Abstract
Objectives
The goal of this study was to quantify CEST related parameters such as chemical exchange rate and fractional concentration of exchanging protons at a clinical 3T scanner. For this purpose, two CEST quantification approaches—the AREX metric (for ‘apparent exchange dependent relaxation’), and the AREX-based Ω-plot method were used. In addition, two different pulsed RF irradiation schemes, using Gaussian-shaped and spin-lock pulses, were compared.
Materials and methods
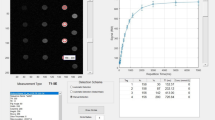
Numerical simulations as well as MRI measurements in phantoms were performed. For simulations, the Bloch–McConnell equations were solved using a two-pool exchange model. MR experiments were performed on a clinical 3T MRI scanner using a cylindrical phantom filled with creatine solution at different pH values and different concentrations.
Results
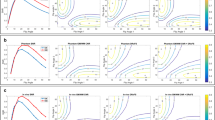
The validity of the Ω-plot method and the AREX approach using spin-lock preparation for determination of the quantitative CEST parameters was demonstrated. Especially promising results were achieved for the Ω-plot method when the spin-lock preparation was employed.
Conclusion
Pulsed CEST at 3T could be used to quantify parameters such as exchange rate constants and concentrations of protons exchanging with free water. In the future this technique might be used to estimate the exchange rates and concentrations of biochemical substances in human tissues in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS (2000) A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J Magn Reson 143:79–87
van Zijl PC, Yadav NN (2011) Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST): what is in a name and what isn’t? Magn Reson Med 65(4):927–948
Vinogradov E, Sherry AD, Lenkinski RE (2013) CEST: from basic principles to applications, challenges and opportunities. J Magn Reson 229:155–172
Zhang S, Malloy CR, Sherry AD (2005) MRI thermometry based on PARACEST agents. J Am Chem Soc 127:17572–17573
Müller-Lutz A, Khalil N, Schmitt B, Jellus V, Pentang G, Oeltzschner G, Antoch G, Lanzman RS, Wittsack HJ (2014) Pilot study of Iopamidol-based quantitative pH imaging on a clinical 3T MR scanner. Magn Reson Mater Phy 27(6):477–485
Longo DL, Sun PZ, Consolino L, Michelotti FC, Uggeri F, Aime S (2014) A general MRI-CEST ratiometric approach for pH imaging: demonstration of in vivo pH map** with Iobitridol. J Am Chem Soc 136(41):14333–14336
Wu R, **ao G, Zhou IY, Ran C, Sun PZ (2015) Quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (qCEST) MRI–omega plot analysis of RF-spillover-corrected inverse CEST ratio asymmetry for simultaneous determination of labile proton ratio and exchange rate. NMR Biomed 28(3):376–383
Kim J, Wu Y, Guo Y, Zheng H, Sun PZ (2014) A review of optimization and quantification techniques for chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI toward sensitive in vivo imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 10(3):163–178
Woessner DE, Zhang S, Merritt ME, Sherry AD (2005) Numerical solution of the Bloch equations provides insights into the optimum design of PARACEST agents for MRI. Magn Reson Med 53:790–799
McMahon MT, Gilad AA, Zhou J, Sun PZ, Bulte JW, van Zijl PC (2006) Quantifying exchange rates in chemical exchange saturation transfer agents using the saturation time and saturation power dependencies of the magnetization transfer effect on the magnetic resonance imaging signal (QUEST and QUESP): pH calibration for poly-l-lysine and a starburst dendrimer. Magn Reson Med 55(4):836–847
Dixon WT, Ren J, Lubag AJ, Ratnakar J, Vinogradov E, Hancu I, Lenkinski RE, Sherry AD (2010) A concentration-independent method to measure exchange rates in PARACEST agents. Magn Reson Med 63(3):625–632
Sun PZ (2012) Simplified quantification of labile proton concentration weighted chemical exchange rate (kws) with RF saturation time dependent ratiometric analysis (QUESTRA): normalization of relaxation and RF irradiation spillover effects for improved quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. Magn Reson Med 67(4):936–942
Sun PZ (2010) Simultaneous determination of labile proton concentration and exchange rate utilizing optimal RF power: radio frequency power (RFP) dependence of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. J Magn Reson 202(2):155–161
Wu R, Liu CM, Liu PK, Sun PZ (2012) Improved measurement of labile proton concentration-weighted chemical exchange rate (kws) with experimental factor-compensated and T1-normalized quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 7(4):384–389
Sun PZ, Wang Y, Dai Z, **ao G, Wu R (2014) Quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (qCEST) MRI–RF spillover effect-corrected omega plot for simultaneous determination of labile proton fraction ratio and exchange rate. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 9(4):268–275
Sun PZ, Wang E, Cheung JS, Zhang X, Benner T, Sorensen AG (2011) Simulation and optimization of pulsed radio frequency (RF) irradiation scheme for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI—demonstration of pH-weighted pulsed-amide proton CEST MRI in an animal model of acute cerebral ischemia. Magn Reson Med 66(4):1042–1048
Schmitt B, Zaiss M, Zhou J, Bachert P (2011) Optimization of pulse train pre-saturation for CEST imaging in clinical scanners. Magn Reson Med 65:1620–1629
Sun PZ, Brenner T, Kumar A, Sorensen AG (2008) Investigation of optimizing and translating pH-sensitive pulsed-chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging to a 3T clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med 60:834–841
Zaiss M, Xu J, Goerke S, Khan IS, Singer RJ, Gore JC, Gochberg DF, Bachert P (2014) Inverse Z-spectrum analysis for spillover-, MT-, and T1- corrected steady-state pulsed CEST-MRI–application to pH-weighted MRI of acute stroke. NMR Biomed 27(3):240–252
Meissner JE, Goerke S, Rerich E, Klika KD, Radbruch A, Ladd ME, Bachert P, Zaiss M (2015) Quantitative pulsed CEST-MRI using Ω-plots. NMR Biomed 28:1196–1208
Zaiss M, Bachert P (2013) Exchange-dependent relaxation in the rotating frame for slow and intermediate exchange–modeling off-resonant spin-lock and chemical exchange saturation transfer. NMR Biomed 26(5):507–518
Roeloffs V, Meyer C, Bachert P, Zaiss M (2014) Towards quantification of pulsed spinlock and CEST at clinical MR scanners: an analytical interleaved saturation-relaxation (ISAR) approach. NMR Biomed 28:40–53
** T, Aution J, Obata T, Kim SG (2011) Spin-locking versus chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI for investigating chemical exchange process between water and labile metabolite protons. Magn Reson Med 65:1448–1460
** T, Kim SG (2014) Advantages of chemical exchange-sensitive spin-lock (CESL) over chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) for hydroxyl- and amine-water proton exchange rates. NMR Biomed 27(11):1313–1324
Cobb JG, Li K, **e J, Gochberg DF, Gore JC (2014) Exchange-mediated contrast in CEST and spin-lock imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 32(1):28–40
Yuan J, Zhou J, Ahuja AT, Wang YX (2013) MR chemical exchange imaging with spin-lock technique (CESL): a theoretical analysis of Z-spectrum using a two-pool R 1ρ relaxation model beyond the fast-exchange limit. Phys Med Biol 57(24):8185–8200
Murase K, Tanki N (2011) Numerical solutions to the time-dependent Bloch equations revisited. Magn Reson Imaging 29(1):126–131
Goerke S, Zaiss M, Bachert P (2014) Characterization of creatine guanidinium proton exchange by water-exchange (WEX) spectroscopy for absolute-pH CEST imaging in vitro. NMR Biomed 27(5):507–518
Kim M, Gillen J, Landmann BA, Zhou J, van Zijl PC (2009) Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer experiments. Magn Reson Med 61(6):1441–1450
Müller-Lutz A, Matuschke F, Schleich C, Wickrath F, Boos J, Schmitt B, Wittsack HJ (2016) Improvement of water saturation shift referencing by sequence and analysis optimization to enhance chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 34(6):771–778
Sun PZ, Farrar CT, Sorensen AG (2007) Correction for artifacts induced by B0 and B1 field inhomogeneities in pH-sensitive chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1207–1215
Randtke EA, Chen LQ, Corrales LR, Pagel MD (2014) The Hanes-Woolf linear QUESP method improves the measurements of fast chemical exchange rates with CEST MRI. Magn Reson Med 71(4):1603–1612
Zhou J, Wilson DA, Sun PZ, Klaus JA, van Zijl PC (2004) Quantitative description of proton exchange processes between water and endogenous and exogenous agents for WEX, CEST and APT experiments. Magn Reson Med 51(5):945–952
Sun PZ, Wang E, Cheung JS (2012) Imaging acute ischemic tissue acidosis with pH-sensitive endogenous amide proton transfer (APT) MRI–correction of tissue relaxation and concomitant RF irradiation effects toward map** quantitative cerebral tissue pH. Neuroimage 60(1):1–6
Gudbjartsson H, Patz S (1995) The Rician distribution of noisy MRI data. Magn Reson Med 34(6):910–914
Henkelman RM, Stanisz GJ, Graham SJ (2001) Magnetization transfer in MRI: a review. NMR Biomed 14:57–64
Jones CK, Huang A, Xu J, Edden RA, Schär M, Hua J, Oskolkov N, Zacà D, Zhou J, McMahon MT, Pillai JJ, van Zijl PC (2013) Nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) imaging in the human brain at 7T. Neuroimage 77:114–124
Keupp J, Togao O, Zhou J, Suzuki Y, Yoshiura T (2012) Optimization of saturation pulse length in parallel transmission based amide proton transfer MRI for oncology applications. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 20:4258
Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Keupp J, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Yoshiura T, Yoneyama M, Kruiskamp MJ, Sagiyama K, Takahashi M, Honda H (2016) Amide proton transfer imaging of diffuse gliomas: effect of saturation pulse length in parallel transmission-based technique. PLoS One 11(5):e0155925
Zhou Z, Bez M, Tawackoli W, Giaconi J, Sheyn D, de Mel S, Maya MM, Pressman BD, Gazit Z, Pelled G, Gazit D, Li D (2016) Quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI of intervertebral disc in a porcine model. Magn Reson Med 76(6):1677–1683
Heo HY, Zhang Y, Leen DH, Jiang S, Zhao X, Zhou J (2016) Accelerating chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI by combining compressed sensing and sensitivity encoding techniques. Magn Reson Med 77:779–786
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Zaiss (German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany) for providing CEST MRI pulse sequence used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Stabinska: Protocol/project development, data management, data analysis. Cronenberg: Protocol/project development, data collection, data analysis. Wittsack: Protocol/project development. Lanzman: Protocol/project development. Müller-Lutz: Protocol/project development.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant from the Forschungskommission of the Faculty of Medicine, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf (Grant No: 13/2015).
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
See Figs. 6 and 7 and Table 2.
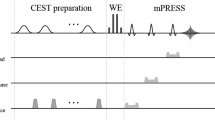
A simplified schematic CEST pulse sequence diagram with a series of a Gaussian-shaped RF saturation pulses and b off-resonant spin-lock saturation pulses. Each saturation block consists of n pulses of average amplitude B 1 and duration t p interleaved by delays t d . Between the saturation pulses spoiling gradients in all three gradient dimensions are applied. After RF saturation a 2-D single-shot gradient echo sequence (GRE) was used for CEST image data acquisition. Diagram was created based on [22, 28]
Z-spectrum and AREX curves obtained with B 1 = 0.5 µT and B 1 = 1.65 µT using pulsed SL (dashed blue lines) and Gaussian-shaped saturation pulses (solid green lines). For the pulsed SL saturation, AREX yields higher contrast at higher B 1 compared to saturation with trains of Gaussian-shaped RF pulses
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stabinska, J., Cronenberg, T., Wittsack, HJ. et al. Quantitative pulsed CEST-MRI at a clinical 3T MRI system. Magn Reson Mater Phy 30, 505–516 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0625-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-017-0625-0