Search
Search Results
-
Lahar risk assessment from source identification to potential impact analysis: the case of Vulcano Island, Italy
Lahars are rapid flows composed of water and volcaniclastic sediments, which have the potential to impact residential buildings and critical...

-
Long-term lahar reconstruction in Jamapa Gorge, Pico de Orizaba (Mexico) based on botanical evidence and numerical modelling
Lahars on volcanic terrain are recurrent phenomena with a high capacity to transform landscape and cause significant economic and life losses. Lahars...

-
Vegetation cover of the lahar valley on the Sarychev Peak volcano (Matua Isl., Middle Kuril Islands) after the Eruption in 2009: current state and features of succession processes
The paper presents the study of the vegetation recovery after the descent of the lahar during the eruption of the Sarychev Peak volcano (Matua Isl.,...
-
Rainfall-Induced Lahar Occurrences Shortly After Eruptions and Its Initiation Processes in Japan
This study examined the eruption magnitude and timing of lahar occurrences in recent eruptions in Japan. The volcanic deposition status and rainfall...
-
The role of volcanic ash thickness on the hydraulic conductivity of the ground and the initiation of debris flows
Lahars are hazardous mixtures of rock and water that flow rapidly in the form of debris flows or mudflows. The continuous eruptions at Sakurajima...

-
Lahars: Origins, Behavior and Hazards
Volcanic debris flows that originate at potentially active volcanoes are called lahars. Lahars are like debris flows in non-volcanic terrain but can...
-
Merapi’s Lahars: Characteristics, Behaviour, Monitoring, Impact, Hazard Modelling and Risk Assessment
Lahar is an Indonesian term, and Merapi volcano is arguably one of the most renowned lahar producers worldwide. Frequent and voluminous lahars at...
-
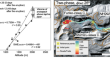
Crisis hazard assessment for snow-related lahars from an unforeseen new vent eruption: the 2018 eruption of Kusatsu-Shirane volcano, Japan
Two-thirds of the 111 active volcanoes in Japan are covered with snow for several months during winter and demonstrate high hazard and risk...
-
Community preparedness for volcanic hazards at Mount Rainier, USA
Lahars pose a significant risk to communities, particularly those living near snow-capped volcanoes. Flows of mud and debris, typically but not...

-
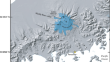
Lava-ice interactions during historical eruptions of Veniaminof Volcano, Alaska and the potential for meltwater floods and lahars
Veniaminof Volcano on the Alaska Peninsula of southwest Alaska is one of a small group of ice-clad volcanoes globally that erupts lava flows in the...
-
Three-dimensional inversion of audio-magnetotelluric data acquired from the crater area of Mt. Tokachidake, Japan
Subvolcanic hydrothermal systems can lead to hydrothermal eruptions as well as unrest phenomena without an eruptive event. Historical eruptions and...

-
The importance of overbank deposits and paleosol analyses for comprehensive volcanic hazard evaluation: the case of Holocene volcanism at Miravalles Volcano, Costa Rica
On the flanks of the dormant Miravalles volcano, systematic fieldwork and radiocarbon dating of buried humus-rich soils (paleosols) and wood...

-
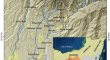
Lahars risk at the Tacaná Volcano Complex (México–Guatemala) from numerical simulations and physical vulnerability analysis
The lahars generated at the active Tacaná Volcanic Complex (Mexico–Guatemala) can be particularly dangerous for three reasons: (1) the high...
-
An Overview of the Large-Magnitude (VEI 4) Eruption of Merapi in 2010
The VEI 4 eruption in 2010 was the worst volcanic disaster at Merapi in 80 years.The unusual size and dynamics of the eruption, the rapid...
-
Estimating the potential risk of the Mt. Baekdu Volcano using a synthetic interferogram and the LAHARZ inundation zone
The Baekdu Volcano is located on the border between Jilin Province, China, and Ryanggang Province, North Korea. Its 946 AD eruption had a Volcanic...
-
Following the tug of the audience from complex to simplified hazards maps at Cascade Range volcanoes
Volcano-hazard maps are broadly recognized as important tools for forecasting and managing volcanic crises and for disseminating spatial information...

-
The Gigantic Volcano-Glacial Edifice (Tuya) Olympus Mons as an Indicator of Ancient Large Glaciation on Mars
AbstractOlympus Mons (basement dimension is 550 × 600 km, absolute height is 21.1 km, relative elevation is 21.9 km, volume is 2.4 × 10 9 km 3 ) is the...

-
Songliao Basin to Changbaishan Mountain Volcanic and Sedimentary Successions and Oil Shale Sedimentary Sequence of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic
The Songliao Basin (SB), situated on the Mongol-North China Plate, contain China's largest oil field, the Daqing Field, which is one of the very few...
-
Approaching the challenge of multi-phase, multi-hazard volcanic impact assessment through the lens of systemic risk: application to Taranaki Mounga
Effective volcanic impact and risk assessment underpins effective volcanic disaster risk management. Yet contemporary volcanic risk assessments face...

-
Vulnerable settlements to debris flows in Arequipa, Peru: population characteristics, hazard knowledge, risk perception, and disaster risk management
Approximately, 75,000 people live in areas prone to volcanic hazards and floods in the large city of Arequipa, Peru. We have conducted three...

