Search
Search Results
-
Artificial light at night reduces earthworm activity but increases growth of invasive ragweed
BackgroundArtificial light at night, also referred to as light pollution (LP), has been shown to affect many organisms. However, little is known...

-
China-US grain trade shapes the spatial genetic pattern of common ragweed in East China cities
Common ragweed is an invasive alien species causing severe allergies in urban residents. Understanding its urban invasion pathways is crucial for...

-
A high diversity of non-target site resistance mechanisms to acetolactate-synthase (ALS) inhibiting herbicides has evolved within and among field populations of common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.)
BackgroundNon-target site resistance (NTSR) to herbicides is a polygenic trait that threatens the chemical control of agricultural weeds. NTSR...

-
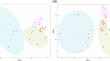
Microbial communities in the rhizosphere soil of Ambrosia artemisiifolia facilitate its growth
PurposeThe invasive weed common ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia [L.]) has become notorious in China as a major weed in agriculture. Soil microbial...
-
Phycitodes subcretacella (Ragonot) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae: Phycitinae)—A New Phytophage of the Quarantine Species Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. in the South of the Far East of Russia
AbstractA species of narrow-winged pyralid moth Phycitodes subcretacella (Ragonot, 1901) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae: Phycitinae), which is an invasive...

-
New Data on the Insects (Orthoptera, Heteroptera, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera) Feeding on Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. (Asteraceae) in the South of the Russian Far East
AbstractNew information is provided on the insects (Orthoptera, Heteroptera, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera) collected from the common ragweed Ambrosia...

-
Distinctive foliar features and volatile profiles in three Ambrosia species (Asteraceae)
Main conclusionAmbrosia species differ both in their trichome types and in metabolic profiles of leaf volatiles. The current study provides tools...

-
Effects of cutting and sowing seeds of native species on giant ragweed invasion and plant diversity in a field experiment
BackgroundAmbrosia trifida is a highly invasive annual plant, but effective control methods have not been proposed. Among various eradication...

-
Russian Three-Component Herbicide Arizon for Corn Crop Protection in the Central Region of Krasnodar Krai
AbstractBiological and economic effectiveness of the Arizon OD herbicide (75 g/L mesotrione + 30 g/L nicosulfuron + 3.5 g/L florasulam) has been...

-
Ecogeographical Potential of the Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. Northward Expansion in European Russia Estimated on the Basis of a Comparison of the Northern Limits of Its Primary and Secondary Ranges
AbstractField studies made it possible to specify the actual modern Ambrosia artemisiifolia naturalization boundary in European Russia. This...

-
Effect of elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide on the allelopathic potential of common ragweed
BackgroundAllelopathy has been suggested as one potential mechanism facilitating the successful colonisation and expansion of invasive plants. The...

-
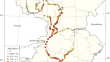
Characterization of the Occurrence and Abundance of the Common Ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) with Regard to Assessment of Its Expansion Potential in European Russia
AbstractA field study of common ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) in European Russia provided information on the occurrence and abundance of the...
-

-
Does adaptation to historical climate shape plant responses to future rainfall patterns? A rainfall manipulation experiment with common ragweed
Climate change is affecting both the volume and distribution of precipitation, which in turn is expected to affect the growth and reproduction of...

-
Giant Ragweed Invasion is Not Well Controlled by Biotic Resistance
The effect of native plant restoration on invasion by giant ragweed ( Ambrosia trifida ), an invasive species, is currently unknown. We hypothesized...
-
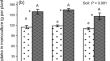
Soil management legacy alters weed-crop competition through biotic and abiotic pathways
AimsAgricultural practices often have persistent effects on soil physicochemical properties and soil biota, which can feedback to influence plant...
-
Litter decomposition rate and nutrient dynamics of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) in the non-native habitat of South Korea
AimAmbrosia trifida L. is designated as an invasive exotic plants in South Korea. Despite its widespread distribution in South Korea, research on A....

-
Integrated Approach to Accounting for Environmental Factors in Models of the Current Distribution and Climatic Dynamics of Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. in the Caucasus
AbstractCurrent climate change, habitat degradation, and road network development contribute to the invasion of alien plant species in areas of more...

-
The potential of common ragweed for further spread: invasibility of different habitats and the role of disturbances and propagule pressure
The infilling of existing suitable habitats within a landscape after establishment is of critical importance for the final outcome of a plant...

-
Biodiversity of Colletotrichum spp. on Several Wild and Cultivated Plants
Abstract —The genus Colletotrichum includes a number of plant pathogens of major importance, causing diseases in a broad variety of woody and...

