Abstract
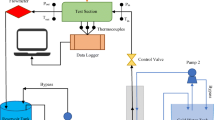
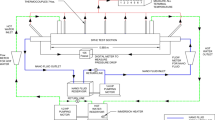
The present study comprises experimental investigation on heat transfer and hydrodynamic characteristics of TiO2 nanofluid as coolant in wavy channel heat sinks having three different channel configurations. The performance of TiO2 nanofluids having concentrations of 0.006, 0.008, 0.01 and 0.012 vol% is compared with that of distilled water under laminar regime at heating powers of 25 W, 35 W and 45 W. Results indicated that for all heat sinks, nanofluids showed better heat transfer characteristics than distilled water. With an increase in heating power, TiO2 nanofluid thermal performance was decreased. Using 0.012% TiO2 nanofluids, minimum wall base temperature and maximum enhancement in Nusselt number are noted as 33.85 °C and 40.57%, respectively, for heat sink with wavelength of 5 mm and amplitude of 0.5 mm corresponding to Reynolds number of 894 at heating power of 25 W. Pum** power requirement is function of flow rate and pressure drop, and its maximum value of 0.0284 W is associated with heat sink with minimum wavelength. Moreover, variation in wavelength of channel is found to have dominating effect on heat transfer performance of heat sink as compared to the width of channel.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A cr :
-
Cross-sectional area of channel (m2)
- A se :
-
Effective surface area of sink (m2)
- \({C_{\text{P}}}\) :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 °C−1)
- d :
-
Diameter (m)
- \({d_{\text{h}}}\) :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- h:
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 °C−1)
- \({h_{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Fin height of heat sink (m)
- \({H_{\text{w}}}\) :
-
Distance between wall and thermocouple (m)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 °C−1)
- L:
-
Length (m)
- LMTD:
-
Log mean temperature difference (°C)
- \(\dot m\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg s−1)
- n :
-
Empirical shape factor
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- ΔP :
-
Pressure drop
- \({P_{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Perimeter of channel (m)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Q :
-
Heat flow rate (W)
- \({Q_{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Volumetric flow rate (m3 s−1)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- R th :
-
Thermal resistance (°C W−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- t c :
-
Total number of channels
- V :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- \({W_{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Width of heat sink channel (m)
- \({W_{\text{cc}}}\) :
-
Center-to-center distance of two consecutive channels (m)
- μ :
-
Viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \(\emptyset\) :
-
Volume fraction
- bf:
-
Base fluid
- c :
-
Channel
- f :
-
Fin
- i :
-
Inlet
- m :
-
Mean
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- o :
-
Outlet
- p :
-
Nanoparticle
- s :
-
Sink
- tc:
-
Thermocouple
- w :
-
Wall
References
Tuckerman DB, Pease RF. High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Dev Lett. 1981;2(5):126–9.
Selvakumar P, Suresh S. Convective performance of CuO/water nanofluid in an electronic heat sink. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2012;40:57–63.
Sohel MR, Khaleduzzaman SS, Saidur R, Hepbasli A, Sabri MFM, Mahbubul IM. An experimental investigation of heat transfer enhancement of a minichannel heat sink using Al2O3–H2O nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;74:164–72.
Ho CJ, Chen WC. An experimental study on thermal performance of Al2O3/water nanofluid in a minichannel heat sink. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;50:516–22.
Jajja SA, Ali W, Ali HM. Multiwalled carbon nanotube nanofluid for thermal management of high heat generating computer processor. Heat Transf Res. 2014;43:653–66.
Peyghambarzadeh SM, Hashemabadi SH, Chabi AR, Salimi M. Performance of water based CuO and Al2O3 nanofluids in a Cu–Be alloy heat sink with rectangular microchannels. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;86:28–38.
Rafati M, Hamidi AA, Niaser MS. Application of nanofluids in computer cooling systems (heat transfer performance of nanofluids). Appl Therm Eng. 2012;45:9–14.
Ali HM, Arshad W. Thermal performance investigation of staggered and inline pin fin heat sinks using water based rutile and anatase TiO2 nanofluids. Energy Convers Manage. 2015;106:793–803.
Ahmed HE, Ahmed MI, Seder IMF, Salman BH. Experimental investigation for sequential triangular double-layered microchannel heat sink with nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;77:104–15.
Chein R, Huang G. Analysis of microchannel heat sink performance using nanofluids. Appl Therm Eng. 2005;25:3104–14.
Ghasemi SE, Ranjbar AA, Hosseini MJ. Experimental evaluation of cooling performance of circular heat sinks for heat dissipation from electronic chips using nanofluid. Mech Res Commun. 2017;84:85–9.
Naphon P, Nakharintr L. Heat transfer of nanofluids in the mini-rectangular fin heat sinks. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;40:25–31.
Ali HM, Arshad W. Effect of channel angle of pin-fin heat sink on heat transfer performance using water based graphene nanoplatelets nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:465–72.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Sahamiyan M. Performance of nanofluid flow in corrugated minichannels heat sink (CMCHS). Energy Convers Manag. 2016;108:297–308.
Zhang J, Diao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang Y. Experimental study of TiO2-water nanofluid flow and heat transfer characteristics in a multiport minichannel flat tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;79:628–38.
Nazari M, Karami M, Ashouri M. Comparing the thermal performance of water, ethylene glycol, alumina and CNT nanofluids in CPU cooling: experimental study. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2014;57:371–7.
Arshad W, Ali HM. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop in a straight minichannel heat sink using TiO2 nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;110:248–56.
Arshad W, Ali HM. Graphene nanoplatelets nanofluids thermal and hydrodynamic performance on integral fin heat sink. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:995–1001.
Sakanova A, Keian CC, Zhao J. Performance improvements of microchannel heat sink using wavy channel and nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;89:59–74.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Hassani SM, Mazloumi SH. Enhancement of laminar forced convection cooling in wavy heat sink with rectangular ribs and Al2O3/water nanofluids. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2017;89:199–210.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Hassani SM, Mazloumi SH. Performance enhancement of straight and wavy miniature heat sinks using pin-fin interruptions and nanofluids. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif. 2017;122:90–108.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Hassani SM, Mazloumi SH. Comparison of hydrothermal performance between plate fins and plate-pin fins subject to nanofluid-cooled corrugated miniature heat sinks. Microelectron Reliab. 2017;70:84–96.
Bahiraei M, Hosseinalipour SM, Saeedan M. Prediction of Nusselt number and friction factor of water-Al2O3 nanofluid flow in shell-and-tube heat exchanger with helical baffles. Chem Eng Commu. 2015;202(2):260–8.
Azizi Z, Alamdari A, Malayeri MR. Thermal performance and friction factor of a cylindrical microchannel heat sink cooled by Cu-water nanofluid. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;99:970–8.
Zhai YL, **a GD, Liu XF, Li YF. Heat transfer enhancement of Al2O3–H2O nanofluids flowing through a micro heat sink with complex structure. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:158–66.
Ijam A, Saidur R, Ganesan P. Cooling of minichannel heat sink using nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39:1188–94.
**a GD, Liu R, Wang J, Du M. The characteristics of convective heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:256–64.
Ambreen T, Kim MH. Effect of fin shape on the thermal performance of nanofluid-cooled micro pin-fin heat sinks. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:245–56.
Hashemi SMH, Fazeli SA, Zirakzadeh H, Ashjaee M. Study of heat transfer enhancement in a nanofluid-cooled miniature heat sink. Int CommunHeat Mass Transf. 2012;39:877–84.
Lelea D. The performance evaluation of Al2O3/water nanofluid flow and heat transfer in microchannel heat sink. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:3891–9.
Izadi M, Shahmardan MM, Norouzi M, Rashidi AM, Behzadmehr A. Cooling performance of a nanofluid flow in a heat sink microchannel with axial conduction effect. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2014;117:1821–33.
Ali HM, Sajid MU, Arshad A. Heat transfer applications of TiO2 nanofluids. In: Janus M, editor. Application of titanium dioxide. Rijekam: InTech; 2017.
Ali HM, Babar H, Shah TR, Sajid MU, Qasim MA, Javed S. Preparation techniques of TiO2 nanofluids and challenges: a review. Appl Sci. 2018;8:587.
Pak BC, Cho YI. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp Heat Transf. 1998;11:151–70.
Xuan Y, Roetzel W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2000;43:3701–7.
Corcione M. Rayleigh–Bénard convection heat transfer in nanoparticle suspensions. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2011;32:65–77.
Hamilton RL, Crosser OK. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind Eng Chem Fundam. 1962;1:87–91.
Kline SJ, McClintock FA. Describing uncertainties in single-sample experiments. Mech Eng. 1953;75:3–8.
Peng XF, Peterson GP. Convective heat transfer and flow friction for water flow in microchannel structures. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1996;19(12):2599–608.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Nozan F. Water cooled corrugated minichannel heat sink for electronic devices: effect of corrugation shape. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:188–96.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Sahamiyan M, Hesampour M, Sartipzadeh O. Experimental study on cooling performance of sinusoidal-wavy minichannel heat sink. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;92:50–61.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Ahmadian E, Sartipzadeh O. Effects of different pin-fin interruptions on performance of a nanofluid-cooled zigzag miniature heat sink (MHS). Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;81:19–27.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Sartipzadeh O, Pazdar S, Sahamiyan M. Experimental and parametric studies on a miniature heat sink with offset-strip pins and Al2O3/water nanofluids. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;111:1342–52.
Chai L, **a G, Zhou M, Li J, Qi J. Optimum thermal design of interrupted microchannel heat sink with rectangular ribs in the transverse microchambers. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;51:880–9.
**a G, Zhai Y, Cui Z. Numerical investigation of thermal enhancement in a micro heat sink with fan-shaped reentrant cavities and internal ribs. ATE. 2013;58:52–60.
Li YF, **a GD, Ma DD, Jia YT, Wang J. Characteristics of laminar flow and heat transfer in microchannel heat sink with triangular cavities and rectangular ribs. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;98:17–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajid, M.U., Ali, H.M., Sufyan, A. et al. Experimental investigation of TiO2–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer inside wavy mini-channel heat sinks. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 1279–1294 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08043-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08043-9