Abstract
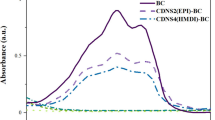
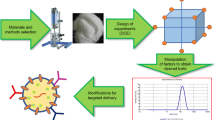
In an endeavor to ameliorate the solubility and subsequent oral bioavailability of Cefixime (CEF), a drug noted for its deficient water solubility, the formulation of ternary inclusion complexes was executed utilizing hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) and sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD), in conjunction with N-methyl-D-glucaminet (MG). This development was realized through the application of a mechanochemistry technique, acknowledged for its “green” credentials. The complexes' physicochemical attributes were meticulously examined through various analytical techniques: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Powder X-ray Diffractometry (XRD), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Notably, the ternary complexes exhibited an uplift in apparent drug solubility, especially when juxtaposed with binary complexes. A prominent augmentation was perceived in the stability constant (Kc) and complexation efficiency (CE) when MG was integrated into the ternary complexes with HP-β-CD or SBE-β-CD. Further exploratory molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies underscored MG’s role in augmenting complex stability by serving as a bridge between CEF and cyclodextrins (CDs). The parallel artificial membrane permeability assay (PAMPA) indicated a conspicuous enhancement of CEF permeability in the ternary complexes relative to the control–free CEF. The particle size and zeta potential of the mechanochemically processed ternary complexes in liquid form were assessed using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). Moreover, in vivo evaluations revealed the ternary complexes to manifest notably superior oral bioavailability when compared to unadulterated CEF. Lastly, through the rapid storage assay, a heightened physicochemical stability was observed in the mechanochemically synthesized CEF ternary supramolecular inclusion complexes, compared to the pure drug, intimating a pioneering approach for the oral delivery of CEF, ensuring improved bioavailability.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Cyclodextrin
- CEF:
-
Cefixime
- CE:
-
Complexation efficiency
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- HP-β-CD:
-
Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
- Kc:
-
Stability constant
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
- MG:
-
N-methyl-d-glucaminet
- PAMPA:
-
The parallel artificial membrane permeability assay
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- PM:
-
Physical mixture
- SBE-β-CD:
-
Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- XRD:
-
Powder X-ray diffractometry
References
Brittain, D.C., Scully, B.E., Hirose, T., Neu, H.C.: The pharmacokinetic and bactericidal characteristics of oral cefixime. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38, 590–594 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1985.229
Brogden, R.N., Campoli-Richards, D.M.: Cefxime. A review of its antibacterial activity. Pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic potential. Drugs 38, 524–550 (1989). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198938040-00004
Talebpour, Z., Pourabdollahi, H., Rafati, H., Abdollahpour, A., Bashpur, Y., Aboul-Enein, H.Y.: Determination of cefixime by avalidated stability-indicating HPLC method and identification of its related substances by LC-MS/MS studies. Sci. Pharm. 81, 493–503 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1301-15
Jadhav, P., Petkar, B., Pore, Y., Kukarni, A., Burade, K.: Physicochemical and molecular modeling studies of cefixime–L-arginine–cyclodextrin ternary inclusion compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 98, 1317–1325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.070
Obaidat, R.M., Khanfar, M., Ghanma, R.A.: comparative solubility enhancement study of cefixime trihydrate using different dispersion techniques. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 20, 194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1395-y
Pamudji, J.S., Mauludin, R., Nurhabibah, A.: Influence of β-cyclodextrin on cefixime stability in liquid suspension dosage form. Procedia Chem. 13, 119–127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.12.015
Mallick, S., Mondal, A., Sannigrahi, S.: Kinetic measurements of the hydrolytic degradation of cefixime: effect of Captisol complexation and water-soluble polymers. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 60, 833–841 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.60.7.0004
Khan, Q., Siddique, M.I., Rasool, F., Naeem, M., Usman, M., Zaman, M.: Development and characterization of orodispersible film containing cefixime trihydrate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 46, 2070–2080 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2020.1843477
Cirri, M., Mennini, N., Nerli, G., Rubia, J., Casalone, E., Melani, F., Maestrelli, F., Mura, P.: Combined use of cyclodextrins and amino acids for the development of cefixime oral solutions for pediatric use. Pharmaceutics 13, 1932 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111923
Agrawal, G.P., Maheshwari, R.K., Mishra, P.: Solubility enhancement of cefixime trihydrate by solid dispersions using hydrotropic solubilization technique and their characterization. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902020000118553
Saifullah, S., Kanwal, T., Ullah, S., Kawish, M., Habib, S.M., Ali, I., Munir, A., Imran, M., Shah, M.R.: Design and development of lipid modified chitosan containing muco-adhesive self-emulsifying drug delivery systems for cefixime oral delivery. Chem. Phys. Lipids 235, 105052 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2021.105052
Mahmood, A., Khan, L., Ijaz, M., Nazir, I., Naseem, M., Tahir, M.A., Aamir, M.N., Rehman, M.U., Asim, M.H.: Enhanced intestinal permeability of cefixime by self-emulsifying drug delivery system: in-vitro and ex-vivo characterization. Molecules 28, 2827 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062827
Balya, H., Radhakrishnan, A., Jabaris, S.L., Gopal, D.V.R.S., Kuppusamy, G., Seetharaman, S.: Fabrication of novel bio-compatible cefixime nanoparticles using chitosan and Azadirachta indica fruit mucilage as natural polymers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 66, 102750 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102750
Mahjoub, M.A., Ebrahimnejad, P., Shahlaee, F., Ebrahimi, P., Sadeghi-Ghadi, Z.: Preparation and optimization of controlled release nanoparticles containing cefixime using central composite design: an attempt to enrich its antimicrobial activity. Curr. Drug Deliv. 19, 369–378 (2022). https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201818666210726160956
Haghighi, D.M., Faghihi, H., Darabi, M., Mirmoeini, M.S., Vatanara, A.: Spray freeze drying to solidify nanosuspension of cefxime into inhalable microparticles. Drug J. Pharm. Sci. 30, 17–27 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-021-00426-4
Kamran, M., Khan, M.A., Rehman, M., Shafique, M., Khan, A., Ahmad, S.: Binary solid lipid nanosuspension containing cefixime: preparation, characterization and comparative in-vivo evaluation. Beilstein Arch. 39, 762–770 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3762/bxiv.2019.109.v1
Ata, S., Rasool, A., Islam, A., Bibi, I., Rizwan, M., Azeem, M.K., Qureshi, A.U.R., Iqbal, M.: Loading of cefixime to pH sensitive chitosan based hydrogel and investigation of controlled release kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 155, 1236–1244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.091
Chaturvedi, P., Soni, P.K., Paswan, S.K.: Designing and development of gastroretentive mucoadhesive microspheres of cefixime trihydrate using spray dryer. Int. J. App. Pharm. 15, 185–193 (2023). https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2023v15i2.45399
Razdan, K., Sahajpal, N.S., Singh, K., Singh, H., Singh, H., Jain, S.K.: Formulation of sustained-release microspheres of cefixime with enhanced oral bioavailability and antibacterial potential. Ther. Deliv. 10, 769–782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4155/tde-2019-0057
Wupper, S., Luersen, K., Rimbach, G.: Cyclodextrins, natural compounds, and plant bioactives–a nutritional perspective. Biomolecules 11, 401 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030401
Periasamy, R.: Cyclodextrin-based molecules as hosts in the formation of supramolecular complexes and their practical applications—a review. J Carbohyd Chem. 40, 135–155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/07328303.2021.1967970
Jacob, S., Nair, A.B.: Cyclodextrin complexes: perspective from drug delivery and formulation. Drug Dev. Res. 79, 201–217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21452
Khushboo, L., Anuj, G.: Inclusion complex of chrysin with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) preparation, characterization, and dissolution study. BioNanoScience. 13, 616–624 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01106-0
Prachi, P., Prabha, S., Arati, P., Sonika, G.: Development and optimization of HP-β-CD inclusion complex-based fast orally disintegrating tablet of pitavastatin calcium. J. Pharm. Innov. 17, 993–1010 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-022-09661-x
Pardeshi, C.V., Kothawade, R.V., Markad, A.R., Pardeshi, S.R., Kulkarni, A.D., Chaudhari, P.J., Longhi, M., Dhas, N., Naik, J.B., Surana, S.J., Garcia, M.C.: Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin: a functional biopolymer for drug delivery applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 301, 120347 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120347
Soe, H.M.H., Chamni, S., Mahalapbutr, P., Kongtaworn, N., Rungrotmongkol, T., Jansook, P.: The investigation of binary and ternary sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with asiaticoside in solution and in solid state. Carbohydr. Res. 498, 108190 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2020.108190
Lateh, L., Kaewnopparat, N., Yuenyongsawad, S.: Panichayupakaranantract using a ternary inclusion complex system: Preparation, characterization, and anti-cancer activity. Food Chem. 368, 130827 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130827
Suvarna, V., Gujar, P., Murahari, M., Sharma, D., Chamariya, R.: Supramolecular ternary inclusion complexes of Irbesartan with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 67, 102964 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102964
Londhe, V.Y., Pawar, A., Kundaikar, H.: Studies on spectral characterization and solubility of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/iloperidone binary and ternary complexes using different auxiliary agents. J. Mol. Struct. 1220, 128615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128615
Zhang, Q.H., Ren, W., Dushkin, A.V., Su, W.K.: Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies of olmesartan medoxomil in a ternary solid dispersion with N-methyl-D-glucamine and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 56, 101546 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101546
Cuccu, F., De Luca, L., Delogu, F., Colacino, E., Solin, N., Mocci, R., Porcheddu, A.: Mechanochemistry: new tools to navigate the uncharted territory of “Impossible” reactions. Chem Sus Chem. 15, e202200362 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202200362
Ardila-Fierro, K.J., Hernandez, J.G.: Sustainability assessment of mechanochemistry by using the twelve principles of green chemistry. Chem. Sus Chem. 14, 2145–2162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202100478
Li, L., Wang, G.W.: Mechanochemical solvent-free synthesis of indenones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkynes. J. Org. Chem. 86, 14102–14112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c01472
Wu, C.Y., Ying, T., Fan, H.Q., Hu, C.H., Su, W.K., Yu, J.B.: C-4 regioselective alkylation of pyridines driven by mechanochemically activated magnesium metal. Org. Lett. 25, 2531–2536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00684
Rincon, E., Balu, A.M., Luque, R.: Mechanochemical extraction of antioxidant phenolic compounds from Mediterranean and medicinal Laurus nobilis: a comparative study with other traditional and green novel techniques. Ind. Crop Prod. 141, 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111805
Zhu, P.X., Hao, M.Y., Su, F., Xu, W.H., Zhang, Q.H., Su, W.K., Adams, E.: Mechanochemical-assisted extraction of essential oils from Citrus aurantium L. var. amara Engl. Ind. Crop Prod. 188, 1–7 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115703
Ferreira, P.O., Almeida, A.C., Costa, G.P., Torquetti, C., Baptista, J.A., Eusébio, M.E.S., Caires, F.J., Castro, R.A.E.: Norfloxacin cocrystals: mechanochemical synthesis and scale-up viability through solubility studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 112, 2230–2239 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2023.03.003
Sun, X.R., Zhu, D.B., Cai, Y., Shi, G.B., Gao, M.S., Zheng, M.Z.: One-step mechanochemical preparation and prominent antitumor activity of SN-38 self-micelle solid dispersion. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 2115–2126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193783
Xu, W.H., Yang, J.L., Gu, X.Y., Su, W.J., Pu, F.X., **e, Z.F., **, K.L., Su, W.K., Mao, L.C.: Mechanochemical prepared ibuprofen-Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide drug delivery system for enhanced bioactivity with reduced renal injury induced by NSAIDs. Drug Deliv. 29, 351–363 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2026533
Kong, R.P., Zhu, X.Y., Meteleva, E.S., Polyakov, N.E., Khvostov, M.V., Baev, D.S., Tolstikova, T.G., Dushkin, A.V., Su, W.K.: Mechanochemical preparation and properties of water-soluble intermolecular complexes of arabinogalactan and disodium glycyrrhizin with atorvastatin calcium. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 8, 1200–1213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0565-x
Rodrigo, E., Wiechert, R., Walter, M.W., Braje, W., Geneste, H.: One-step hydroxylation of aryl and heteroaryl fluorides using mechanochemistry. Green Chem. 24, 1469–1473 (2022)
Pagola, S.: Outstanding advantages, current drawbacks, and significant recent developments in mechanochemistry: a perspective view. Crystals 13, 124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13010124
Nart, V., França, M.T., Anzilaggo, D., Riekes, M.K., Kratz, J.M., de Campos, C.E., Simões, C.M., Stulzer, H.K.: Ball-milled solid dispersions of BCS class IV drugs: impact on the dissolution rate and intestinal permeability of acyclovir. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 53, 229–238 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.04.028
Zhang, Q.H., Feng, Z.M., Ren, W., Zhao, Y.C., Dushkin, A.V., Su, W.K.: Preparation of olmesartan medoxomil solid dispersion with sustained release performance by mechanochemical technology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12, 589–602 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00959-w
Kawasaki, R., Kawamura, S., Kodama, T., Yamana, K., Maeda, A., Yimiti, D., Miyaki, S., Hino, S., Ozawa, N., Nishimura, T., Kawamoto, S., Ikeda, A.: Development of a water-dispersible supramolecular complex of polyphenol with polypeptides for attenuation of the allergic response using a mechanochemical strategy. Macromol. Biosci. 23, e2200462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.202200462
Higuchi, T.A., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. In: Reilley, C.N. (ed.) Advances in Analytical Chemistry and Instrumentation, ume 4, pp. 117–212. Wiley, New York (1965)
Brewster, M.E., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 645–666 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012
Suvarna, V., Thorat, S., Nayak, U., Sherje, A., Murahari, M.: Host-guest interaction study of Efavirenz with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and L-arginine by computational simulation studies: Preparation and characterization of supramolecular complexes. J. Mol. Liq. 259, 55–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.131
Trott, O., Olson, A.J.: AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 455–461 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Huang, T., Zhao, Q., Su, Y., Ouyang, D.F.: Investigation of molecular aggregation mechanism of glipizide/cyclodextrin complexation by combined experimental and molecular modeling approaches. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 14, 609–620 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2018.10.008
Mura, P., Maestrelli, F., Cirri, M., Furlanetto, S., Pinzauti, S.: Differential scanning calorimetry as an analytical tool in the study of drug-cyclodextrin interactions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 73, 635–646 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025494500283
Aloisioa, C., de Oliveira, A.G., Longhi, M.: Solubility and release modulation effect of sulfamerazine ternary complexes with cyclodextrins and meglumine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 100, 64–73 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.008
Dushkin, A.V., Tolstikova, T.G., Khvostov, M.V., Tolstikov, G.A.: Complexes of polysaccharides and glycyrrhizic acid with drug molecules. Mechanochemical synthesis and pharmacological activity. In: Karunaratne, D.N. (ed.) The Complex World of Polysaccharides, vol. 22, pp. 573–602. InTech, Rijeka (2012). https://doi.org/10.5772/48095
Sahu, K.M., Patra, S., Swain, S.K.: Host-guest drug delivery by β-cyclodextrin assisted polysaccharide vehicles: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 240, 124338 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124338
Kong, R.P., Zhu, X.Y., Meteleva, E.S., Chistyachenko, Y.S., Suntsova, L.P., Polyakov, N.E., Khvostov, M.V., Baev, D.S., Tolstikova, T.G., Yu, J.M., Dushkin, A.V., Su, W.K.: Enhanced solubility and bioavailability of simvastatin by mechanochemically obtained complexes. Int. J. Pharmaceutics. 534, 108–118 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.10.011
Kong, R.P., Zhu, X.Y., Meteleva, E.S., Dushkin, A.V., Su, W.K.: Physicochemical characteristics of the complexes of simvastatin and atorvastatin calcium with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin produced by mechanochemical activation. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 46, 436–445 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2018.05.018
Alvi, Z., Akhtar, M., Mahmood, A., Ur-Rahman, N., Nazir, I., Sadaquat, H., Ijaz, M., Syed, S.K., Waqas, M.K., Wang, Y.: Enhanced oral bioavailability of epalrestat SBE7-β-CD complex loaded chitosan nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and in-vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 16, 8353–8373 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S339857
Kerns, E.H., Di, L., Petusky, S., Farris, M., Ley, R., Jupp, P.: Combined application of parallel artificial membrane permeability assay and Caco-2 permeability assays in drug discovery. J. Pharm. Sci. 93, 1440–1453 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20075
Loftsson, T., Konrádsdóttir, F., Másson, M.: Development and evaluation of an artificial membrane for determination of drug availability. Int. J. Pharm. 326, 60–68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.009
Brewster, M.E., Noppe, M., Peeters, J., Loftsson, T.: Effect of the unstirred water layer on permeability enhancement by hydrophilic cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 342, 250–253 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.04.029
Chougule, M.B., Patel, A.R., Patlolla, R., Jackson, T., Singh, M.: Epithelial transport of noscapine across cell monolayer and influence of absorption enhancers on in vitro permeation and bioavailability: Implications for intestinal absorption. J. Drug Target. 22, 498–508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2014.894046
Onoue, S., Nakamura, T., Uchida, A., Ogawa, K., Yuminoki, K., Hashimoto, N., Hiza, A., Tsukaguchi, Y., Asakawa, T., Kan, T., Yamada, S.: Physicochemical and biopharmaceutical characterization of amorphous solid dispersion of nobiletin, a citrus polyethoxylated flavone, with improved hepatoprotective effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 49, 453–460 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2013.05.014
Banik, S., Sato, H., Onoue, S.: Self-micellizing solid dispersion of atorvastatin with improved physicochemical stability and oral absorption. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 68, 103065 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.103065
Loftsson, T., Vogensen, S.B., Brewster, M.E., Konrádsdóttir, F.: Effects of cyclodextrins on drug delivery through biological membranes. J. Pharm. Sci. 96, 2532–2546 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20992
Rong, W.T., Lu, Y.P., Tao, Q., Guo, M., Lu, Y., Ren, Y., Yu, S.Q.: Hydroxypropyl-sulfobutyl-β-cyclodextrin improves the oral bioavailability of edaravone by modulating drug efflux pump of enterocytes. J. Pharm. Sci. Feb. 103, 730–742 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23807
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Food and Pharmaceutical Science College (Grant No. JSFP2019002), by grants HAB202240 from the Huai'an Municipal Science and Technology Bureau in Jiangsu, and the Major Basic Research Project of the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Grant No. 23KJA350001). We would like to thank Shuang Zheng (Jiangsu Food and Pharmaceutical Science College) for help with the bioavailability experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by RPK, LWX, LZ and YRS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by RPK, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, R., Xu, L., Zhu, L. et al. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of cefixime ternary inclusion complexes formated by mechanochemical strategy. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 104, 51–71 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01214-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-023-01214-0