Search
Search Results
-
Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS): An Emerging Strategy for the Control of Fungal Plant Diseases
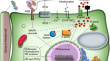
Fungal pathogens are the important bio-agents that cause severe diseases in plants like blight, anthracnose, rots, mildews, wilting, rusts, and many...
-
Host RNAi-mediated silencing of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici specific-fasciclin-like protein genes provides improved resistance to Fusarium wilt in Solanum lycopersicum
Main conclusionTomato transgenics expressing dsRNA against FoFLPs act as biofungicides and result in enhanced disease resistance upon Fol infection,...

-
Advanced strategies to control plant pathogenic fungi by host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) and spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS)
Plant pathogenic fungi and oomycetes cause severe losses of crop yield worldwide. Fungicides are widely applied to manage plant diseases caused by...

-
Host-induced gene silencing: an effective control strategy against Fusarium species
Fusarium , a genus of Pezizomycotina, consists of approximately 300 species. Some species like F. graminearum, F. oxysporum , F. proliferatum, F. solani ...
-
Control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum via an RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated targeting of SsPac1 and SsSmk1
Main conclusionThe study evaluates the potential of Spray-Induced Gene Silencing and Host-Induced Gene Silencing for sustainable crop protection...

-
Chitin synthases containing myosin motor-like domain are required for cell wall integrity and virulence of vascular wilt pathogen Verticillium dahliae
Verticillium wilt (VW) of cotton poses a serious threat to the quality and yield of cotton. Verticillium dahliae is the primary causal agent of...

-
A secreted catalase contributes to Puccinia striiformis resistance to host-derived oxidative stress
Plants can produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) to counteract pathogen invasion, and pathogens have also evolved corresponding ROS scavenging...
-
Extracellular vesicles isolated from dsRNA-sprayed barley plants exhibit no growth inhibition or gene silencing in Fusarium graminearum
Numerous reports have shown that incorporating a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-expressing transgene into plants or applying dsRNA by spraying it onto...

-
Transgenic Technologies for Fusarium Wilt Management in Banana
Banana production is severely affected by the fungal wilt disease. The fungal wilt/Panama wilt disease caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense...
-
A candidate effector protein PstCFEM1 contributes to virulence of stripe rust fungus and impairs wheat immunity
Common in Fungal Extracellular Membrane (CFEM) domain proteins are considered to be unique to fungi and closely related to pathogenicity. However,...

-
Pyramiding dsRNAs increases phytonematode tolerance in cotton plants
Main conclusionHost-derived suppression of nematode essential genes decreases reproduction of
Abstract ...Meloidogyne incognita in cotton.
-
Host Resistance, Current Status, and Emerging Advances
Plant parasitic nematodes are among the most important biotic constraints with potential for causing crop yield losses of 8–15% across a wide range...
-
Host-induced gene silencing of brown planthopper glutathione S-transferase gene enhances rice resistance to sap-sucking insect pests
Host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) of insect growth and development is a promising measure for pest control in practice; the feasibility of disarming...

-
Insights to Gossypium defense response against Verticillium dahliae: the Cotton Cancer
The soil-borne pathogen Verticillium dahliae , also referred as “The Cotton Cancer,” is responsible for causing Verticillium wilt in cotton crops, a...

-
Application of Genome Editing for Improving Nematode Resistance in Plants: How far we have progressed?
Plant-parasitic nematodes (PPNs) cause immense yield loss in crop plants that ultimately affects the global crop productivity. The sedentary...
-
Synthetic modulation of ROS scavenging during host—Sclerotinia sclerotiorum interaction: a new strategy for the development of highly resistant plants
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a widespread fungal pathogen responsible for significant crop losses across the globe. The challenge of breeding...

-
Roles of small RNAs in crop disease resistance
Small RNAs (sRNAs) are a class of short, non-coding regulatory RNAs that have emerged as critical components of defense regulatory networks across...

-
An efficient protocol for inoculation of Fusarium graminearum in detached leaves of Arabidopsis
Fusarium graminearum is the main cause of Fusarium head blight, a fungal disease that reduces yield and affects the quality of wheat and other small...

-
RNA interference (RNAi) mediated technique for combating plant diseases: Harnessing nanoparticles for effective delivery and enhanced efficacy
Crop production is severely affected by insects and plant pathogens causing one-third of the total produced food losses. Conventional agricultural...

-
Genome editing for resistance against plant pests and pathogens
The conventional breeding of crops struggles to keep up with increasing food needs and ever-adapting pests and pathogens. Global climate changes have...