Search
Search Results
-
Physiological roles of connexins and pannexins in reproductive organs
Reproductive organs are complex and well-structured tissues essential to perpetuate the species. In mammals, the male and female reproductive organs...

-
Tissue Characteristics and Development in Myxozoa
For most of the time that they have been recognised, myxozoans were viewed to lack any tissue-level of development. However, the discovery of...
-
Connexin and pannexin signaling pathways, an architectural blueprint for CNS physiology and pathology?
The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of a highly heterogeneous population of cells. Dynamic interactions between different compartments...

-
Endothelial function is impaired in conduit arteries of pannexin1 knockout mice
Pannexin1 is ubiquitously expressed in vertebrate tissues, but the role it plays in vascular tone regulation remains unclear. We found that Pannexin1...

-
Annelida
Annelids are a taxon of protostomes comprising more than 17,000 worldwide-distributed species, which can be found in marine, limnic, and terrestrial...
-
Regeneration and Growth as Modes of Adult Development: The Platyhelminthes as a Case Study
Some species of Platyhelminthes have become model systems in which to study whole-body regeneration in adults. Before describing how this capacity is...
-
Endoplasmic reticulum: Membrane contact sites
This paper presents a review of modern data on the functional designation of membrane contact sites (MCSs) of endoplasmic reticulum. Problems of...
-
Hexapoda: A Drosophila’s View of Development
By any criterion, Insecta (as a subtaxon of Hexapoda) is the most successful taxon on the planet (see Chaps. 2 and 3 for the inclusion of the various...
-
The medicinal leech genome encodes 21 innexin genes: different combinations are expressed by identified central neurons
Gap junctional proteins are important components of signaling pathways required for the development and ongoing functions of all animal tissues,...

-

-
Cell-to-cell communication in plants, animals, and fungi: a comparative review
Cell-to-cell communication is a prerequisite for differentiation and development in multicellular organisms. This communication has to be tightly...

-
Transcriptome analysis of Anopheles stephensi embryo using expressed sequence tags
Germ band retraction (GBR) stage is one of the important stages during insect development. It is associated with an extensive epithelial...
-
Osteocytes: Master Orchestrators of Bone
Osteocytes comprise the overwhelming majority of cells in bone and are its only true “permanent” resident cell population. In recent years,...

-
The Schistosoma mansoni phylome: using evolutionary genomics to gain insight into a parasite’s biology
BackgroundSchistosoma mansoni is one of the causative agents of schistosomiasis, a neglected tropical disease that affects about 237 million people...

-
Gap junctions in Nematostella vectensis sea anemone embryos
Gap junctions (GJs) are composed of membrane protein molecules and form intercellular channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells and are...
-
The Arthropod Cuticle
What accounts for the beauty and singularity of arthropods is the cuticle that enables them to compete in their small world. What we see is the...
-

-
Patterns of heterogeneous expression of pannexin 1 and pannexin 2 transcripts in the olfactory epithelium and olfactory bulb
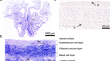
Pannexins form membrane channels that release biological signals to communicate with neighboring cells. Here, we report expression patterns of...
-
Pannexin 1 Ohnologs in the Teleost Lineage
Advances in genomic analysis indicate that the early chordate lineage underwent two whole-genome duplication events in fairly rapid succession around...

-
Connexin43 and Pannexin1 Channels in Osteoblasts: Who Is the “Hemichannel”?
Osteoblasts sense and respond to mechanical stimuli in a process involving influx and release of large ions and signaling molecules. Unapposed gap...

