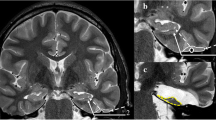
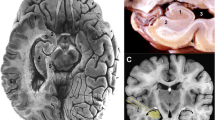
Abstract
Background
Surgery is superior over medicamentous treatment of pharmacoresistant mesial temporal lobe epilepsy caused by hippocampal sclerosis. The armamentarium of surgical procedures comprises standard temporal lobectomy and more selective procedures. Selective amygdalohippocampectomy can be performed via transcortical, transsylvian or subtemporal approach.
Method
Describe the selective amygdalohippocampectomy through the subtemporal approach
Conclusion
After the detailed preoperative epilepsy evaluation, surgery can be offered to pharmacoresistant epilepsy patient with hippocampal sclerosis. Selective amygdalohippocampectomy can be safely performed through the subtemporal approach. The good knowledge of the mesial temporal lobe anatomy is necessary when performing this procedure.
Key points
• Perform the subtemporal craniotomy with additional bone removal up to temporal petrous part to minimize retraction of the brain.
• Release the CSF from the subarachnoid sulcal space in order to relax the temporal lobe. Dissect the arachnoid around basal temporal veins and protect them with hemostatic material in order to avoid vein rupture.
• After gyrus fusiformis corticotomy, always follow the white matter in order to enter the temporal horn.
• Place the self-retraining retractor gently to secure an unobstructed view of the intraventricular mesial temporal lobe structures.
• Visualize the choroid plexus and the inferior choroidal point. They represent the two most important landmarks.
• While performing the anterior disconnection the goal is to reach the arachnoid of the interpeduncular and crural cistern medially and the tentorial edge laterally.
• Follow the tentorial edge and the arachnoid of the temporal base to securely perform the lateral disconnection.
• Perform the posterior disconnection at the level of the mesencephalon superior colliculi.
• During the medial disconnection the dissection of the arachnoid of the hippocampal sulcus must be done as close to the hippocampus as possible in order to avoid damage to the brain stem perforators or the loop of the anterior choroidal artery.
• Knowledge of mesial temporal lobe anatomy is crucial.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartha L, Trinka E, Ortler M, Donnemiller E, Felber S, Bauer G, Benke T (2004) Linguistic deficits following left selective amygdalohippocampectomy: a prospective study. Epilepsy Behav 5(3):348–357
Hori T, Tabuchi S, Kurosaki M, Kondo S, Takenobu A, Watanabe T (1993) Subtemporal amygdalohippocampectomy for treating medically intractable temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosurgery 33:50–57
Jefferys JGR (1999) Hippocampal sclerosis and temporal lobe epilepsy: cause or consequence? Brain 122(6):1007–1008
Niemeyer P (1958) The transventricular amygdala-hippocampectomy in the temporal lobe epilepsy. In: Baldwin M, Bailey P (eds) The temporal lobe epilepsy. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, pp 461–482
Olivier A (2000) Transcortical selective amygdalohippocampectomy in temporal lobe epilepsy. Can J Neurol Sci 27:S68–S76, S92–S96
Sincoff EH, Tan Y, Abdulrauf SI (2004) White matter fiber dissection of the optic radiations of the temporal lobe and implications for surgical approaches to the temporal horn. J Neurosurg 101(5):739–746
Tanriverdi T, Olivier A, Poulin N, Andermann F, Dubeau F (2008) Long-term seizure outcome after mesial temporal lobe epilepsy surgery: corticalamygdalohippocampectomy versus selective amygdalohippocampectomy. J Neurosurg 108:517–524
Taoka T, Sakamoto M, Nakagawa H, Nakase H, Iwasaki S, Takayama K, Taoka K, Hoshida T, Sakaki T, Kichikawa K (2008) Diffusion tensor tractography of the meyer loop in cases of temporal lobe resection for temporal lobe epilepsy: correlation between postsurgical visual field defect and anterior limit of meyer loop on tractography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1329–1334
Wen HT, Rhoton AL Jr, de Oliveira E, Cardoso AC, Tedeschi H, Baccanelli M, Marino R Jr (1999) Microsurgical anatomy of the temporal lobe: Part 1: mesial temporal lobe anatomy and its vascular relationships as applied to amygdalohippocampectomy. Neurosurgery 45:549–591
Wieser HG, Yasargil MG (1982) Selective amygdalohippocampectomy as a surgical treatment of mesiobasal limbic epilepsy. Surg Neurol 17:445–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(MPG 28826 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajko, T., Škoro, I. & Rotim, K. How I do it – selective amygdalohippocampectomy via subtemporal approach. Acta Neurochir 155, 2381–2387 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1846-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1846-2