Abstract
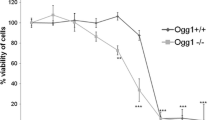
Zinc oxide nanoparticle is one of the nanomaterials people engaged most in their life and its health effect has been taken into concern. In this work, A549 cell line was used as cell model, and the cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles was revealed to be concentration-dependent. Through the measurement of cellular proteome, much more differentially expressed proteins were observed after the cells being treated for 9 h than 24 h. Also, most of these proteins expressed in the pattern which showed a significant decrease after exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles and then an increase at 24 h. Intracellular reactive oxygen species and glutathione determination indicated that high level of oxidative stress was presented in cell after treatment with zinc oxide nanoparticles for 9 h. It can be observed from western blot analysis that the expression of NF-κB p65, PNPase, and HSP90 rose significantly after 9 h of exposure. Thus, a deduction was reached that toxicity of nanoparticles consists both of particle toxicity and ion toxicity, and a long-time treatment may conceal the toxicity induced by particles. The conclusion we made highlighted the importance of exposure time in the study of nanoparticle toxicity and would provide a new perspective for studying toxicity mechanism of nanoparticles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin AS (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.649
Chang C, Chen S, Ho S, Yang CY, Wang HD, Tsai ML (2007) Proteomic analysis of proteins from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid reveals the action mechanism of ultrafine carbon black-induced lung injury in mice. Proteomics 7:4388–4397. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200700164
Cho WS, Duffin R, Thielbeer F, Bradley M, Megson IL, MacNee W, Poland CA, Tran CL, Donaldson K (2012) Zeta potential and solubility to toxic ions as mechanisms of lung inflammation caused by metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 126:469–477. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs006
Csermely P, Schnaider T, Soti C, Prohászka Z, Nardai G (1998) The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications. A comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 79:129–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-7258(98)00013-8
Deng X, Luan Q, Chen W, Wang Y, Wu M, Zhang H, Jiao Z (2009) Nanosized zinc oxide particles induce neural stem cell apoptosis. Nanotechnology 20:115101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/11/115101
Ealick SE, Rule SA, Carter DC, Greenhough TJ, Babu YS, Cook WJ, Habash J, Helliwell JR, Stoeckler JD, Parks RE Jr, Chen SF, Bugg CE (1990) Three-dimensional structure of human erythrocytic purine nucleoside phosphorylase at 3.2 Å resolution. J Biol Chem 265:1812–1820. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb27124.x
Fooksman DR, Vardhana S, Vasiliver-Shamis G, Liese J, Blair DA, Waite J, Sacristán C, Victora GD, Zanin-Zhorov A, Dustin ML (2010) Functional anatomy of T cell activation and synapse formation. Annu Rev Immunol 28:79–105. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101308
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappa B puzzle. Cell 109:S81–S96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00703-1
Hackenberg S, Scherzed A, Technau A, Kessler M, Froelich K, Ginzkey C, Koehler C, Burghartz M, Hagen R, Kleinsasser N (2011) Cytotoxic, genotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human nasal mucosa cells in vitro. Toxicol Vitro 25:657–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2011.01.003
Huang CC, Aronstam RS, Chen DR, Huang YW (2010) Oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and altered gene expression in human lung epithelial cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Vitro 24:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.09.007
Jeng HA, Swanson J (2006) Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:2699–2711. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520600966177
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-kappa B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage-T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lin WS, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma Y (2006) In vitro toxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol App Pharm 217:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.004
Lin W, Xu Y, Huang CC, Ma YF, Shannon KB, Chen DR, Huang YW (2009) Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized ZnO particles in human lung epithelial cells. J Nanopart Res 11:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1829-5
Meyer DE, Curran MA, Gonzalez MA (2009) An examination of existing data for the industrial manufacture and use of nanocomponents and their role in the life cycle impact of nanoproducts. Environ Sci Technol 43:1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8023258
Nel A, **a T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114397
Okamoto T, Sakurada S, Yang JP, Merin JP (1997) Regulation of NF-kappa B and disease control: identification of a novel serine kinase and thioredoxin as effectors for signal transduction pathway for NF-kappa B activation. Curr Top Cell Regul 35:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0070-2137(97)80006-4
Park E, Yi J, Chung Y, Choi J, Park K (2008) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett 180:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.06.869
Prach M, Stone V, Proudfoot L (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticles and monocytes: impact of size, charge and solubility on activation status. Appl Pharmacol 266:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.10.020
Rao PN, Walsh TR, Makowka L, Rubin RS, Weber T, Snyder JT, Starzl TE (1990) Purine nucleoside phosphorylase: a new marker for free oxygen radical injury to the endothelial cell. Hepatology 11:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840110206
Sharma V, Anderson D, Dhawan A (2011) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human liver cells (HepG2). J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:98–99. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2011.1220
Song WH, Zhang JY, Guo J, Zhang J, Ding F, Li L, Sun Z (2010) Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 199:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.10.003
The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies Consumer Products Inventory. Available at http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/
Triboulet S, Aude-Garcia C, Armand L, Gerdil A, Diemer H, Proamer F, Collin-Faure V, Habert A, Strub JM, Hanau D, Herlin N, Carriѐre M, Van Dorsselaer A, Rabilloud T (2014) Analysis of cellular responses of macrophages to zinc ions and zinc oxide nanoparticles: a combined targeted and proteomic approach. Nanoscale 6:6102–6114. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR00319E
**a T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, Yeh JI, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2:2121–2134. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800511k
Yang YH, Bazhin AV, Werner J, Karakhanova S (2013) Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Inter Rev Immunol 32:249–270. https://doi.org/10.3109/08830185.2012.755176
Zhao WJ, Song Q, Wang YH, Li KJ, Mao L, Hu X, Lian HZ, Zheng WJ, Hua ZC (2014) Zn-responsive proteome profiling and time-dependent expression of proteins regulated by MTF-1 in A549 cells. PLoS One 9:e105797. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105797
Zhao WJ, Song Q, Zhang ZJ, Mao L, Zheng WJ, Hu X, Lian HZ (2015) The kinetic response of the proteome in A549 cells exposed to ZnSO4 stress. PLoS One 10:e0133451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133451
Zhong L, Yu Y, Lian HZ, Hu X, Fu H, Chen YJ (2017) Solubility of nano-sized metal oxides evaluated by using in vitro simulated lung and gastrointestinal fluids: implication for health risks. J. Nanopart. Res 19:375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4064-7
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91643105, 21577057, 91543129, 81072712, and 90913012), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20171335), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, 2011CB911003). We thank Mr. LY Huang for assistance in the ICP-MS determination of zinc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 104 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Zj., Tang, Zj., Zhu, Zy. et al. The time-dependent cellular response mechanism upon exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 20, 263 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4333-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4333-0