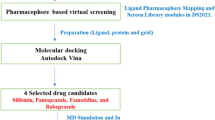
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death in women worldwide. Initially, it develops in the epithelium of the ducts or lobules of the breast glandular tissues with limited growth and the potential to metastasize. It is a highly heterogeneous malignancy; however, the common molecular mechanisms could help identify new targeted drugs for treating its subtypes. This study uses computational drug repositioning approaches to explore fresh drug candidates for breast cancer treatment. We also implemented reversal gene expression and gene expression–based signatures to explore novel drug candidates computationally. The drug activity profiles and related gene expression changes were acquired from the DrugBank, PubChem, and LINCS databases, and then in silico drug screening, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, replica exchange MD simulations, and simulated annealing molecular dynamics (SAMD) simulations were conducted to discover and verify the valid drug candidates. We have found that compounds like furosemide, gold, and dopamine showed significant outcomes. Furthermore, the expression of genes related to breast cancer was observed to be reversed by these shortlisted drugs. Therefore, we postulate that combining furosemide, gold, and dopamine would be a potential combination therapy measurement for breast cancer patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the primary author upon a reasonable request.
References
Adey A et al (2013) The haplotype-resolved genome and epigenome of the aneuploid HeLa cancer cell line. Nature 500:207–211
Barretina J et al (2012) The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 483:603–607
Barretina J et al (2019) Addendum: The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 565:E5–E6
Barrett T, Edgar R (2006) Mining microarray data at NCBIʼs Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)*. Methods Mol Biol 338:175–190
Bouhaddou M et al (2016) Drug response consistency in CCLE and CGP. Nature 540:E9–E10
Wishart DS et al (2008) DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D901–D906
Bowers KJ et al. (2006) Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In: conference on high performance computing (supercomputing)
Chen W et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66:115–132
Chen I-J, Foloppe N (2013) Tackling the conformational sampling of larger flexible compounds and macrocycles in pharmacology and drug discovery. Bioorg Med Chem 21:7898–7920
Chong CR, Sullivan DJ Jr (2007) New uses for old drugs. Nature 448:645–646
Xue H, Li J, **e H, Wang Y (2018) Review of drug repositioning approaches and resources. Int J Biol Sci 14:1232–1244
DiMasi JA, Hansen RW, Grabowski HG (2003) The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. J Health Econ 22:151–185
Doucet N, Pelletier JN (2007) Simulated annealing exploration of an active‐site tyrosine in TEM‐1β‐lactamase suggests the existence of alternate conformations. Proteins 69:340–348
Dovrolis N, Kolios G, Spyrou G, Maroulakou I (2017) Laying in silico pipelines for drug repositioning: a paradigm in ensemble analysis for neurodegenerative diseases. Drug Discov Today 22:805–813
Taqi MM, Waseem D, Ismatullah H, Haider SA, Faisal M (2016) In silico transcriptional regulation and functional analysis of dengue shock syndrome associated SNPs in PLCE1 and MICB genes. Funct Integr Genomics 16:335–345
Sirota M et al. (2011) Discovery and preclinical validation of drug indications using compendia of public gene expression data. Sci Transl Med 3:96ra77
Duan Q et al (2014) LINCS Canvas Browser: interactive web app to query, browse and interrogate LINCS L1000 gene expression signatures. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W449-460
Gagnon JK, Law SM, Brooks CL III (2016) Flexible CDOCKER: Development and application of a pseudo-explicit structure-based docking method within CHARMM. J Comput Chem 37:753–762
Giuliano AE, et al. (2017) Breast cancer-major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin 67:290–303
Global Burden of Disease Cancer C et al. (2017) Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol 3:524–548
Golestan S, Soltani BM, Jafarzadeh M, Ghaemi Z, Nafisi N (2023) LINC02381 suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via attenuating IGF1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23:40
Tseng GC, Ghosh D, Feingold E (2012) Comprehensive literature review and statistical considerations for microarray meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 40:3785–3799
Guo Z, Mohanty U, Noehre J, Sawyer TK, Sherman W, Krilov G (2010) Probing the alpha-helical structural stability of stapled p53 peptides: molecular dynamics simulations and analysis. Chem Biol Drug Des 75:348–359
Harvell DM et al (2013) Genomic signatures of pregnancy-associated breast cancer epithelia and stroma and their regulation by estrogens and progesterone. Horm Cancer 4:140–153
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJ, Fraaije JG (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472
Huang CS, Lin CH, Lu YS, Shen CY (2010) Unique features of breast cancer in Asian women–breast cancer in Taiwan as an example. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 118:300–303
Huang G, Li J, Wang P, Li W (2017) A review of computational drug repositioning approaches. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen
Iorio F, Rittman T, Ge H, Menden M, Saez-Rodriguez J (2013) Transcriptional data: a new gateway to drug repositioning? Drug Discov Today 18:350–357
Jao CC, Hegde BG, Chen J, Haworth IS, Langen R (2008) Structure of membrane-bound α-synuclein from site-directed spin labeling and computational refinement. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:19666–19671
Jiang Y, Wang M (2010) Personalized medicine in oncology: tailoring the right drug to the right patient. Biomark Med 4:523–533
Kang DD, Sibille E, Kaminski N, Tseng GC (2012) MetaQC: objective quality control and inclusion/exclusion criteria for genomic meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e15
Keenan AB et al (2018) The library of integrated network-based cellular signatures NIH program: system-level cataloging of human cells response to perturbations. Cell Syst 6:13–24
Kim S et al (2016) PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1202-1213
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD Jr, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by Simulated Annealing Science 220:671–680
Koleti A et al (2018) Data Portal for the Library of Integrated Network-based Cellular Signatures (LINCS) program: integrated access to diverse large-scale cellular perturbation response data. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D558–D566
Lang JE et al (2015) Expression profiling of circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 149:121–131
Law V et al (2014) DrugBank 4.0: shedding new light on drug metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1091-1097
Lee SH, van der Werf JH, Hayes BJ, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2008) Predicting unobserved phenotypes for complex traits from whole-genome SNP data. PLoS Genet 4:e1000231
Lee J, Gross SP, Lee J (2012) Modularity optimization by conformational space annealing. Phys Rev E 85:056702
Li WX et al (2017) Comprehensive tissue-specific gene set enrichment analysis and transcription factor analysis of breast cancer by integrating 14 gene expression datasets. Oncotarget 8:6775–6786
Simon R, Roychowdhury S (2013) Implementing personalized cancer genomics in clinical trials. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:358–369
Li J, Zheng S, Chen B, Butte AJ, Swamidass SJ, Lu Z (2016) A survey of current trends in computational drug repositioning. Brief Bioinform 17:2–12
Li D, Chen P, Shi T, Mehmood A, Qiu J (2021) HD5 and LL-37 inhibit SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 binding to human ACE2 by molecular simulation. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences 13:766–777
Shivakumar D, Williams J, Wu Y, Damm W, Shelley J, Sherman W (2010) Prediction of absolute solvation free energies using molecular dynamics free energy perturbation and the OPLS force field. J Chem Theory Comput 6:1509–1519
Wang Y, **ao J, Suzek TO, Zhang J, Wang J, Bryant SH (2009) PubChem: a public information system for analyzing bioactivities of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W623–W633
Li M, Zhao Y, Li H, Deng X, Sheng M (2023) Application value of circulating LncRNA in diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23:61
Wang L, Wang Y, Bi J (2022) In silico development and experimental validation of a novel 7-gene signature based on PI3K pathway-related genes in bladder cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 22:797–811
Locke WJ, Clark SJ (2012) Epigenome remodelling in breast cancer: insights from an early in vitro model of carcinogenesis. Breast Cancer Res 14:215
Lu S, Li J, Song C, Shen K, Tseng GC (2010) Biomarker detection in the integration of multiple multi-class genomic studies. Bioinformatics 26:333–340
Mediratta K, El-Sahli S, D'Costa V, Wang L. (2020) Current progresses and challenges of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers 12
Mehla K, Ramana J (2017) Surface proteome mining for identification of potential vaccine candidates against Campylobacter jejuni: an in silico approach. Funct Integr Genomics 17:27–37
Mehmood A, Khan MT, Kaushik AC, Khan AS, Irfan M, Wei D-Q (2019) Structural dynamics behind clinical mutants of PncA-Asp12Ala, Pro54Leu, and His57Pro of Mycobacterium tuberculosis associated with pyrazinamide resistance. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 7:404
Mehmood A, Nawab S, ** Y, Hassan H, Kaushik AC, Wei D-Q (2023a) Ranking breast cancer drugs and biomarkers identification using machine learning and pharmacogenomics. ACS Pharmacol Translat Sci
Mehmood A, Nawab S, ** Y, Kaushik AC, Wei D-Q (2023b) Mutational impacts on the N and C terminal domains of the MUC5B protein: a transcriptomics and structural biology study. ACS Omega
Mehmood A, Kaushik AC, Wang Q, Li C-D, Wei D-Q (2021) Bringing structural implications and deep learning-based drug identification for KRAS mutants. J Chem Inf Model 61:571–586
Mehmood A, Nawab S, Wang Y, Kaushik AC, Wei D-Q (2022) Discovering potent inhibitors against the Mpro of the SARS-CoV-2. A medicinal chemistry approach. Comp Biol Med 143:105235
Mishra A, Verma M (2010) Cancer biomarkers: are we ready for the prime time? Cancers (basel) 2:190–208
Mobasheri MB et al (2015) Transcriptome analysis of the cancer/testis genes, DAZ1, AURKC, and TEX101, in breast tumors and six breast cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol 36:8201–8206
Morris GM et al (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791
Wang X, Lin Y, Song C, Sibille E, Tseng GC (2012) Detecting disease-associated genes with confounding variable adjustment and the impact on genomic meta-analysis: with application to major depressive disorder. BMC Bioinformatics 13:52
Morris GM et al (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791
Nederlof I et al (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of methods to assess overall and cell-specific immune infiltrates in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 21:151
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108
Nogales-Cadenas R et al (2016) MicroRNA expression and gene regulation drive breast cancer progression and metastasis in PyMT mice. Breast Cancer Res 18:75
Ober U et al (2012) Using whole-genome sequence data to predict quantitative trait phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet 8:e1002685
Oliver S (2000) Guilt-by-association goes global. Nature 403:601–603
O’Shaughnessy J (2005) Extending survival with chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 10(Suppl 3):20–29
Pan Y, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Kong F (2023) Prognostic and immune microenvironment analysis of cuproptosis-related LncRNAs in breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23:38
Reddy SM et al (2018) Long-term survival outcomes of triple-receptor negative breast cancer survivors who are disease free at 5 years and relationship with low hormone receptor positivity. Br J Cancer 118:17–23
Sawyers CL (2008) The cancer biomarker problem. Nature 452:548–552
Schrödinger L, DeLano W (2020) The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020
Seashore-Ludlow B et al (2015) Harnessing connectivity in a large-scale small-molecule sensitivity dataset. Cancer Discov 5:1210–1223
Acknowledgements
The simulations in this work were supported by the Center for High-Performance Computing, Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no: 31900528), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20190601), Research Project of Public Health Research Center of Jiangnan University (grant number: JUPH201822), and Youth Fund for Basic Research Project of Jiangnan University (grant number: JUSRP11953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. C. K. designed the experiment. A. C. K., Z. W., and A. M. performed the entire computational experiments. A. C. K. and A. M. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. A. C. K., D. Q. W., Z. W., A. M., J. Y., H. Z., M. A-S., and L. W. read the manuscript and advised on method development. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Mehmood, A., Yao, J. et al. Combination of furosemide, gold, and dopamine as a potential therapy for breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 94 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01007-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01007-1