelagic sediments: identification of the carrier of Ce anomaly. Geochem J 25:95–119
Tsukuda S, Sugiyama M, Harita Y, Nishimura K (2006) Atmospheric phosphorus deposition in Ashiu, Central Japan—source apportionment for the estimation of true input to a terrestrial ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 77:117–138
Uno I, Eguchi K, Yumimoto K, Takemura T, Shimizu A, Uematsu M, Liu Z, Wang Z, Hara Y, Sugimoto N (2009) Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe. Nature Geosci 2:557–560
Urabe J, Iwata T, Yagami Y, Kato E, Suzuki T, Hino S, Band S (2011) Within-lake and watershed determinants of carbon dioxide in surface water: a comparative analysis of a variety of lakes in the Japanese Islands. Limnol Oceanogr 56:49–60
Vreca P, Muri G (2006) Changes in accumulation of organic matter and stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in sediments of two Slovenian mountain lakes (Lake Ledvica and Lake Planina), induced by eutrophication changes. Limnol Oceanogr 51:781–790
Wolfe AP, Baron JS, Cornett RJ (2001) Anthropogenic nitrogen deposition induces rapid ecological changes in alpine lakes of the Colorado Front Range (USA). J Paleolimnol 25:1–7
Yamamoto M, Yasui M, Ishikawa T (2008) Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic compositions of volcanic rocks from the Inaniwadake district, Northeast Japan arc. Jpn Mag Min Petr Sci 37:15–25 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Yang L, Qin B, Hu W, Luo L, Song Y (2007) The atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Taihu Lake. Oceanol Et Limnol Sinica 38:104–110
Yoshioka K, Kamiya H, Kano Y, Saki Y, Yamamuro M, Ishitobi Y (2009) The relationship between seasonal variations of total-nitrogen and total-phosphorus in rainfall and air mass advection paths in Matsue, Japan. Atmos Environ 43:3496–3501
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. M. Kawata, T. Suzuki, J. Yokoyama, and F. Kato for their help with the field work and Dr. F. Hyodo for discussions. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research A (no. 19207003) from the MEXT Japan, by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (D-1002) of the Ministry of the Environment, Japan, and by the Global COE (Centers of Excellence) Program (J03, E07) of the MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tsugeki, N.K., Agusa, T., Ueda, S. et al. Eutrophication of mountain lakes in Japan due to increasing deposition of anthropogenically produced dust. Ecol Res 27, 1041–1052 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-012-0984-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-012-0984-y