Abstract
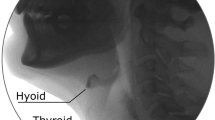
In swallowing, the hyoid bone moves up and forward in response to the activation of suprahyoid muscles, opening the upper esophageal sphincter and aiding the airway protection mechanism. This displacement measure has been analyzed with ultrasound images because this method does not expose the patient to radiation, has a good cost–benefit ratio, and is safe for the patient. However, there is no consensus on the reliability of this ultrasound measure. The objective of this study was to analyze the reliability of measuring hyoid bone displacement amplitude in swallowing with ultrasound. The systematic review encompassed five databases (MEDLINE, Scopus, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library) and gray literature. There was no limitation of language or year of publication. The search/selection/extraction methodology was conducted by two authors blindly and independently, and differences were solved by a third rater. Three studies met the eligibility criteria: two of them analyzed the reliability in non-dysphagic populations and the other, in dysphagic patients. The transducer was positioned in the submandibular region in all studies. The authors were not clear about the training time to acquire and analyze ultrasound images. The meta-analysis had an interrater reliability of 0.858 (95% CI: 0.744–0.924) and intrarater reliability of 0.968 (95% CI: 0.903–0.990). There was, however, heterogeneity of p = 0.005 for intrarater reliability. Despite good reliability, the heterogeneity reinforces the importance of training and protocol standardization for image acquisition and analysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearson WG, Langmore SE, Zumwalt AC. Evaluating the structural properties of suprahyoid muscles and their potential for moving the hyoid. Dysphagia. 2011;26(4):345–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9315-z.
Khan YS, Bordoni B. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Suprahyoid Muscle. StatPearls. June 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546710/. Accessed July 31, 2021.
Mioche L, Hiiemae KM, Palmer JB. A postero-anterior videofluorographic study of the intra-oral management of food in man. Arch Oral Biol. 2002;47(4):267–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-9969(02)00007-9.
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Cheng J, et al. Closure mechanisms of laryngeal vestibule during swallow. Am J Physiol - Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1992;262(2):G338–44.
Pearson WG Jr, Langmore SE, Yu LB, Zumwalt AC. Structural analysis of muscles elevating the hyolaryngeal complex. Dysphagia. 2012;27(4):445. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00455-011-9392-7.
Padovani AR, Moraes DP, Mangili LD, de Andrade CRF. Dysphagia risk evaluation protocol. Rev da Soc Bras Fonoaudiol. 2007;12(3):199–205. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-80342007000300007.
Kim Y, McCullough GH. Maximum hyoid displacement in normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2008;23(3):274–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9135-y.
Chi-Fishman G, Sonies BC. Effects of systematic bolus viscosity and volume changes on hyoid movement kinematics. Dysphagia. 2002;17(4):278–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0070-7.
Hsiao MY, Chang YC, Chen WS, Chang HY, Wang TG. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38(9):1522–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.04.017.
Bingjie TZ, **nting S, Jianmin X, Guijun J. Quantitative videofluoroscopic analysis of penetration-aspiration in post-stroke patients. Neurol India. 2010;58(1):42.
Chen YC, Hsiao MY, Wang YC, Fu CP, Wang TG. Reliability of ultrasonography in evaluating hyoid bone movement. J Med Ultrasound. 2017;25(2):90–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2017.01.002.
Ohkubo M, Scobbie JM. Tongue shape dynamics in swallowing using sagittal ultrasound. Dysphagia. 2019;34(1):112–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9921-8.
Sonies BC, Chi-Fishman G, Miller JL. Ultrasound Imaging and Swallowing. In: Normal and Abnormal Swallowing. New York: Springer; 2003. p. 119–38.
Scarborough DR, Waizenhofer S, Siekemeyer L, Hughes M. Sonographically measured hyoid bone displacement during swallow in preschool children: a preliminary study. J Clin Ultrasound. 2010;38(8):430–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.20733.
de Leite KKA, Mangilli LD, Sassi FC, Limongi SCO, de Andrade CRF. Ultrassonografia e deglutição: revisão crítica da literatura. Audiol - Commun Res. 2014;19(4):412–20.
Rocha SG, da Silva RG, Berti LC. Qualitative and quantitative ultrasound analysis of oropharyngeal swallowing. CODAS. 2015;27(5):437–45. https://doi.org/10.1590/2317-1782/20152015015.
Okada T, Aoyagi Y, Inamoto Y, et al. Dynamic change in hyoid muscle length associated with trajectory of hyoid bone during swallowing: analysis using 320-row area detector computed tomography. J App Physiol. 2013;115(8):1138–45.
Allen JE, Clunie GM, Winiker K. Ultrasound: an emerging modality for the dysphagia assessment toolkit? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;29(3):213–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0000000000000708.
Page MJ, McKenzie J, Bossuyt P. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. 2020;88:105906.
Akobeng AK. Principles of evidence based medicine. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90:837–40. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2005.071761.
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Lucas NP, Macaskill P, Irwig L, Bogduk N. The development of a quality appraisal tool for studies of diagnostic reliability (QAREL). J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63(8):854–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.10.002.
Miura Y, Tamai N, Kitamura A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound examination in detecting aspiration and pharyngeal residue in patients with dysphagia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Japan J Nurs Sci. 2021;18(2):e12396.
Macrae PR, Doeltgen SH, Jones RD, Huckabee ML. Intra- and inter-rater reliability for analysis of hyoid displacement measured with sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012;40(2):74–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.20874.
Stone M. A three-dimensional model of tongue movement based on ultrasound and x-ray microbeam data. J Acoust Soc Am. 1990;87(5):2207–17. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.399188.
da Costa BOI, de Rodrigues DSB, de Magalhães DDD, et al. Quantitative ultrasound assessment of hyoid bone displacement during swallowing following thyroidectomy. Dysphagia. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10180-5.
Chi-Fishman G, Sonies BC. Kinematic strategies for hyoid movement in rapid sequential swallowing. J Speech, Lang Hear Res. 2002;45(3):457–68. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2002/036).
Feng X, Cartwright MS, Walker FO, Bargoil JH, Hu Y, Butler SG. Ultrasonographic evaluation of geniohyoid muscle and hyoid bone during swallowing in young adults. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(8):1886–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25224.
Huckabee M-L, Macrae P, Lamvik K. Expanding instrumental options for dysphagia diagnosis and research: ultrasound and manometry. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2015;67(6):269–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444636.
Shawker TH, Sonies B, Stone M, Baum BJ. Real-time ultrasound visualization of tongue movement during swallowing. J Clin Ultrasound. 1983;11(9):485–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.1870110906.
Sonies BC, Wang C, Sapper DJ. Evaluation of normal and abnormal hyoid bone movement during swallowing by use of ultrasound duplex-Doppler imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22(9):1169–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-5629(96)00158-5.
Kwak HJ, Kim L, Ryu BJ, et al. Influence of nasogastric tubes on swallowing in stroke patients: Measuring hyoid bone movement with ultrasonography. Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(4):551–9. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.551.
Steele C, Sasse C, Bressmann T. Tongue-pressure and hyoid movement timing in healthy liquid swallowing. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2012;47(1):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-6984.2011.00082.x.
Acknowledgements
The review protocol named Ultrasonographic reliability in the process of evaluation of the swallowing biomechanics was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under number CRD42020164655. It is available at: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=164655. The protocol underwent some adjustments throughout the review, its title was changed, the PICO question was readapted, and the search strategy was readjusted.
Funding
The first author of this review received financial support from DS/CAPES. This paper was conducted with support from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel Brazil (CAPES) Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade, R.A.d., do Sales Coriolano, M.d.G.W., de Souza, E.L.H. et al. Reliability of Ultrasound Examination of Hyoid Bone Displacement Amplitude: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dysphagia 37, 1375–1385 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10429-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10429-1