Search
Search Results
-
Composting and fermentation: mitigating hop latent viroid infection risk in hop residues
Hop cultivation, integral to the brewing industry, faces challenges from viroids, especially the citrus bark cracking viroid (CBCVd) but also the hop...

-
Risk potential of international fruit trade for viroid spreading - case study on hop viroids in Europe
Most hops are produced in Europe; therefore, it is alarming that the citrus bark cracking viroid (CBCVd), the causal agent of the severe hop stunt...

-
Predicting the distribution of European Hop Hornbeam: application of MaxEnt algorithm and climatic suitability models
Ostrya carpinifolia Scop. (European Hop Hornbeam) is a native tree in Europe as a species of the Betulaceae family. European Hop Hornbeam has a...

-
First report of Paramyrothecium foliicola causing leaf spots on hop
Paramyrothecium foliicola is reported for the first time in Brazil and worldwide causing leaf spots on hop ( Humulus lupulus ). The fungus was...

-
Degradation of hop latent viroid during anaerobic digestion of infected hop harvest residues
The citrus bark cracking viroid (CBCVd) was identified as causal agent for a severe stunting disease in hops. Viroids are highly stable parasitic...

-
Geographic range extension of hop cyst nematode, Heterodera humuli, from Tasmania to the Australian mainland
Hop cyst nematode, Heterodera humuli Filipjev, 1934 was found in soil samples collected from hop farms in Bushy Park, Tasmania and in Merriang,...

-
High sensitivity of hop plants (Humulus lupulus L.) to limited soil water availability: the role of stomata regulation and xylem vulnerability to embolism
Drought poses a serious threat to the productivity of hop, an important perennial crop. However, the precise physiological mechanisms that make it...

-
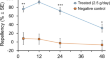
Potential utilization of the brewery’s hop wastes as an insecticidal synergist and repellent against Spodoptera frugiperda
The fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda , is becoming a serious invasive insect pest in Asia, Africa, and Oceania due to its broad spectrum of host...
-
Vitro-derived hop (Humulus lupulus L.) leaves and roots as source of bioactive compounds: antioxidant activity and polyphenolic profile
Bioactive compounds extracted from plant are of great value for those enterprises interested in the use of natural products; plant tissue culture...

-
Hsp70/Hsp90 Organising Protein (Hop): Coordinating Much More than Chaperones
The Hsp70/Hsp90 organising protein (Hop, also known as stress-inducible protein 1/STI1/STIP1) has received considerable attention for diverse...
-
First report of Fusarium meridionale causing canker in hop plants
Fusarium canker in hop is caused by Fusarium spp. Its symptoms are wilting, cankers in the crown, foliar necrosis and death of infected plants....

-
Long-distance dependency combined multi-hop graph neural networks for protein–protein interactions prediction
BackgroundProtein–protein interactions are widespread in biological systems and play an important role in cell biology. Since traditional...

-
Effect of Extraction Time on the Yield, Chemical Composition, and Antibacterial Activity of Hop Essential Oil Against Lactic Acid Bacteria (Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus casei) Beer Spoilage
Hop essential oil (EO) generates interest for its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, in addition to the volatile compounds that are...

-
Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with R1-mediated resistance to powdery mildew and sex determination in hop (Humulus lupulus L.)
Key messageTwo QTL were identified using linkage map** approaches, one on hop linkage group 3 ( qHl_Chr3.PMR1 ) associated with powdery mildew...

-
Agronomic, genetic and chemical tools for hop cultivation and breeding
Humulus lupulus L. (hop) is a dioecious climbing plant of which the females bear particular inflorescences, called hops, ‘cones’ or ‘strobiles’, made...

-
Molecular phylogeny and secondary structure analysis of hop stunt viroid (HSVd) associated with Mulberry (Morus alba) in India
Hop stunt viroid (HSVd), a small, single stranded, circular, non-coding infectious RNA known to cause infection in various economically important...

-
Hop bitter acids: resources, biosynthesis, and applications
AbstractDiversified members of hop bitter acids (α- and β-acids) have been found in hop ( Humulus lupulus ). Mixtures of hop bitter acids have been...

-
Detection of hop stunt viroid variants from naturally infected kumquat and limequat trees in Mazandaran Province, Iran
Viroids are important citrus pathogens, and cachexia disease is caused by pathogenic variants, CVd-IIb and CVd-IIc, of hop stunt viroid (HSVd). In...

-
Hop (Humulus lupulus L.): Traditional and Present Use, and Future Potential
Hop ( Humulus lupulus L.): Traditional and Present Use, and Future Potential. Hop ( Humulus lupulus ) is best known for its use in beer brewing owing to...
