Abstract
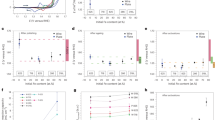
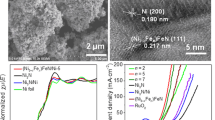
The development of efficient and durable oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts is of great significance for the application of high-efficiency alkaline water electrolysis hydrogen production technology. In this work, a highly efficient and stable OER catalyst with a layered structure, in which layered hydroxides of FeCoNi(OH)x are prepared on a Ni mesh substrate by electrodeposition. In three-electrode tests, the FeCoNi(OH)x/Ni mesh has an overpotential of 138 mV at 10 mA cm−2, much lower than that of Ni mesh (341 mV) and Raney Ni/Ni mesh (277 mV). Under the condition of 50 mA cm−2, FeCoNi(OH)x/Ni mesh exhibits excellent stability for 80 h. Moreover, when installed in a single cell of an alkaline electrolysis cell, the FeCoNi(OH)x/Ni mesh electrode cell voltage is 2.003 V at 8000 A m−2, much lower than the Ni mesh (2.224 V) and Raney Ni/Ni mesh (2.086 V), demonstrating excellent OER performance. Tafel slope, contact angles, and EIS tests reveal that the synthesized FeCoNi(OH)x/Ni mesh shows favorable kinetics, super hydrophilic surface, and fast bubble detachment, ultimately reducing the OER overpotential and promoting electrocatalytic activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
L. Wan, Z. Xu, Q. Xu, M. Pang, D. Lin, J. Liu, B. Wang, Key components and design strategy of the membrane electrode assembly for alkaline water electrolysis. Energ. Environ. Sci. 16, 1384–1430 (2023)
Y.M. Wang, Y.Y. Li, T. Huang, W.Q. Huang, S.F. Ma, F. Zeng, X. Li, Y.F. Chai, G.F. Huang, Co-Cu-P nanosheet-based open architecture for high-performance oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 127, 224 (2021)
P. Zhou, H. Bai, J. Feng, D. Liu, L. Qiao, C. Liu, S.P. Wang, H. Pan, Recent progress on bulk Fe-based alloy for industrial alkaline water electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 1551–1574 (2023)
J. Brauns, T. Turek, Alkaline water electrolysis powered by renewable energy: a review. Processes 8, 248 (2020)
N. Guillet, P. Millet, Alkaline water electrolysis, in Hydrogen Production, ed. A. Godula-Jopek A. Smith (WILEY, Weinheim, 2015), p. 117
A. Manabe, M. Kashiwase, T. Hashimoto, T. Hayashida, A. Kato, K. Hirao, I. Shimomura, I. Nagashima, Basic study of alkaline water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 100, 249–256 (2013)
J. Wang, Y. Gao, H. Kong, J. Kim, S. Choi, F. Ciucci, Y. Hao, S. Yang, Z. Shao, J. Lim, Non-precious-metal catalysts for alkaline water electrolysis: operando characterizations, theoretical calculations, and recent advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 9154–9196 (2020)
M.P. Kumar, G. Murugadoss, R.V. Mangalaraja, M.R. Kumar, Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of CuO-SnO2 nanocomposite in alkaline medium. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 66, 127 (2021)
Z. Ali, M. Mehmood, J. Ahmad, M. Ali, T. Ghani, S. Qamar, A. Fatima, Formation of carbon nanostructures on nickel acetate alcogel by cvd method and its oer electrocatalytic study in alkaline media. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 655, 127 (2021)
S.H. Ahn, I. Choi, H.Y. Park, S.J. Hwang, S.J. Yoo, E. Cho, H.J. Kim, D. Henkensmeier, S.W. Nam, S.K. Kim, Effect of morphology of electrodeposited ni catalysts on the behavior of bubbles generated during the oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water electrolysis. Chem. Commun. 49, 9323–9325 (2013)
K.S. Anuratha, M. Rinawati, T.-H. Wu, M.-H. Yeh, J.-Y. Lin, Recent development of nickel-based electrocatalysts for urea electrolysis in alkaline solution. Nanomaterials 12, 2970 (2022)
A.L. Hoang, S. Balakrishnan, A. Hodges, G. Tsekouras, A. Al-Musawi, K. Wagner, C.-Y. Lee, G.F. Swiegers, G.G. Wallace, High-performing catalysts for energy-efficient commercial alkaline water electrolysis. Sustain. Energ. Fuels 7, 31–60 (2023)
D. Zhou, P. Li, W. Xu, S. Jawaid, J. Mohammed-Ibrahim, W. Liu, Y. Kuang, X. Sun, Recent advances in non-precious metal-based electrodes for alkaline water electrolysis. ChemNanoMat 6, 336–355 (2020)
X. Cao, Z. Yang, X. Wu, X. Wang, X. Teng, J. Yun, J. Zhang, X. Liang, Multilayered NiMo/CoMn/Ni cathodic electrodes with enhanced activity and stability toward alkaline water electrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15(28), 34181–34194 (2023)
S.H. Ahn, H.Y. Park, I. Choi, S.J. Yoo, S.J. Hwang, H.J. Kim, E. Cho, C.W. Yoon, H. Park, H. Son, Electrochemically fabricated NiCu alloy catalysts for hydrogen production in alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 13493–13501 (2013)
J. Li, M. Song, Y. Hu, Y. Zhu, J. Zhang, D. Wang, J. Li, M. Song, Y. Hu, Y. Zhu, J. Zhang, D. Wang, Hybrid heterostructure Ni3N| NiFeP/FF self-supporting electrode for high-current-density alkaline water electrolysis. Small Methods 7, 2201616 (2023)
Q. Chen, X. Han, Z. Xu, Q. Chen, Q. Wu, T. Zheng, P. Wang, Z. Wang, J. Wang, H. Li, Atomic phosphorus induces tunable lattice strain in high entropy alloys and boosts alkaline water splitting. Nano Energy 110, 108380 (2023)
H. Chen, H.B. Huang, H.H. Li, S.Z. Zhao, L.D. Wang, J. Zhang, S.L. Zhong, C.F. Lao, L.M. Cao, C.T. He, Self-supporting Co/CeO2 heterostructures for ampere-level current density alkaline water electrolysis. Inorg. Chem. 62, 3297–3304 (2023)
Q. Zhou, L. Liao, H. Zhou, D. Li, D. Tang, F. Yu, Innovative strategies in design of transition metal-based catalysts for large-current-density alkaline water/seawater electrolysis. Mater. Today Phys. 26, 100727 (2022)
F. Rocha, R. Delmelle, C. Georgiadis, J. Proost, Electrochemical performance enhancement of 3D printed electrodes tailored for enhanced gas evacuation during alkaline water electrolysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2203087 (2023)
S. Jiang, L. Zhu, Z. Yang, Y. Wang, Morphological-modulated FeNi-based amorphous alloys as efficient alkaline water splitting electrocatalysts. Electrochim. Acta 389, 138756 (2021)
S. Bi, Z. Geng, Y. Wang, Z. Gao, L. **, M. Xue, C. Zhang, Multi-stage porous Nickel-Iron oxide electrode for high current alkaline water electrolysis. Adv. Funct. Mater.Funct. Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202214792
T. Haq, Y. Haik, A roadmap towards sustainable anode design for alkaline water electrolysis. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 334, 122853 (2023)
X. Liu, R. Guo, K. Ni, F. **a, C. Niu, B. Wen, J. Meng, P. Wu, J. Wu, X. Wu, L. Mai, Reconstruction-determined alkaline water electrolysis at industrial temperatures. Adv. Mater. 32, 2001136 (2020)
M. Chen, D. Liu, J. Feng, P. Zhou, L. Qiao, W. Feng, Y. Chen, K. Wei Ng, S. Wang, W. Fai Ip, H. Pan, In-situ generation of Ni-CoOOH through deep reconstruction for durable alkaline water electrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 443, 136432 (2022)
W. Ju, M.V.F. Heinz, L. Pusterla, M. Hofer, B. Fumey, R. Castiglioni, M. Pagani, C. Battaglia, U.F. Vogt, Lab-scale alkaline water electrolyzer for bridging material fundamentals with realistic operation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(4), 4829–4837 (2018)
X. Ji, Y. Lin, J. Zeng, Z. Ren, Z. Lin, Y. Mu, Y. Qiu, J. Yu, Graphene/MoS2/FeCoNi(OH)x and Graphene/MoS2/FeCoNiPx multilayer-stacked vertical nanosheets on carbon fibers for highly efficient overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 12, 1380 (2021)
Duan, X. Wei, Y. Huang, Y. Yang, B. Liu, B. Jia, X. Liu, Y. Zhou, G. Ke, H. He, Performance evolution of typical electrocatalysts with electrolyte temperature during alkaline water electrolysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 127, 8041–8047 (2023)
W. Li, Z. Sun, R. Ge, J. Li, Y. Li, J.M. Cairney, R. Zheng, Y. Li, S. Li, Q. Li, Nanoarchitectonics of La-Doped Ni3S2/MoS2 hetetostructural electrocatalysts for water electrolysis. Small Struct. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202300175
S. Kim, C. Ahn, Y. Cho, G. Hyun, S. Jeon, J.H. Park, Suppressing buoyant force: new avenue for long-term durability of oxygen evolution catalysts. Nano Energy 54, 184–191 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledged the support from Shanghai Science and Technology Committee.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (No: 21DZ1207902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the work. SW: design of the work, providing idea, synthesizing materials, analyzing data, and writing and revising—original draft. CT and SX: measuring and collating data. HG: resources, review, and supervision. DG: resources, review, and supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Ethical approval
We approved all ethics.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Xue, S., Tang, C. et al. FeCoNi(OH)x/Ni mesh electrode boosting oxygen evolution reaction for high-performance alkaline water electrolysis. Appl. Phys. A 129, 789 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07077-z