Abstract
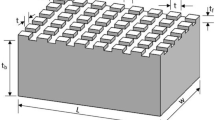
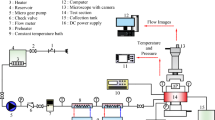
In this document, the numerical analysis of the non-uniformity of the height of fins of a pin fin heat sink on the firs law and second law performances of the heat sink is conducted. Five different designs for changing the height of pin fins in the longitudinal and transverse directions are considered and their hydrothermal performance and entropy generation characteristics at different Reynolds numbers are investigated. After examining the changes in convection coefficient, maximum CPU temperature, uniformity of temperature distribution, thermal resistance and overall hydrothermal performance index, it was found that the best first law performance belongs to the case in which the height of the pin fins elevates in the longitudinal direction and linearly by moving away from the inlet of the device. For this case, the maximum overall hydrothermal performance index was equal to 1.099, which occurred at Reynolds number of 500. Investigating the performance of the heat sinks from the entropy generation viewpoint also revealed that the lowest total entropy generation rate belongs to the device in which the height of the fins declines in the longitudinal direction and linearly by moving away from the inlet.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cirillo L, Greco A, Masselli C. Development of an electronic circuit cooling system using elastocaloric effect: a FEM comparison among different configurations. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;219: 119463.
Aviles JE, Paniagua-Guerra LE, Ramos-Alvarado B. Liquid-cooled heat sink design for a multilevel inverter switch with considerations for heat spreading and manufacturability. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;219: 119588.
Sajid MU, Ali HM, Sufyan A, Rashid D, Zahid SU, Rehman WU. Experimental investigation of TiO2–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer inside wavy mini-channel heat sinks. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:1279–94.
Samadi H, Hosseini MJ, Ranjbar AA, Pahamli Y. Thermohydraulic performance of new minichannel heat sink with grooved barriers. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2023;144: 106753.
Emam M, Soliman AMA, Abdelrahman MA, Attia AAA. Performance improvement of single-junction photovoltaic systems using a new design of a heat pipe-based heat sink: Experimental study. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;219: 119653.
Hu X, Gong X, Zhu F, **ng X, Li Z, Zhang X. Thermal analysis and optimization of metal foam PCM-based heat sink for thermal management of electronic devices. Renew Energy. 2023;212:227–37.
Zhang DX, Zhu CY, Duan XY, Gong L, Huang BH, Xu MH, Chen Y. Design and transient temperature control performance analysis of a novel hybrid PCM-based heat sink. J Energy Storage. 2023;72: 108450.
Shailesh K, Naresh Y, Banerjee J. Heat transfer performance of a novel PCM based heat sink coupled with heat pipe: an experimental study. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;229: 120552.
Khan A, Hadi F, Akram N, Bashir MA, Ali HM, Janjua MM, Hussain A, Pasha RA, Janjua AB, Farukh F. Review of micro and mini channels, porous heat sinks with hydrophobic surfaces for single phase fluid flow. J Taiwan Inst Chem. 2022;132: 104186.
Fathi M, Heyhat MM, Targhi MZ, Bigham S. Porous-fin microchannel heat sinks for future micro-electronics cooling. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2023;202: 123662.
Ronge H, Upalkar S, Wagh A, Krishnan S, Ramamoorthy S. Evaluations of corrugated macro-structure porous heat sinks for the combined heat dissipation and noise reduction performance. Int J Therm Sci. 2023;18: 108157.
Zhong JF, Sedeh SN, Lv YP, Arzani B, Toghraie D. Investigation of Ferro-nanofluid flow within a porous ribbed microchannel heat sink using single-phase and two-phase approaches in the presence of constant magnetic field. Powder Technol. 2021;387:251–60.
Jalili B, Rezaeian A, Jalili P, Ommi F, Ganji DD. Numerical modeling of magnetic field impact on the thermal behavior of a microchannel heat sink. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2023;45:102944.
Hajmohammadi MR, Gholamrezaie S, Ahmadpour A, Mansoori Z. Effects of applying uniform and non-uniform external magnetic fields on the optimal design of microchannel heat sinks. Int J Mech Sci. 2020;186: 105886.
Wang Y, **a G, Li R, Li Q, Yan Z. Heat transfer enhancement in porous wall mini-channel heat sinks utilizing electric field: An experimental study. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2023;203: 123803.
Li T, Luo X, He B, Wang L, Zhang J, Liu Q. Flow boiling heat transfer enhancement in vertical minichannel heat sink with non-uniform microcavity arrays under electric field. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2023;149: 110997.
Tilehnoee MH, Seyyedi SM, del Barrio EP, Sharifpour M. Heat transfer intensification of NEPCM-water suspension filled heat sink cavity with notches cooling tubes by applying the electric field. J Energy Storage. 2023;59: 106492.
Sajid MU, Ali HM, Bicer Y. Exergetic performance assessment of magnesium oxide–water nanofluid in corrugated minichannel heat sinks: An experimental study. Int J Energy Res. 2022;46:9985–10001.
Mukherjee S, Wcislik S, Khadanga V, Mishra PC. Influence of nanofluids on the thermal performance and entropy generation of varied geometry microchannel heat sink. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2023;49:103241.
Wang H, Chen X. Performance improvements of microchannel heat sink using Koch fractal structure and nanofluids. Structure. 2023;50:1222–31.
Shahsavar A, Jafari M, Yildiz C, Moradvandi M, Arici M. On the cooling performance and entropy generation characteristics of a heat sink under ultrasonic vibration: Exploring the impact of porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2023;215: 124500.
Shahsavar A, Ghazizade-Ahsaee H, Askari IB, Setareh M. Numerical feasibility study of using ultrasonic surface vibration as a new technique for thermal management of the electronic devices. Energy Convers Manag. 2023;276: 116481.
Shahsavar A, Ahsaee HG, Askari IB, Rashidi MM. The numerical analysis in heat transfer, fluid flow, and irreversibility of a pin-fin heatsink under the ultrasonic vibration with different transducer power assignment scenarios. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2024;49: 102480.
Acharya S. Thermo-fluidic analysis of microchannel heat sink with inline/staggered square/elliptical fins. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2023;147: 106961.
Zhao Z, Hu B, He J, Lin M, Ke H. Effect of fin shapes on flow boiling heat transfer with staggered fin arrays in a heat sink. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;225: 120179.
Nawaz S, Babar H, Ali HM, Sajid MU, Janjua MM, Said Z, Tiwari AK, Sundar LS, Li C. Oriented square shaped pin-fin heat sink: Performance evaluation employing mixture based on ethylene glycol/water graphene oxide nanofluid. Appl Therm Eng. 2022;206: 118085.
Ndao S, Peles Y, Jensen MK. Effects of pin fin shape and configuration on the single-phase heat transfer characteristics of jet im**ement on micro pin fins. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;70:856–63.
Bhandari P, Rawat KS, Prajapati YK, Padalia D, Ranakoti L, Singh T. Design modifications in micro pin fin configuration of microchannel heat sink for single phase liquid flow: a review. J Energy Storage. 2023;66: 107548.
Shahsavar A, Shahmohammadi M, Askari IB. CFD simulation of the impact of tip clearance on the hydrothermal performance and entropy generation of a water-cooled pin-fin heat sink. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126: 105400.
Atas A, Benam BP, Yagci V, Malyemez MC, Parlak M, Sadaghiani AK, Kosar A. On the effect of elliptical pin Fins, distribution pin Fins, and tip clearance on the performance of heat sinks in flow boiling. Appl Therm Eng. 2022;212: 118648.
Bhandari P. Numerical investigations on the effect of multi-dimensional stepness in open micro pin fin heat sink using single phase liquid fluid flow. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2022;138: 106392.
Bejan A. Entropy generation minimization: the method of thermodynamic optimization of finite-size systems and finite-time processes. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1995.
Ali HM, Arshad W. Thermal performance investigation of staggered and inline pin fin heat sinks using water based rutile and anatase TiO2 nanofluids. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;106:793–803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahsavar, A., Mohammadnazar, P. & Ali, H.M. Numerical comparison of hydrothermal performance and entropy generation features of micro pin fin heat sinks with different multi-dimensional stepnesses. J Therm Anal Calorim (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13064-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13064-0