Search
Search Results
-
The aminosteroid U73122 promotes oligodendrocytes generation and myelin formation
Oligodendrocytes (OLs) are glial cells that ensheath neuronal axons and form myelin in the central nervous system (CNS). OLs are differentiated from...

-
U73122 and m-3M3FBS Regulate the GABAergic Neuron Regeneration via PLCβ in Planarian Dugesia japonica
AbstractThe planarian Dugesia japonica has a powerful regenerative capacity and can regenerate its whole body, including complete and functional...

-
The phospholipase C inhibitor U73122 is a potent agonist of the polymodal transient receptor potential ankyrin type 1 (TRPA1) receptor channel
The aminosteroid U73122 is frequently used as a phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor and as such was used to investigate PLC-dependent activation and...

-
Extracellular CIRP Induces Calpain Activation in Neurons via PLC-IP3-Dependent Calcium Pathway
Abnormal calcium homeostasis, activation of protease calpain, generation of p25 and hyperactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) have all been...

-
The Impact of the Antipsychotic Medication Chlorpromazine on Cytotoxicity through Ca2+ Signaling Pathway in Glial Cell Models
Chlorpromazine, an antipsychotic medication, is conventionally applied to cope with the psychotic disorder such as schizophrenia. In cellular...

-
Single-cell transcriptomics dissects the transcriptome alterations of hematopoietic stem cells in myelodysplastic neoplasms
BackgroundMyelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS) are myeloid neoplasms characterized by disordered differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and a...

-
Phospholipase C-β3 is dispensable for vascular constriction but indispensable for vascular hyperplasia
Angiotensin II (AngII) induces the contraction and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). AngII activates phospholipase C-β (PLC-β),...

-
Sodium oligomannate activates the enteroendocrine-vagal afferent pathways in APP/PS1 mice
Enteroendocrine cells (EECs) and vagal afferent neurons constitute functional sensory units of the gut, which have been implicated in bottom-up...
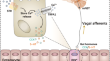
-
TRPV4 Activation and its Intracellular Modulation Mediated by Kinin Receptors Contribute to Painful Symptoms Induced by Anastrozole
Anastrozole, an aromatase inhibitor, induces painful musculoskeletal symptoms, which affect patients’ quality of life and lead to therapy...

-
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) as a modulator of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase from basolateral membranes of kidney proximal tubules
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) acts through the activation of G protein-coupled receptors, in a Ca 2+ -dependent manner. We show the effects of LPA on the...

-
The Chemokine CCL2 Promotes Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal Neurons via GluA1 Subunit Trafficking
The CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2, also known as MCP-1) and its cognate receptor CCR2 have well-characterized roles in chemotaxis. CCL2 has been...

-
Angiotensin II Triggers NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by a Ca2+ Signaling-Dependent Pathway in Rat Cardiac Fibroblast Ang-II by a Ca2+-Dependent Mechanism Triggers NLRP3 Inflammasome in CF
Angiotensin II (Ang-II) is a widely studied hypertensive, profibrotic, and pro-inflammatory peptide. In the heart, cardiac fibroblasts (CF) express...

-
Ca2+ signaling as a mechanism of haloperidol-induced cytotoxicity in human astrocytes and assessing the protective role of a Ca2+ chelator
Haloperidol, a typical antipsychotic medication, has been shown to possess various biological effects in different brain models. However, the impact...

-
Cytotoxic Effects of Mesaconitine, the Aconitum carmichaelii Debx Bioactive Compound, on HBEC-5i Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Role of Ca2+ Signaling-Mediated Pathway
Mesaconitine, one of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx bioactive compounds, was shown to evoke Ca 2+ homeostasis and its related physiological effects in...

-
Rh-CSF1 attenuates neuroinflammation via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE
BackgroundHypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a life-threatening cerebrovascular disease. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in the...

-
PLCγ1 in dopamine neurons critically regulates striatal dopamine release via VMAT2 and synapsin III
Dopamine neurons are essential for voluntary movement, reward learning, and motivation, and their dysfunction is closely linked to various...

-
Signaling Mechanism for Modulation by GLP-1 and Exendin-4 of GABA Receptors on Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is expressed in retinal neurons, but its role in the retina is largely unknown. Here, we demonstrated that GLP-1 or...

-
Growth hormone/IGF-I-dependent signaling restores decreased expression of the myokine SPARC in aged skeletal muscle
AbstractSkeletal muscle exerts many beneficial effects on the human body including the contraction-dependent secretion of peptides termed myokines....
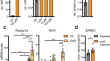
-
Mechanism of contractile dysfunction induced by serotonin in coronary artery in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Hypertension is one of the risk factors for coronary heart disease. The present study investigated the mechanism of contractile dysfunction induced...

-
Burst firing is required for induction of Hebbian LTP at lateral perforant path to hippocampal granule cell synapses
High frequency burst firing is critical in summation of back-propagating action potentials (APs) in dendrites, which may greatly depolarize dendritic...

