Search
Search Results
-
Striated muscle: an inadequate soil for cancers
Many organs of the body are susceptible to cancer development. However, striated muscles—which include skeletal and cardiac muscles—are rarely the...
-
Replenishing NAD+ content reduces aspects of striated muscle disease in a dog model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked disease caused by mutations in DMD gene and loss of the protein dystrophin, which ultimately leads...

-
Esophageal striated muscle hypertrophy and muscle fiber type transformation in MSTN knockout pigs
Myostatin (MSTN) is a member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily that inhibits skeletal muscle growth and development. The esophagus is...

-
Bladder Covering by Striated Muscle
Bladder acontractility caused by a lower motor neuron lesion is an irreversible and debilitating voiding disorder affecting a large number of...
-
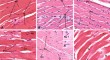
Histological changes in lingual striated muscle tissue of human cadavers to estimate the postmortem interval
Although there are physiological methods to determine the postmortem interval (PMI), interval forensic histopathology can be applied to obtain...
-
Ultrastructural and proteomic profiling of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes reveal aging signatures in striated muscle
Aging is a major risk for develo** cardiac and skeletal muscle dysfunction, yet the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Here we demonstrated that...

-
Alpha kinase 3 signaling at the M-band maintains sarcomere integrity and proteostasis in striated muscle
Muscle contraction is driven by the molecular machinery of the sarcomere. As phosphorylation is a critical regulator of muscle function, the...

-
Expression of LIM domain-binding 3 (LDB3), a striated muscle Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-motif protein in the nervous system
LIM domain-binding 3 (LDB3) is a member of the Enigma family of PDZ–LIM proteins. LDB3 has been reported as a striated muscle-specific Z-band...
-
Bladder Covering by Striated Muscle
Bladder acontractility caused by a lower motor neuron lesion is an irreversible and debilitating voiding disorder affecting a large number of...
-
Trichinella spiralis (Owen, 1835) Induces Increased Dystrophin Expression in Invaded Cross-striated Muscle
PurposeDystrophin and the dystrophin glycoprotein complex serve as a cytoskeletal integrator, critical for muscle membrane stability. The aim of the...

-
A chromosome-level genome of the striated frogfish (Antennarius striatus)
The striated frogfish ( Antennarius striatus ), a member of the sub-order Antennarioidei within the order Lophiiformes, possesses remarkable...

-
Striated muscle proteins are regulated both by mechanical deformation and by chemical post-translational modification
All cells sense force and build their cytoskeleton to optimize function. How is this achieved? Two major systems are involved. The first is that load...

-
Striated muscle-specific base editing enables correction of mutations causing dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the second most common cause for heart failure with no cure except a high-risk heart transplantation. Approximately 30% of...

-
John Squire and the myosin thick filament structure in muscle
The structure of the thin, actin-containing filament of muscle is both highly conserved across a broad range of muscle types and is now well...

-
Eliminating elevated p53 signaling fails to rescue skeletal muscle defects or extend survival in lamin A/C-deficient mice
Lamins A and C, encoded by the LMNA gene, are nuclear intermediate filaments that provide structural support to the nucleus and contribute to...

-
Differential Expression of Titin and Obscurin mRNA in Striated Muscles of the Long-Tailed Ground Squirrel Urocitellus undulatus
AbstractSeasonal changes in mRNA levels of the giant sarcomeric cytoskeletal proteins titin and obscurin were studied in the skeletal m....

-
Basic Structure of Skeletal Muscle
Building on the foundational understanding established in the first chapter, Chap. 2 explores the burgeoning...
-
Whole-genome SNP allele frequency differences between Tibetan and Large white pigs reveal genes associated with skeletal muscle growth
BackgroundThe skeletal muscle growth rate and body size of Tibetan pigs (TIB) are lower than Large white pigs (LW). However, the underlying genetic...

-
Striated preferentially expressed gene deficiency leads to mitochondrial dysfunction in develo** cardiomyocytes
A deficiency of striated preferentially expressed gene ( Speg ), a member of the myosin light chain kinase family, results in abnormal myofibril...

-
A new organisational design in skeletal muscle fibres
In vertebrate skeletal muscles, the architecture of myofibrils is particularly well conserved throughout the taxa. It is composed of suites of...

