Abstract
The large natural variation existing in Brassica oleracea offers a promising approach to improving B. napus (rapeseed). However, the cytogenetic and genetic characterizations of the interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea remain poorly understood. Here, the chromosome behavior of F1 triploid hybrids between B. napus and B. oleracea was observed. Various chromosome pairings in pollen mother cells at diakinesis were found with the predominant configuration of 9II + 10I. The segregation pattern of 9:19 had the highest frequency relative to theoretical distribution estimated at anaphase I. Although the fertility was poor in the F1 generation, it recovered to normal levels in only a few generations. Additionally, B. napus-like individuals in the F3 and F4 generations, referred as new-type rapeseed, showed diverse genetic variation relative to current B. napus and strong heterotic potential. Accordingly, a significantly positive correlation between the introgressed B. oleracea genomic components and heterosis was observed in hybrids made with the new-type rapeseed lines. Our data suggest that the introgression of genetic components of B. oleracea can expand the genetic variation and improve the heterotic potential of rapeseed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte R, Harney PM, Souza MV (1988a) The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. II. Morphology, fertility and cytology of the F1 hybrid. Euphytica 37:189–197
Ayotte R, Harney PM, Souza MV (1988b) The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. III. First backcross to parental species. Euphytica 38:137–142
Bancroft I, Morgan C, Fraser F, Higgins J, Wells R, Clissold L, Baker D, Long Y, Meng J, Wang X, Liu S, Trick M (2011) Dissecting the genome of the polyploid crop oilseed rape by transcriptome sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 29:762–766
Becker HC, Engqvist GM, Karlsson B (1995) Comparison of rapeseed cultivars and resynthesized lines based on allozyme and RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:62–67
Bus A, Körber N, Snowdon RJ, Stich B (2011) Patterns of molecular variation in a species-wide germplasm set of Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 123:1413–1423
Chiang BY, Grant WF, Chiang MS (1978) Transfer of resistance to race 2 of plasmodiophora Brassica from Brassica napus to cabbage (B. oleracea var. capitata). II. Meiosis in the interspecific hybrids between B. napus and 2x and 4x cabbage. Euphytica 27:81–93
Choi SR, Teakle GR, Plaha P, Kim JH, Allender CJ, Beynon E, Piao ZY, Soengas P, Han TH, King GJ, Barker GC, Hand P, Lydiate DJ, Batley J, Edwards D, Koo DH, Bang JW, Park BS, Lim YP (2007) The reference genetic linkage map for the multinational Brassica rapa genome sequencing project. Theor Appl Genet 115:777–792
Cifuentes M, Eber F, Lucas MO, Lode M, Chèvre AM, Jenczewski E (2010) Repeated polyploidy drove different levels of crossover suppression between homoeologous chromosomes in Brassica napus allohaploids. Plant Cell 22:2265–2276
Delourme R, Falentin C, Fomeiu BF, Boillot M, Lassalle G, André I, Duarte J, Gauthier V, Lucante N, Marty A, Pauchon M, Pichon JP, Ribière N, Trotoux G, Blanchard P, Ribière N, Martinant JP, Pauquet J (2013) High-density SNP-based genetic map development and linkage disequilibrium assessment in Brassica napus L. BMC Genom 14:120
Diers BW, Osborn TC (1994) Genetic diversity of oilseed Brassica napus germplasm based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 88:662–668
Eickermann M, Ulber B, Vidal S (2011) Resynthesized lines and cultivars of Brassica napus L. provide sources of resistance to the cabbage stem weevil (Ceutorhynchus pallidactylus (Mrsh.)). Bull Entomol Res 101:287–294
Foley JA, Ramankutty N, Brauman KA, Cassidy ES, Gerber JS, Johnston M, Mueller ND, O’Connell C, Ray DK, West PC, Balzer C, Bennett EM, Carpenter SR, Hill J, Monfreda C, Polasky S, Rockström J, Sheehan J, Siebert S, Tilman D, Zaks DP (2011) Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 478(7369):337–342
Fu D, Qian W, Zou J, Meng J (2012) Genetic dissection of intersubgenomic heterosis in Brassica napus carrying genomic components of B. rapa. Euphytica 184:151–164
Fujii K, Ohmido N (2011) Stable progeny production of the amphidiploid resynthesized Brassica napus cv. Hanakkori, a newly bred vegetable. Theor Appl Genet 123:1433–1443
Gaeta RT, Pires JC (2010) Homoeologous recombination in allopolyploids: the polyploid ratchet. New Phytol 186:18–28
Gaeta RT, Pires JC, Iniguez-Luy F, Leon E, Osborn TC (2007) Genomic changes in resynthesized Brassica napus and their effect on gene expression and phenotype. Plant Cell 19:3403–3417
Girke A, Schierholt A, Becker HC (2012a) Extending the rapeseed gene pool with resynthesized Brassica napus I: genetic diversity. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59:1441–1447
Girke A, Schierholt A, Becker HC (2012b) Extending the rapeseed gene pool with resynthesized Brassica napus II: heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 124:1017–1026
Gomez-Campo C, Prakash S (1999) Origin and domestication. In: Gomez-Campo C (ed) Biology of Brassica coenospecies. Elsevier Science B.V, The Netherlands, pp 33–58
Hasan M, Seyis F, Badani AG, Pons-Kühnemann J, Friedt W, Lühs W, Snowdon RJ (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity in the Brassica napus L. gene pool using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:793–802
Jesske T, Olberg B, Schierholt A, Becker HC (2013) Resynthesized lines from domesticated and wild Brassica taxa and their hybrids with B. napus L.: genetic diversity and hybrid yield. Theor Appl Genet 126:1053–1065
Leflon M, Eber F, Letanneur JC, Chelysheva L, Coriton O, Huteau V, Ryder CD, Barker G, Jenczewski E, Chèvre AM (2006) Pairing and recombination at meiosis of Brassica rapa (AA) × Brassica napus (AACC) hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 113:1467–1480
Leflon M, Grandont L, Eber F, Huteau V, Coriton O, Chelysheva L, Jenczewski E, Chèvre AM (2010) Crossovers get a boost in Brassica allotriploid and allotetraploid hybrids. Plant Cell 22:2253–2264
Li Z, Liu HL, Luo P (1995) Production and cytogenetics of intergeneric hybrids between Brassica napus and Orychophragmus violaceus. Theor Appl Genet 91:131–136
Li M, Chen X, Meng J (2006) Intersubgenomic heterosis in rapeseed production with a partial new-type Brassica containing subgenome Ar from B. rapa and Cc from Brassica carinata. Crop Sci 46:234–242
Li Q, Mei J, Zhang Y, Li J, Ge X, Li Z, Qian W (2013) A large-scale introgression of genomic components of Brassica rapa into B. napus by bridge of hexaploid derived from hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 126:2073–2080
Liu HL (2000) Genetics and breeding in rapeseed. Chinese Agricultural Universities Press, Bei**g
Long Y, Shi J, Qiu D, Li R, Zhang C, Wang J, Hou J, Zhao J, Shi L, Park B-S, Choi SR, Lim YP, Meng J (2007) Flowering time quantitative trait loci analysis of oilseed Brassica in multiple environments and genomewide alignment with Arabidopsis. Genetics 177:2433–2444
Lowe AJ, Moule C, Trich M, Edwards KJ (2003) Efficient large-scale development of microsatellites for marker and map** applications in Brassica crop species. Theor Appl Genet 108:1103–1112
Lu C, Kato M (2001) Fertilization fitness and relation to chromosome number in interspecific progeny between Brassica napus and B. rapa: a comparative study using natural and resynthesized B. napus. Breed Sci 51:73–81
Mei J, Li Q, Yang X, Qian L, Liu L, Yin J, Frauen M, Li J, Qian W (2010) Genomic relationships between wild and cultivated Brassica oleracea L. with emphasis on the origination of cultivated crops. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57:687–692
Mei JQ, Fu Y, Qian LW, Xu XF, Li JN, Qian W (2011a) Effectively widening the gene pool of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) by using Chinese B. rapa in a ‘virtual allopolyploid’ approach. Plant Breed 130:333–337
Mei J, Li Q, Qian L, Fu Y, Li J, Frauen M, Qian W (2011b) Genetic investigation of the origination of allopolyploid with virtually synthesized lines: application to the C subgenome of Brassica napus. Heredity 106:955–961
Mikkelsen TR, Jensen J, Jørgensen RB (1996) Inheritance of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) RAPD markers in a backcross progeny with Brassica campestris. Theor Appl Genet 92:492–497
Namai H (1987) Inducing cytogenetical alteration by means of interspecific and intergeneric hybridization in Brassica crops. Gamma Field Symp 26:41–87
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endouncleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Olsson G (1960) Species crossing within the genus Brassica napus. II. Artificial Brassica napus L. Hereditas 46:351–396
Qian W, Chen X, Fu D, Zou J, Meng J (2005) Intersubgenomic heterosis in seed yield potential observed in a new-type of Brassica napus introgressed with partial Brassica rapa genome. Theor Appl Genet 110:1187–1194
Qian W, Meng J, Li M, Frauen M, Sass O, Noack J, Jung C (2006) Introgression of genomic components from Chinese Brassica rapa contributes to widening the genetic diversity in rapeseed (B. napus L.), with emphasis on the evolution of Chinese rapeseed. Theor Appl Genet 113:49–54
Qiu D, Morgan C, Shi J, Long Y, Liu J, Li R, Zhuang X, Wang Y, Tan X, Dietrich E, Weihmann T, Everett C, Vanstraelen S, Beckett P, Fraser F, Trick M, Barnes S, Wilmer J, Schmidt R, Li J, Li D, Meng J, Bancroft I (2006) A comparative linkage map of oilseed rape and its use for QTL analysis of seed oil and erucic acid content. Theor Appl Genet 114:67–80
Quazi MH (1988) Interspecific hybrids between Brassica napus L. and B. oleracea L. developped by embryo culture. Theor Appl Genet 75:309–318
Rahman MH, Bennett RA, Yang RC, Thiagarajah MR (2011) Exploitation of the late flowering species Brassica oleracea L. for the improvement of earliness in B. napus L.—an untraditional approach. Euphytica 177:365–374
Ren JP, Dickson MH, Earle ED (2000) Improved resistance to bacterial soft root by protoplast fusion between Brassica rapa and B. oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 100:810–819
Ripley VL, Beversdorf WD (2003) Development of self-incompatible Brassica napus (I) introgression of S-alleles from Brassica oleracea through interspecific hybridization. Plant Breed 122:1–5
Rohlf F (1997) NTSYS-PC 2.1. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Exeter Software. In, Setauket, NY
SAS Institute (1999) SAS Online Doc (R), version 8.0. Cary, NC, USA
Seyis F, Snowdon RJ, Luhs W, Friedt W (2003) Molecular characterization of novel resynthesized rapeseed (Brassica napus) lines and analysis of their genetic diversity in comparison with spring rapeseed cultivars. Plant Breed 122:473–478
Shiga T (1970) Rapa breeding by interspecific crossing between Brassica napus and Brassica campestris in Japan. Jpn Agric Res Quart 5:5–10
Szadkowski E, Eber F, Huteau V, Lodé M, Huneau C, Belcram H, Coriton O, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Delourme R, King GJ, Chalhoub B, Jenczewski E, Chèvre AM (2010) The first meiosis of resynthesized Brassica napus, a genome blender. New Phytol 186:102–112
Szadkowski E, Eber F, Huteau V, Lodé M, Coriton O, Jenczewski E, Chèvre AM (2011) Polyploid formation pathways have an impact on genetic rearrangements in resynthesized Brassica napus. New Phytol 191:884–894
Szewc-McFadden AK, Kresovich S, Bliek SM, Mitchell SE, McFerson JR (1996) Identification of polymorphic, conserved simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in cultivated Brassica species. Theor Appl Genet 93:534–538
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Toxopeus H (1979) The domestication of Brassica crops. In: Proceedings of Eucarpia conference on the breeding of cruciferous crops, Wageningen, Netherlands, pp 47–56
UN (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Uzunova MI, Ecke W (1999) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic map** of microsatellites in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Breed 118:323–326
Wen J, Tu JX, Li ZY, Fu TD, Ma CZ, Shen JX (2008) Improving ovary and embryo culture techniques for efficient resynthesis of Brassica napus from reciprocal crosses between yellow-seeded diploids B. rapa and B. oleracea. Euphytica 162:81–89
**ao Y, Chen L, Zou J, Tian E, **a W, Meng J (2010) Development of a population for substantial new type Brassica napus diversified at both A/C genomes. Theor Appl Genet 121:1141–1150
**ong Z, Gaeta RT, Pires JC (2011) Homoeologous shuffling and chromosome compensation maintain genome balance in resynthesized allopolyploid Brassica napus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7908–7913
Zhao M, Du J, Lin F, Tong C, Yu J, Huang S, Wang X, Liu S, Ma J (2013) Shifts in the evolutionary rate and intensity of purifying selection between two Brassica genomes revealed by analyses of orthologous transposons and relics of a whole genome triplication. Plant J 76:211–222
Zhou YM, Scarth R (1995) Microspore culture of hybrids between Brassica napus and B. campestris. Acta Bot Sin 37:848–855
Zou J, Zhu J, Huang S, Tian E, **ao Y, Fu D, Tu J, Fu T, Meng J (2010) Broadening the avenue of intersubgenomic heterosis in oilseed Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 120:283–290
Acknowledgments
This study is partly supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2013A013, XDJK2014C148), the Key Projects in the National Science & Technology (2010BAD01B02), 111 project (B12006), NSFC (31171585), and the open funds of the National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qinfei Li and Qinghong Zhou have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2014_153_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
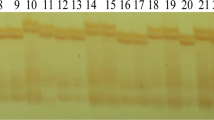
Supplementary materials S1. List of current Brassica napus lines to compare with new type lines for genetic variation revealed with simple sequence repeat markers (XLSX 11 kb)
11032_2014_153_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary materials S2. Distribution of loci amplified with simple sequence repeat primers. The primers were prefixed with BRAS/CB from Celera AgGen Brassica Consortium; SWUC, AG, Pod, YD, Br, h, Bn, CEN from Southwest University; Na, Ra, Ol from BBSRC (Lowe et al. 2003); NIAB from The National Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology; PUT from http://www.plantgdb.org; sR, sN, sS from Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada; BRMS from Suwabe et al. (2002); CNU from Chungnam National University; FITO from http://www.asbornlab.agronomy.wisc.edu/research/maps/ssrs.html; BN were from Szewc-McFadden et al. (1996); MR from Uzanova and Ecke (1999); sOR from Qiu et al.(2006); with ENA and GOL from Choi et al.(2007); CN from Long et al.(2007) (XLSX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Zhou, Q., Mei, J. et al. Improvement of Brassica napus via interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea . Mol Breeding 34, 1955–1963 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0153-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0153-9