Summary
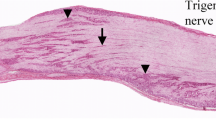
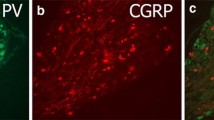
By use of fluorescence immunohistochemistry it is shown that sciatic nerve section in cat and rat induces increased levels of immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in axotomized motoneurons. In the rat, this effect was clearly seen at 2–5 days postoperatively, but could not be demonstrated after 11–21 days. These findings are discussed in relation to previously proposed roles for CGRP in motoneurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldskogius H, Arvidsson J, Grant G (1985) The reaction of primary sensory neurons to peripheral nerve injury with particular emphasis on transganglionic changes. Brain Res Rev 10:27–46
Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM (1982) Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 298:240–244
Arvidsson U, Cullheim S, Ulfhake B, Hökfelt T, Terenius L (1989) Altered levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-like immunoreactivity of cat lumbar motoneurons after chronic spinal cord transection. Brain Res 489:387–391
Barron KD (1983) Comparative observations on the cytological reactions of central and peripheral nerve cells to axotomy. In: Kao CC, Bunge RP, Reier PJ (eds) Spinal cord reconstruction. Raven Press, pp 7–40
Coons AH (1958) Fluorescent antibody methods. In: Danielli JF (ed) General cytochemical methods. Academic Press, New York, pp 399–422
Cullheim S, Kellerth J-O (1978) A morphological study of the axons and recurrent axon collaterals of cat α-motoneurones supplying different hind limb muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 281:285–299
Fontaine B, Klarsfeld A, Hökfelt T, Changeux J-P (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide, a peptide present in spinal cord motoneurons, increases the number of acetylcholine receptors in primary cultures of chick embryo myotubes. Neurosci Lett 71:59–65
Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Sabate IM, Mulderry PM, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Morrison JFB, Kelly JS, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and of eight other species. J Neurosci 4:3101–3111
Johnson DG, de C Nogueira Araujo GM (1981) A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods 43:349
Kosaka T, Nagatsu I, Wu J-Y, Hama K (1986) Use of high concentrations of glutaraldehyde for immunocytochemistry of transmitter-syntheszing enzymes in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 18:975–990
Kreutzberg GW (1982) Acute neuronal reaction to injury. In: Nicholls JG (ed) Repair and regeneration of the nervous system. Springer, Berlin, pp 57–69
Lieberman AR (1971) The axon reaction: a review of the principal features of perikaryal responses to axon injury. Int Rev Neurobiol 14:49–124
New HV, Mudge AW (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates muscle acetylcholine receptor synthesis. Nature (Lond) 323:809–811
Platt JL, Michael AF (1983) Retardation of fading and enhancement of intensity of immunofluorescence by p-phenylenediamine. J Histochem Cytochem 31:840–842
Réthelyi M, Metz CB, Lund PK (1989) Distribution of neurons expressing calcitonin gene-related peptide mRNA in the brain stem, spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia of rat and guinea-pig. Neuroscience 29:225–239
Romanes GJ (1951) The motor cell columns of the lumbo-sacral spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol 94:313–363
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod J-J, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature (Lond) 304:129–135
Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide: detailed immunohistochemical distribution in the central nervous system. Peptides 6:721–745
Takami K, Kawai Y, Shiosaka S, Lee Y, Girgis S, Hillyard J, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Immunohistochemical evidence for the coexistence of calcitonin generelated peptide- and choline acetyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in neurons of the rat hypoglossal, facial and ambiguus nuclei. Brain Res 328:386–389
Takami K, Kawai Y, Uchida S, Tohyama M, Shiotani Y, Yoshida H, Emson PC, Girgis SH, Hillyard CJ, MacIntyre I (1985) Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on contraction of striated muscle in the mouse. Neurosci Lett 60:227–230
Willingham MC (1983) An alternative fixation-processing method for preembedding ultrastructural immunocytochemistry of cytoplasmic antigens: the GBS (glutaraldehyde-borohydride-saponin) procedure. J Histochem Cytochem 31:791–798
Zamboni L, de Martino C (1967) Buffered picric acid formaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 35:148A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arvidsson, U., Johnson, H., Piehl, F. et al. Peripheral nerve section induces increased levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-like immunoreactivity in axotomized motoneurons. Exp Brain Res 79, 212–216 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228891
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228891