Abstract
Introduction
GreenLight photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) has gained widespread adoption as an option to traditional transurethral resection of the prostate. Prior reports expressed concern with the use of PVP in large prostates. The aim of this study was to investigate the adjusted outcomes of GreenLight PVP in men with large (≥ 80 cc) vs. small prostates (< 80 cc).
Methods
Data were obtained from the Global Greenlight Group which pools data from 7 high volume centers. Men with established benign prostatic hyperplasia who underwent GreenLight PVP using the XPS-180 W system between 2011 and 2019 were eligible and assigned into two groups based on their prostate size (≥ 80 and < 80 cc). 11 functional and perioperative covariates were collected. Analyses were adjusted for patient age and presence of median lobe.
Results
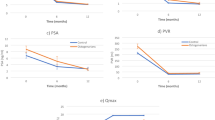
3426 men met the inclusion criteria. 34.6% (n = 1187) of patients had a large prostate size. Baseline age and prostate volume were significantly different between the groups. The magnitude of absolute improvement in unadjusted international prostate symptom score was significantly greater in the large (≥ 80 cc) prostate group at 12 months, with an absolute change of 19.17 points (95% CI 18.46–19.88; p < 0.01). There was also a significant drop in PVR at both 6- (p = 0.007) and 12 months (p = 0.005). There were no significant differences in transfusion (p = 0.42), hematuria (p = 0.80), or 30-day readmission rates (p = 0.28).
Conclusions
Greenlight PVP is a safe and effective alternative for patients with prostate sizes ≥ 80 cc, with durable outcomes relatively independent from prostate size.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann A, Tubaro A, Barber N et al (2014) 180-W XPS greenlight laser vaporisation versus transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction: 6-month safety and efficacy results of a European multicentre randomised trial—the GOLIATH study. Eur Urol 65(5):931–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.10.040
Hueber PA, Bienz MN, Valdivieso R et al (2015) Photoselective vaporization of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia using the 180 watt system: multicenter study of the impact of prostate size on safety and outcomes. J Urol 194(2):462–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2015.03.113
Lerner LB, McVary KT, Barry MJ et al (2021) Management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia: AUA GUIDELINE PART II—surgical evaluation and treatment. J Urol 206(4):818–826
Elshal AM, Soltan M, El-Tabey NA, Laymon M, Nabeeh A (2020) Randomised trial of bipolar resection vs holmium laser enucleation vs Greenlight laser vapo-enucleation of the prostate for treatment of large benign prostate obstruction: 3-years outcomes. BJU Int 126(6):731–738. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15161
McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM et al (2003) The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. 25. http://www.nejm.org
Campobasso D, Marchioni M, Altieri V et al (2020) GreenLight photoselective vaporization of the prostate: one laser for different prostate sizes. J Endourol 34(1):54–62. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2019.0478
Stone BV, Chughtai B, Kaplan SA, Te AE, Lee RK (2015) GreenLight laser for prostates over 100 ml: what is the evidence? Curr Opin Urol 26(1):28–34. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOU.0000000000000237
Meskawi M, Hueber PA, Valdivieso R et al (2017) Multicenter international experience of 532 nm-laser photo-vaporization with Greenlight XPS in men with large prostates (prostate volume > 100 cc). World J Urol 35(10):1603–1609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2007-7
Law KW, Tholomier C, Nguyen DD et al (2021) Global Greenlight Group: largest international Greenlight experience for benign prostatic hyperplasia to assess efficacy and safety. World J Urol 39(12):4389–4395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03688-4
Nickel JC, Aaron L, Barkin J, Elterman D, Nachabé M, Zorn KC (2018) Canadian Urological Association guideline on male lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia (MLUTS/BPH): 2018 update. Can Urol Assoc J 12(10):303–312. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.5616
Foster HE, Barry MJ, Dahm P et al (2018) Surgical management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hyperplasia: AUA guideline. J Urol 200(3):612–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.048
Gratzke C, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A et al (2015) EAU guidelines on the assessment of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 67(6):1099–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.038
Eri LM, Thomassen H, Brennhovd B, Håheim LL (2002) Accuracy and repeatability of prostate volume measurements by transrectal ultrasound. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 5(4):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500568
Wang X (2014) Firth logistic regression for rare variant association tests. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00187
Thoulouzan M, Perrouin-Verbe MA, Calves J et al (2017) Outcomes of GreenLight XPS-180W laser photovaporization for BPH larger than 80 mL. Progres en urologie journal de l’Association francaise d’urologie et de la Societe francaise d’urologie 27(8–9):489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.purol.2017.04.001
Altay B, Erkurt B, Kiremit MC, Guzelburc V, Boz MY, Albayrak S (2015) 180-W XPS GreenLight laser vaporization for benign prostate hyperplasia: 12-month safety and efficacy results for glands larger than 80 mL. Lasers Med Sci 30(1):317–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1667-4
Lanchon C, Fiard G, Long JA et al (2018) Adénomectomie voie haute versus vaporisation prostatique au laser GreenLight 180-W XPS: résultats fonctionnels à long terme pour les adénomes > 80 g. Prog Urol 28(3):180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.purol.2017.12.008
Enikeev D, Misrai V, Rijo E et al (2022) EAU, AUA and NICE guidelines on surgical and minimally invasive treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia: a critical appraisal of the guidelines using the AGREE-II tool. Urol Int 106(1):1–10
Management of non-neurogenic male LUTS—DISEASE MANAGEMENT—Uroweb
Zorn K, Zorn KC, Liberman D (2011) How i do it GreenLight 180W XPS photovaporization of the prostate: how i do it, vol 18. http://www.AmericanMedicalSystems.com
Valdivieso R, Meyer CP, Hueber PA et al (2016) Assessment of energy density usage during 180W lithium triborate laser photoselective vaporization of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Is there an optimum amount of kilo-Joules per gram of prostate? BJU Int 118(4):633–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13479
Nguyen DD, Misraï V, Bach T et al (2020) Operative time comparison of aquablation, greenlight PVP, ThuLEP, GreenLEP, and HoLEP. World J Urol 38(12):3227–3233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03137-8
Meskawi M, Hueber PA, Valdivieso R et al (2019) Complications and functional outcomes of high-risk patient with cardiovascular disease on antithrombotic medication treated with the 532-nm-laser photo-vaporization Greenlight XPS-180 W for benign prostate hyperplasia. World J Urol 37(8):1671–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2560-8
Masucci L, Erman A, Krahn MD, Elterman D (2018) Cost analysis of Greenlight photoselective vaporization of the prostate compared to transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Can Urol Assoc J. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.5267
Nguyen DD, Sadri I, Law K et al (2021) Impact of the presence of a median lobe on functional outcomes of greenlight photovaporization of the prostate (PVP): an analysis of the Global Greenlight Group (GGG) database. World J Urol 39(10):3881–3889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03529-w
Lichy I, Law K, Tholomier C et al (2022) Global experience and progress in GreenLight-XPS 180-Watt photoselective vaporization of the prostate. World J Urol. Published online May 2, 2022
Campobasso D, Marchioni M, De Nunzio C et al (2021) Predictors of re-intervention after greenlight laser photoselective vaporization of the prostate: multicenter long/mid-term follow-up experience. MIS. Published online 2021
Law KW, Tholomier C, Nguyen D-D et al (2021) Global Greenlight group: largest international Greenlight experience for benign prostatic hyperplasia to assess efficacy and safety. World J Urol. Published online April 10, 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NC: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. DDN: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. AA: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. IS: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. KL: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. DB: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. CD: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing. NB: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. DSE: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. FB: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. LC: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. GF: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. CVL: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. TBB: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. EFB: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. HC: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. MR: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. ER: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. VM: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. BC: Data Collection or Management, Manuscript Writing and Editing. KCZ: Protocol/Project Development, Data Collection or Management, Data Analysis, Manuscript Writing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Consultants and proctors for Boston Scientific for greenlight: KZ, DSE, VM, ER, HC, EFB, BC. Investigators and consultants for PROCEPT BioRobotics: VM, TB, NB, KZ. Surgical tutors for Greenlight Xcelerated Performance System (American Medical System-AMS, Minnetonka, MN) and received honoraria for their tutorship: GF, LC. All other authors do not report any relevant conflicts of interest.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are readily available from the corresponding author upon request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Corsi, N., Nguyen, DD., Arezki, A. et al. Functional outcomes of GreenLight 180-W photoselective vaporization in patients with large (≥ 80 cc) prostates: an analysis of over 3000 men in the Global Greenlight Group (GGG) database. World J Urol 41, 529–536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04260-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04260-4