Abstract
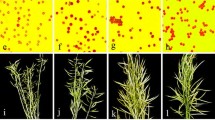
Intertribal somatic hybrids of Brassica napus and Camelina sativa were developed by protoplast electrofusion. Hybrid identity of the regenerants was determined using flow cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA content and simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker analysis. Three hybrids exhibited specific bands for B. napus and C. sativa. These hybrids showed intermediate leaf, flower and seed morphology compared with the two parental species. The seeds of these three hybrids had a modified fatty acid profile, indicating higher level of linolenic and eicosanoic acids than those of B. napus. Our results suggest that somatic hybridization offers opportunities for transferring entire genomes between B. napus and C. sativa in improving rapeseed breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-Benzyladenine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- FAME:
-
Fatty acid methyl ethers
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- NAA:
-
Naphthaleneacetic acid
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Brewer EP, Saunders JA, Angle JS, Chaney RL, McIntosh MS (1999) Somatic hybridization between the zinc accumulator Thlaspi caerulescens and Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 99:761–771
Broun P, Boddupalli S, Somerville C (1998) A bifunctional oleate 12-hydroxylase: desaturase from Lesquerella fendleri. Plant J 13(2):201–210
Conn KL, Tewari JP, Dahiya JS (1988) Resistance to Alternaria brassicae and phytoalexin-elicitation in rapeseed and other crucifers. Plant Sci 56:21–25
Du XZ, Ge XH, Zhao ZG, Li ZY (2008) Chromosome elimination and fragment introgression and recombination producing intertribal partial hybrids from Brassica napus × Lesquerella fendleri crosses. Plant Cell Rep 27:261–271
Fahleson J, Eriksson I, Landgren M, Stymne S, Glimelius K (1994a) Intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Thlaspi perfoliatum with high content of the T. perfoliatum-specific nervonic acid. Theor Appl Genet 87:795–804
Fahleson J, Eriksson I, Glimelius K (1994b) Intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Barbarea vulgaris production of in vitro plantlets. Plant Cell Rep 13:411–416
Forsberg J, Landgren M, Glimelius K (1994) Fertile somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 95:213–223
Friedt W, Lühs W (1998) Recently development and perspectives of industrial rapeseed breeding. Fett/Lipid 100:219–226
Glimelius K (1999) Somatic hybridization. In: sar Gòmez-Campo C (ed) Biology of Brassica coenospecies. Elsevier Science Press, Amsterdam, pp 107–148
Kresovich S, Szewc-McFadden AK, Bliek SM, McFerson JR (1995) Abundance and characterization of simple-sequence repeats (SSRs) isolated from a sized-fractionated genomic library of Brassica napus L. (rapeseed). Theor Appl Genet 91:206–211
Langridge U, Schwall M, Langridge P (1991) Squashes of plant tissue as substrate for PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 19(24):6954
Leonard EC (1998) Camelina oil: α-linolenic source. Inform 9(9):830–838
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:472–493
Narasimhulu SB, Kirti PB, Bhatt SR (1994) Intergeneric protoplast fusion between Brassica carinata and Camelina sativa. Plant Cell Rep 13:657–660
Putnam DH, Budin JT, Field LA, Breene WM (1993) Camelina: a promising low-input oilseed. In: Janick J, Simon J (eds) New Crops. Wiley, New York, pp 314–322
Schroder-Pontoppidan M, Skarzhinskaya M, Dixelius C, Stymne S, Glimelius K (1999) Very long chain and hydroxylated fatty acids in offspring of somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Lesquerella fendleri. Theor Appl Genet 99:108–114
Sigareva MA, Earle ED (1999) Camalexin induction in intertribal somatic hybrids between Camelina sativa and rapid-cycling Brassica oleracea. Theo Appl Genet 98:164–170
Skarzhinskaya M, Landgren M, Glimelius K (1996) Production of intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus L. and Lesquerella fendleri (Gray) Wats. Theor Appl Genet 93:1242–1250
Szewc-McFadden AK, Kresovich S, Bliek SM, Mitchell SE, McFerson JR (1996) Identification of polymorphic, conserved simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in cultivated Brassica species. Theor Appl Genet 93:534–538
Thies W (1971) Schnelle und einfache analyse der fettsäurezusammensetzung in einzelnen raps-kotelydonen. I. Gaschromatographische und papierchromatographische methoden. Z Pflanzenzüchtg 65:181–202
Voelker TA, Worrell AC, Anderson L, Bleibaum J, Fan C, Hawkins DJ, Radke SE, Davies HM (1992) Fatty acid biosynthesis redirected to medium chains in transgenic oilseed plants. Science 257:72–74
Weier D, Hanke C, Eickelkamp A, Luehs W, Dettendorfer J, Schaffert E, Moellers C, Friedt W, Wolter FP, Frentzen M (1997) Trierucoylglycerol biosynthesis in transgenic plants of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Fett/Lipid 99:160–165
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Key Project 973 (2006CB101603) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2007554, BK2008210).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. J. Jiang and X. X. Zhao have equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J.J., Zhao, X.X., Tian, W. et al. Intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Camelina sativa with high linolenic acid content. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 99, 91–95 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9579-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9579-x