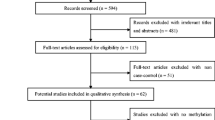
Abstract
Objective
Some studies have shown that the methylation status of the GSTP1 gene promoter is related to the incidence of prostate cancer, but this finding is still controversial. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between glutathione-S-transferase p1 (GSTP1) promoter methylation and the incidence of prostate cancer.
Methods
The Medline, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane CENTRAL databases were searched from their inception to February 22, 2019. According to the inclusion criteria, studies of the association between the methylation status of the GSTP1 gene promoter and prostate cancer were included. The difference in the incidence of GSTP1 promoter methylation in tissues, blood, or urine between patients with prostate cancer and those without prostate cancer were compared, and the results were expressed as the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The pooled OR of each study was estimated using a fixed-effects model or a random-effects model to generate forest plots.
Results
Ultimately, 15 studies (1540 samples) were included. The estimated effect from our meta-analysis showed that the incidence of GSTP1 promoter methylation was higher in patients with prostate cancer than in those without prostate cancer (OR 18.58, 95% CI 9.60–35.95, P = 0.000). GSTP1 promoter methylation was highly correlated with the incidence of prostate cancer.
Conclusions
Methylation of the GSTP1 promoter may increase the risk of prostate cancer. This study may provide a strategic direction for prostate cancer research. Pending validation of these findings, the methylation of the GSTP1 promoter may be a potential biomarker to diagnose prostate cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GSTP1 :
-
Glutathione-S-transferase P1
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- PSA:
-
Prostate-specific antigen
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- NOS:
-
Newcastle–Ottawa Scale
- MSP:
-
Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction
- Q-MSP:
-
Quantitative methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction
- BPH:
-
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
References
Arai T, Miyoshi Y, Kim SJ, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S (2006) Association of GSTP1 CpG islands hypermethylation with poor prognosis in human breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9241-9
Bastian PJ, Ellinger J, Schmidt D, Wernert N, Wellmann A, Muller SC, von Rucker A (2004) GSTP1 hypermethylation as a molecular marker in the diagnosis of prostatic cancer: is there a correlation with clinical stage, Gleason grade, PSA value or age? Eur J Med Res 9:523–527
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Chu DC, Chuang CK, Fu JB, Huang HS, Tseng CP, Sun CF (2002) The use of real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction to detect hypermethylation of the CpG islands in the promoter region flanking the GSTP1 gene to diagnose prostate carcinoma. J Urol 167:1854–1858
Chuang CK, Chu DC, Tzou RD, Liou SI, Chia JH, Sun CF (2007) Hypermethylation of the CpG islands in the promoter region flanking GSTP1 gene is a potential plasma DNA biomarker for detecting prostate carcinoma. Cancer Detect Prevent 31:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdp.2006.11.001
Cook ED, Nelson AC (2011) Prostate cancer screening. Curr Oncol Rep 13:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-010-0136-x
Damaschke NA, Yang B, Bhusari S, Svaren JP, Jarrard DF (2013) Epigenetic susceptibility factors for prostate cancer with aging. Prostate 73:1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22716
Dimitriadis E et al (2013) Study of genetic and epigenetic alterations in urine samples as diagnostic markers for prostate cancer. Anticancer Res 33:191–197
Esteller M, Corn PG, Urena JM, Gabrielson E, Baylin SB, Herman JG (1998) Inactivation of glutathione S-transferase P1 gene by promoter hypermethylation in human neoplasia. Cancer Res 58:4515–4518
Fleshner K, Carlsson SV, Roobol MJ (2017) The effect of the USPSTF PSA screening recommendation on prostate cancer incidence patterns in the USA. Nat Rev Urol 14:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2016.251
Fukushige S, Horii A (2013) DNA methylation in cancer: a gene silencing mechanism and the clinical potential of its biomarkers. Tohoku J Exp Med 229:173–185
Hanson JA et al (2006) Gene promoter methylation in prostate tumor-associated stromal cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djj051
Haroun RA, Zakhary NI, Mohamed MR, Abdelrahman AM, Kandil EI, Shalaby KA (2014) Assessment of the prognostic value of methylation status and expression levels of FHIT, GSTP1 and p16 in non-small cell lung cancer in Egyptian patients. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prevent APJCP 15:4281–4287
Hashad DI, Hashad MM, Talaat IM, Ibrahim MA (2011) Role of glutathione-S-transferase P1 hypermethylation in molecular detection of prostate cancer. Genet Test Mol Biomark 15:667–670. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2010.0262
Jeronimo C et al (2002) I105 V polymorphism and promoter methylation of the GSTP1 gene in prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prevent 11:445–450
Kang GH, Lee S, Lee HJ, Hwang KS (2004) Aberrant CpG island hypermethylation of multiple genes in prostate cancer and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. J Pathol 202:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1503
Krassenstein R, Sauter E, Dulaimi E, Battagli C, Ehya H, Klein-Szanto A, Cairns P (2004) Detection of breast cancer in nipple aspirate fluid by CpG island hypermethylation. Clin Cancer Res 10:28–32
Lan VT, Trang NT, Van DT, Thuan TB, Van To T, Linh VD, Uyen NQ (2015) A methylation-specific dot blot assay for improving specificity and sensitivity of methylation-specific PCR on DNA methylation analysis. Int J Clin Oncol 20:839–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0780-5
Mahapatra S et al (2012) Global methylation profiling for risk prediction of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18:2882–2895. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2090
Maldonado L et al (2014) GSTP1 promoter methylation is associated with recurrence in early stage prostate cancer. J Urol 192:1542–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.04.082
Mancuso N, Gayther S, Gusev A (2018) Large-scale transcriptome-wide association study identifies new prostate cancer risk regions. Nat Commun 9:4079. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06302-1
Martignano F et al (2016a) GSTP1 Methylation and protein expression in prostate cancer: diagnostic implications. Dis Mark 2016:6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4358292
Martignano F et al (2016b) GSTP1 methylation and protein expression in prostate cancer: diagnostic implications. Dis Mark 2016:4358292. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4358292
Maruyama R et al (2002) Aberrant promoter methylation profile of prostate cancers and its relationship to clinicopathological features. Clin Cancer Res 8:514–519
Massie CE et al (2015) HES5 silencing is an early and recurrent change in prostate tumourigenesis. Endocr-Relat Cancer 22:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-14-0454
Mian OY et al (2016) GSTP1 Loss results in accumulation of oxidative DNA base damage and promotes prostate cancer cell survival following exposure to protracted oxidative stress. Prostate 76:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23111
Miyake T et al (2012) GSTP1 expression predicts poor pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci 103:913–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02231.x
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Nakamura J, Tanaka T, Kitajima Y, Noshiro H, Miyazaki K (2014) Methylation-mediated gene silencing as biomarkers of gastric cancer: a review. World J Gastroenterol 20:11991–12006. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.11991
Pandey M, Shukla S, Gupta S (2010) Promoter demethylation and chromatin remodeling by green tea polyphenols leads to re-expression of GSTP1 in human prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 126:2520–2533. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24988
Pongtheerat T, Pakdeethai S, Purisa W, Chariyalertsak S, Petmitr S (2011) Promoter methylation and genetic polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase P1 gene (GSTP1) in Thai breast-cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prevent APJCP 12:2731–2734
Richiardi L, Fiano V, Grasso C, Zugna D, Delsedime L, Gillio-Tos A, Merletti F (2013) Methylation of APC and GSTP1 in non-neoplastic tissue adjacent to prostate tumour and mortality from prostate cancer. PLoS one 8:e68162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068162
Rosenbaum E et al (2005) Promoter hypermethylation as an independent prognostic factor for relapse in patients with prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer Res 11:8321–8325. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1183
Sanchez BE et al (2018) Using genetic and epigenetic markers to improve differential diagnosis of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia by noninvasive methods in mexican patients. Clin Genitourin Cancer 16:e867–e877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2018.02.004
Saxena A et al (2012) GSTP1 methylation and polymorphism increase the risk of breast cancer and the effects of diet and lifestyle in breast cancer patients. Exp Ther Med 4:1097–1103. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.710
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2018(68):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Stuck AE, Rubenstein LZ, Wieland D (1998) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Asymmetry detected in funnel plot was probably due to true heterogeneity. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 316:469 (author reply 470–461)
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Trock BJ et al (2012) Evaluation of GSTP1 and APC methylation as indicators for repeat biopsy in a high-risk cohort of men with negative initial prostate biopsies. BJU Int 110:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410x.2011.10718.x
Van Neste L, Herman JG, Otto G, Bigley JW, Epstein JI, Van Criekinge W (2012) The epigenetic promise for prostate cancer diagnosis. Prostate 72:1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22459
Vo TT, Ta BT, Ta VT, Vuong DL, Nguyen QU (2016) Promoter methylation profile of GSTP1 and RASSF1A in prostate cancer and benign hyperplasia in Vietnamese men. Turk J Med Sci 46:228–235. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1410-65
Wallis CJD et al (2016) Surgery versus radiotherapy for clinically-localized prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 70:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.11.010
Zhang W et al (2015) Correlation between the expression of DNMT1, and GSTP1 and APC, and the methylation status of GSTP1 and APC in association with their clinical significance in prostate cancer. Mol Med Rep 12:141–146. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3402
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Chinese Evidence Based Medicine Center at West China Hospital of Sichuan University for providing the Stata 14.0 statistical software.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the present study.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Jiao, D., Dou, M. et al. Association of glutathione-S-transferase p1 gene promoter methylation and the incidence of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 1939–1948 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02962-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02962-8