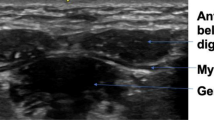
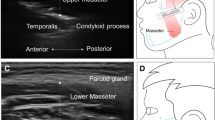
Abstract
B-mode ultrasound is a safe noninvasive procedure that has been used to characterize aspects of the oropharyngeal swallow. The submental suprahyoid muscles are often investigated with ultrasound because of their contributions to hyolaryngeal elevation. There are several techniques for positioning the ultrasound transducer in the coronal plane, however, there is limited research on how reliability of measurement of the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the geniohyoid differs across transducer placement technique. This study examined three methods of transducer placement in the coronal plane by two examiners to determine the reliability of measurement of CSA of the geniohyoid muscle. Forty healthy adults participated in the study. Each participant’s geniohyoid muscles were imaged using B-mode ultrasound under three transducer placement conditions in the coronal plane by two examiners. Geniohyoid CSA was measured from each ultrasound image. A three-way mixed-methods ANOVA was used to determine whether there were significant differences in geniohyoid CSA among transducer position conditions, trials, and examiners. There were significant differences among the transducer placement conditions, indicating that each condition was measuring a different portion of the muscle. There were no significant differences among repeated trials nor between examiners within each method of transducer placement. All three conditions of transducer placement were reliable at measuring geniohyoid CSA across trials and examiners. This study emphasizes the need for consistency of placement, whichever method is selected. It also highlights the need for researchers to provide a precise description of methods for positioning the transducer so that placement is reproducible.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Allen JE, Clunie GM, Winiker K. Ultrasound: an emerging modality for the dysphagia assessment toolkit? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;29(3):213–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0000000000000708.
Hsiao MY, Wu CH, Wang TG. Emerging role of ultrasound in dysphagia assessment and intervention: a narrative review. Front Rehabilit Sci. 2021;2: 708102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fresc.2021.708102.
Miura Y, Tamai N, Kitamura A, Yoshida M, Takahashi T, Mugita Y, Tobita I, Arita M, Urai T, Dai M, Noguchi H, Matsumoto M, Mukai K, Nakagami G, Ota E, Sugama J, Sanada H. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound examination in detecting aspiration and pharyngeal residue in patients with dysphagia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Japan J Nurs Sci. 2021;18(2): e12396. https://doi.org/10.1111/jjns.12396.
Magalhães DDD, Bandeira JF, Pernambuco L. Quantitative approach to analyze hyoid bone movement during swallowing by ultrasound: an integrative review. Abordagem quantitativa por ultrassonografia para análise do movimento do osso hioide durante a deglutição: revisão integrativa. CoDAS. 2023;35(4):e20220002. https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20232022002pt.
Maeda K, Nagasaka M, Nagano A, Nagami S, Hashimoto K, Kamiya M, Masuda Y, Ozaki K, Kawamura K. Ultrasonography for eating and swallowing assessment: a narrative review of integrated insights for noninvasive clinical practice. Nutrients. 2023;15(16):3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163560.
Potente P, Buoite Stella A, Vidotto M, Passerini M, Furlanis G, Naccarato M, Manganotti P. Application of ultrasonography in neurogenic dysphagia: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2023;38(1):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10459-9.
McKinnis LN. Fundamentals of musculoskeletal imaging. 4th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company; 2014.
Li C, Li J, Zhang C, Cao X, Li N, Song D, Yu T. Application of B+M-mode ultrasonography in assessing deglutitive tongue movements in healthy adults. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1648–55. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.893591.
Ogawa N, Mori T, Fujishima I, Wakabayashi H, Itoda M, Kunieda K, Shigematsu T, Nishioka S, Tohara H, Yamada M, Ogawa S. Ultrasonography to measure swallowing muscle mass and quality in older patients with sarcopenic dysphagia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;19(6):516–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.11.007.
Chantaramanee A, Tohara H, Nakagawa K, Hara K, Nakane A, Yamaguchi K, Yoshimi K, Junichi F, Minakuchi S. Association between echo intensity of the tongue and its thickness and function in elderly subjects. J Oral Rehabil. 2019;46(7):634–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12788.
Ohkubo M, Scobbie JM. Tongue shape dynamics in swallowing using sagittal ultrasound. Dysphagia. 2019;34(1):112–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9921-8.
Jung YJ, Kim HJ, Choi JB, Park JS, Hwang NK. Effect of dysphagia rehabilitation using kinesiology ta** on oropharyngeal muscle hypertrophy in post-stroke patients: a double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;8(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040411.
Nienstedt JC, Müller F, Rösler A, Pflug C. Presbyphagia diagnostics using M-mode ultrasound: changes in the tongue movement pattern. Dysphagia. 2020;35(4):696–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10076-z.
Yamaguchi K, Hara K, Nakagawa K, Yoshimi K, Ariya C, Nakane A, Furuya J, Tohara H. Ultrasonography shows age-related changes and related factors in the tongue and suprahyoid muscles. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22(4):766–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.10.012.
Yamaguchi K, Nakagawa K, Yoshimi K, Ariya C, Nakane A, Okumura T, Tohara H. The cross-sectional area of the middle and base of the tongue is associated with swallowing-related muscle strength. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1723–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10431-7.
Recasens BB, Guillen-Sola A, Llorens JMM, Corberó AB, Moreno MV, Claramunt AA, Escobar GG, Rubio MA. Ultrasonographic and manometric study of the tongue as biomarkers of dysphagia in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol Sci. 2023;44(3):931–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-022-06486-x.
van der Heul AMB, Nievelstein RAJ, van Eijk RPA, Asselman F, Erasmus CE, Cuppen I, Bittermann AJN, Gerrits E, van der Pol WL, van den Engel-Hoek L. Swallowing problems in spinal muscular atrophy types 2 and 3: a clinical, videofluoroscopic and ultrasound study. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2023;10(3):427–38. https://doi.org/10.3233/JND-221640.
Umay E, Akaltun MS, Uz C. Association between swallowing muscle mass and dysphagia in older adults: a case-control study. J Oral Rehabil. 2023;50(6):429–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.13439.
Yamaguchi K, Nakagawa K, Yoshimi K, Ariya C, Nakane A, Ishii M, Hasegawa S, Tohara H. Associations of swallowing-related muscle quantity and quality with sarcopenic parameters. Eur Geriatr Med. 2023;14(1):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-023-00747-4.
Van Den Engel-Hoek L, Lagarde M, Van Alfen N. Ultrasound of oral and masticatory muscles: why every neuromuscular swallow team should have an ultrasound machine. Clin Anat. 2017;30(2):183–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.22818.
Park JS, Jung YJ, Kim MJ. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation synchronized with chewing exercises on bite force and masseter muscle thickness in community-dwelling older adults in South Korea: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134902.
Yamaguchi K, Tohara H, Hara K, Chantaramanee A, Nakagawa K, Yoshimi K, Nakane A, Minakuchi S. Tongue thickness is associated with masticatory performance of perioral muscles: ultrasonographic study of perioral muscle characteristics in healthy young subjects. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;47(3):325–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12909.
Huang YL, Hsieh SF, Chang YC, Chen HC, Wang TG. Ultrasonographic evaluation of hyoid-larynx approximation in dysphagic stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35(7):1103–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.02.006.
Macrae PR, Doeltgen SH, Jones RD, Huckabee ML. Intra- and inter-rater reliability for analysis of hyoid displacement measured with sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012;40(2):74–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.20874.
Perry SE, Winkelman CJ, Huckabee ML. Variability in ultrasound measurement of hyoid bone displacement and submental muscle size using 2 methods of data acquisition. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2016;68(5):205–10. https://doi.org/10.1159/000473876.
Matsuo T, Matsuyama M, Nakatani K, Mori N. Evaluation of swallowing movement using ultrasonography. Radiol Phys Technol. 2020;13(1):62–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-019-00547-1.
Picelli A, Modenese A, Poletto E, Businaro V, Varalta V, Gandolfi M, Bonetti B, Smania N. May ultrasonography be considered a useful tool for bedside screening of dysphagia in patients with acute stroke? A cohort study. Minerva Med. 2021;112(3):354–8. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4806.20.06571-4.
Costa BOID, Rodrigues DSB, Magalhães DDD, Santos AS, Santos RV, Azevedo EHM, Almeida AA, Pernambuco L. Quantitative ultrasound assessment of hyoid bone displacement during swallowing following thyroidectomy. Dysphagia. 2021;36(4):659–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10180-5.
Kwong E, Ng KK, Leung MT, Zheng YP. Application of ultrasound biofeedback to the learning of the Mendelsohn Maneuver in non-dysphagic adults: a pilot study. Dysphagia. 2021;36(4):650–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10179-y.
Winiker K, Burnip E, Gozdzikowska K, Guiu Hernandez E, Hammond R, Macrae P, Huckabee ML. Ultrasound: validity of a pocket-sized system in the assessment of swallowing. Dysphagia. 2021;36(6):1010–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10232-w.
Peng CH, Pauloski BR. Ultrasonography as biofeedback to increase muscle activation during the Mendelsohn Maneuver in healthy adults. Dysphagia. 2023;38(4):1156–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10542-1.
Ahn D, Lee GJ, Sohn JH. Ultrasonographic swallowing examination for early detection of neopharyngeal fistula after salvage total laryngectomy: a preliminary study. Head Neck. 2019;41(6):1804–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25617.
Yabunaka K, Konishi H, Nakagami G, Sanada H, Iizaka S, Sanada S, Ohue M. Ultrasonographic evaluation of geniohyoid muscle movement during swallowing: a study on healthy adults of various ages. Radiol Phys Technol. 2012;5(1):34–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-011-0132-3.
Shimizu S, Hanayama K, Metani H, Sugiyama T, Abe H, Seki S, Hiraoka T, Tsubahara A. Retest reliability of ultrasonic geniohyoid muscle measurement. Jpn J Compr Rehabilit Sci. 2016;7:55–60. https://doi.org/10.11336/jjcrs.7.55.
Shimizu S, Hanayama K, Nakato R, Sugiyama T, Tsubahara A. Ultrasonographic evaluation of geniohyoid muscle mass in perioperative patients. Kawasaki Med J. 2016;42:47–56. https://doi.org/10.11482/KMJ-E42(2)47.
Baba T, Goto T, Fujimoto K, Honda T, Yagi K, Nagao K, Ichikawa T. Age-related changes in geniohyoid muscle morphology predict reduced swallowing function. J Oral Health Biosci. 2017;30(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.20738/johb.30.1_18.
Cheng DTH, Lee KYS, Ahuja AT, Tong MCF. Sonographic assessment of swallowing in irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Laryngoscope. 2018;128(11):2552–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27222.
Oh JC. Effect of the head extension swallowing exercise on suprahyoid muscle activity in elderly individuals. Exp Gerontol. 2018;110:133–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.06.004.
Mori T, Izumi S, Suzukamo Y, Okazaki T, Iketani S. Ultrasonography to detect age-related changes in swallowing muscles. Eur Geriatr Med. 2019;10(5):753–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-019-00223-y.
Choi JB, Jung YJ, Park JS. Comparison of 2 types of therapeutic exercise: jaw opening exercise and head lift exercise for dysphagic stroke: a pilot study. Medicine. 2020;99(38): e22136. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000022136.
Miura Y, Nakagami G, Tohara H, Ogawa N, Sanada H. The association between jaw-opening strength, geniohyoid muscle thickness and echo intensity measured by ultrasound. Med Ultrason. 2020;22(3):299–304. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-2317.
Yano J, Yamamoto-Shimizu S, Yokoyama T, Kumakura I, Hanayama K, Tsubahara A. Effects of tongue-strengthening exercise on the geniohyoid muscle in young healthy adults. Dysphagia. 2020;35(1):110–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10011-2.
Ogawa N, Wakabayashi H, Mori T, Fujishima I, Oshima F, Itoda M, Kunieda K, Shigematsu T, Nishioka S, Tohara H, Ohno T, Nomoto A, Shimizu A, Yamada M, Ogawa S. Digastric muscle mass and intensity in older patients with sarcopenic dysphagia by ultrasonography. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021;21(1):14–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.14079.
Wakabayashi H, Kishima M, Itoda M. Improvement of swallowing-related muscle mass assessed by ultrasonography in malnourished patient with Wallenberg syndrome: a case report. J Gen Family Med. 2021;22(6):341–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgf2.428.
Pauloski BR, Yahnke K. Using ultrasound to document the effects of expiratory muscle strength training (EMST) on the geniohyoid muscle. Dysphagia. 2022;37:788–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10328-x.
Lu F, Okazaki T, Okuyama J, Izumi SI. Impacts of body positions on the geniohyoid muscle contraction and swallowing difficulty in healthy adults. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/cre2.760.
Geddes DT, Chadwick LM, Kent JC, Garbin CP, Hartmann PE. Ultrasound imaging of infant swallowing during breast-feeding. Dysphagia. 2010;25(3):183–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-009-9241-0.
Dharmarathna I, Miles A, Allen JE. Current approaches to instrumental assessment of swallowing in children. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;26(6):349–55. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0000000000000492.
Nakamori M, Imamura E, Fukuta M, Tachiyama K, Kamimura T, Hayashi Y, Matsushima H, Ogawa K, Nishino M, Hirata A, Mizoue T, Wakabayashi S. Tongue thickness measured by ultrasonography is associated with tongue pressure in the Japanese elderly. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(8): e0230224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230224.
Huckabee ML, Macrae P, Lamvik K. Expanding instrumental options for dysphagia diagnosis and research: ultrasound and manometry. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2015;67(6):269–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444636.
Blyth KM, McCabe P, Madill C, Ballard KJ. Ultrasound in dysphagia rehabilitation: a novel approach following partial glossectomy. Disabil Rehabil. 2017;39(21):2215–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2016.1219400.
Nachalon Y, Nativ-Zeltzer N, Evangelista LM, Dhar SI, Lin SJ, Shen SC, Belafsky PC. Cervical fibrosis as a predictor of dysphagia. Laryngoscope. 2021;131(3):548–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28880.
Takuro B, Takaharu G, Keiko F, Tsuyoshi H, Kazutomo Y, Kan N, Tetsuo I. Age-related changes in geniohyoid muscle morphology predict reduced swallowing function. J Oral Health Biosci. 2017;30(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.20738/johb.30.1_18.
Feng X, Cartwright MS, Walker FO, Bargoil JH, Hu Y, Butler SG. Ultrasonographic evaluation of geniohyoid muscle and hyoid bone during swallowing in young adults. Laryngoscope. 2015;125:1886–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25224.
Watkin KL, Diouf I, Gallagher TM, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Ettema SL. Ultrasonic quantification of geniohyoid cross-sectional area and tissue composition: a preliminary study of age and radiation effects. Head Neck. 2001;23(6):467–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.1061.
Winiker K, Burnip E, Gozdzikowska K, Hernandez EG, Hammond R, Macrae P, Thomas P, Huckabee ML. Ultrasound: reliability of a pocket-sized system in the assessment of swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2021;64(8):2928–40. https://doi.org/10.1044/2021_JSLHR-21-00026.
Winiker K, Hammond R, Thomas P, Dimmock A, Huckabee ML. Swallowing assessment in patients with dysphagia: validity and reliability of a pocket-sized ultrasound system. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022;57(3):539–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/1460-6984.12703.
Chen YC, Hsiao MY, Wang YC, Fu CP, Wang TG. Reliability of ultrasonography in evaluating hyoid bone movement. J Med Ultrasound. 2017;25(2):90–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2017.01.002.
Andrade RA, do Sales Coriolano, M. D. G. W., de Souza, E. L. H., da Silva, J. H. C., da Cunha, M. D., Pernambuco, L., Ribeiro, V. V., & da Silva, H. J. Reliability of ultrasound examination of hyoid bone displacement amplitude: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1375–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10429-1.
Stone M, Davis EP. A head and transducer support system for making ultrasound images of tongue/jaw movement. J Acoust Soc Am. 1995;98(6):3107–12. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.413799.
Derrick D, Carignan C, Chen WR, Shujau M, Best CT. Three-dimensional printable ultrasound transducer stabilization system. J Acoust Soc Am. 2018;144(5):392. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.5066350.
Ma JK, Wrench AA. Automated assessment of hyoid movement during normal swallow using ultrasound. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022;57(3):615–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/1460-6984.12712.
Allen JE, Clunie G, Ma JK, Coffey M, Winiker K, Richmond S, Lowell SY, Volkmer A. Translating ultrasound into clinical practice for the assessment of swallowing and laryngeal function: a speech and language pathology-led consensus study. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1586–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10413-9.
Hollinghurst J, Smithard DG. Identifying dysphagia and demographic associations in older adults using electronic health records: a national longitudinal observational study in Wales (United Kingdom) 2008–2018. Dysphagia. 2022;37(6):1612–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10425-5.
van den Engel-Hoek L, Erasmus CE, Hendriks JC, Geurts AC, Klein WM, Pillen S, Sie LT, de Swart BJ, de Groot IJ. Oral muscles are progressively affected in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implications for dysphagia treatment. J Neurol. 2013;260(5):1295–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6793-y.
Hutcheson KA, Lewin JS, Barringer DA, Lisec A, Gunn GB, Moore MW, Holsinger FC. Late dysphagia after radiotherapy-based treatment of head and neck cancer. Cancer. 2012;118(23):5793–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.27631.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Stephen C. Cobb, Ph.D., for his support and guidance in the early phases of this study.
Funding
This research was supported by a College of Health Sciences Stimulus for Extramural Enhancement & Development (SEED) Award, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pauloski, B.R., Yahnke, K.M. Reliability of Measuring Geniohyoid Cross-Sectional Area with B-Mode Ultrasound. Dysphagia (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-024-10712-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-024-10712-3