Search
Search Results
-
Progress of antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting c-Met in cancer therapy; insights from clinical and preclinical studies
The cell-surface receptor tyrosine kinase c-mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) is overexpressed in a wide range of solid tumors, making...

-
Molecular mechanism(s) of regulation(s) of c-MET/HGF signaling in head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common cancer across the globe. This is generally associated with tobacco and alcohol consumption. Cancer in...

-
Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of BPI-9016M in c-MET overexpression or MET exon 14 skip** mutation patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase Ib study
BackgroundAs a potential target receptor tyrosine kinase, mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor ( MET ) exhibits high aberrant expression across...

-
Silencing CircEIF3I/miR-526b-5p Axis Epigenetically Targets HGF/c-Met Signal to Hinder the Malignant Growth, Metastasis and Angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
BackgroundHepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-Met) is important for the diagnosis and prognosis of...

-
Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury
BackgroundRadiation-induced lung fibrosis (RILF) is a common complication of thoracic radiotherapy. Alveolar epithelial cells play a crucial role in...

-
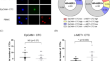
c-MET-positive circulating tumor cells and cell-free DNA as independent prognostic factors in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer
BackgroundEndocrine therapy resistance in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer (BC) is a significant clinical challenge...
-
Molecular mechanism study of HGF/c-MET pathway activation and immune regulation for a tumor diagnosis model
BackgroundHepatocyte growth factor (HGF) binds to the c-mesenchymal-epithelial transition (C-MET) receptor and activates downstream signaling...

-
Suppression of TNBC metastasis by doxazosin, a novel dual inhibitor of c-MET/EGFR
BackgroundTriple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by aggressive growth and a high propensity for recurrence and metastasis....

-
HGF-mediated elevation of ETV1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating PTK2 and c-MET
BackgroundMetastasis is a major determinant of death in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Dissecting key molecular mediators that promote...

-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetamide chalcone hybrids as potential c-Met kinase inhibitors
c-Met is involved in cellular processes that lead to the development and progression of cancer. A series of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetamide-chalcones...

-
Verticillin A inhibits colon cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting c-Met
Verticillin A is a diketopiperazine compound which was previously isolated from Amanita flavorubescens Alk (containing parasitic fungi Hypomyces...
-
HGF/c-Met Signalling in the Tumor Microenvironment
Recently, it has become clearer that tumor plasticity increases the chance that cancer cells could acquire new mechanisms to escape immune...
-
LncRNA HOTTIP Knockdown Attenuates Acute Myocardial Infarction via Regulating miR-92a-2/c-Met Axis
Increasing investigations have focused on long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in various human diseases, including acute myocardial infarction (AMI)....

-
Role of c-Met/HGF Axis in Altered Cancer Metabolism
c-Met (mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that belongs to the Met family and is majorly expressed on the...
-
Anti-cancer therapeutic strategies based on HGF/MET, EpCAM, and tumor-stromal cross talk
As an intelligent disease, tumors apply several pathways to evade the immune system. It can use alternative routes to bypass intracellular signaling...

-
Critical transition and reversion of tumorigenesis
Cancer is caused by the accumulation of genetic alterations and therefore has been historically considered to be irreversible. Intriguingly, several...

-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy for Breast Cancer: Lessons from Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
Immune checkpoint blockade therapies have generated efficacious responses in certain tumor types; however, the responses of breast carcinomas have...

-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression: unraveling the immunosuppressive module driving therapy resistance
Cancer cells undergo phenotypic switching (cancer cell plasticity) in response to microenvironmental cues, including exposure to therapy/treatment....

-
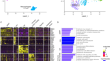
Mesenchymal–epithelial transition in lymph node metastases of oral squamous cell carcinoma is accompanied by ZEB1 expression
BackgroundOral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), an HPV-negative head and neck cancer, frequently metastasizes to the regional lymph nodes but only...
-
A re-appraisal of mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) in endometrial epithelial remodeling
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) is a mechanism of endometrial epithelial regeneration. It is also implicated in adenocarcinoma and...

