Search
Search Results
-
Intermedin1–53 Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Targeting IRE1α in Cardiac Fibrosis
Intermedin (IMD), a paracrine/autocrine peptide, protects against cardiac fibrosis. However, the underlying mechanism remains poorly understood....

-
A new approach of nano-metformin as a protector against radiation-induced cardiac fibrosis and inflammation via CXCL1/TGF-Β pathway
The present work investigates the potential role of metformin nanoparticles (MTF-NPs) as a radio-protector against cardiac fibrosis and inflammation...

-
Hederagenin protects against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via attenuating ALOX5-mediated ferroptosis
Hederagenin (HDG), a medical herb, is known for its beneficial activities against diverse diseases. The cardioprotective effect of HDG has been...

-
Imaging at the nexus: how state of the art imaging techniques can enhance our understanding of cancer and fibrosis
Both cancer and fibrosis are diseases involving dysregulation of cell signaling pathways resulting in an altered cellular microenvironment which...

-
PCSK9 Knockdown Can Improve Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Autophagy
This study investigates the effect and mechanism of proprotein convertase subtilisin/Kexin type 9 (PCSK9) on myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury...

-
Modulation of anti-cardiac fibrosis immune responses by changing M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages
BackgroundMacrophages play a crucial role in the development of cardiac fibrosis (CF). Although our previous studies have shown that glycogen...

-
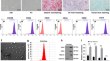
Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect rats against acute myocardial infarction-induced heart failure
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are suggested to promote angiogenesis in a rat model of...
-
Concurrent vitamin D supplementation and exercise training improve cardiac fibrosis via TGF-β/Smad signaling in myocardial infarction model of rats
Although the role of vitamin D in various types of disorders such as cancer and diabetes has been well recognized, its relation to cardiovascular...

-
Research progress on the mechanism of anti-myocardial infarction effect and clinical application of effective components of Salvia miltiorrhiza
Salvia miltiorrhiza , a plant in the Labiatae family, is a traditional Chinese herb. The small molecular components in S. miltiorrhiza can be divided...

-
sST2: A Bridge Between Sirt1/p53/p21 Signal-Induced Senescence and TGF-β1/Smad2/3 Regulation of Cardiac Fibrosis in Mouse Viral Myocarditis
Soluble interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 (sST2) is a novel predictor of poor outcomes, which is involved in inflammatory response and fibrosis of...

-
Altered acylcarnitine metabolism and inflexible mitochondrial fuel utilization characterize the loss of neonatal myocardial regeneration capacity
Myocardial regeneration capacity declines during the first week after birth, and this decline is linked to adaptation to oxidative metabolism....

-
Wnt5a/β-catenin-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a key driver of subretinal fibrosis in neovascular age-related macular degeneration
BackgroundNeovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD), accounts for up to 90% of AMD-associated vision loss, ultimately resulting in the...

-
Mild therapeutic hypothermia upregulates the O-GlcNAcylation level of COX10 to alleviate mitochondrial damage induced by myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury
ObjectiveMild therapeutic hypothermia (MTH) is an important method for perioperative prevention and treatment of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion...

-
Cardiac-specific deletion of BRG1 ameliorates ventricular arrhythmia in mice with myocardial infarction
Malignant ventricular arrhythmia (VA) after myocardial infarction (MI) is mainly caused by myocardial electrophysiological remodeling. Brahma-related...

-
Knockdown of SOX9 alleviates tracheal fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
AbstractTrachealfibrosis is an important cause of tracheal stenosis without effective treatments, and new drug targets need to be developed. The role...

-
LncRNA MALAT1 Regulates USP22 Expression Through EZH2-Mediated H3K27me3 Modification to Accentuate Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), has been confirmed to recruit enhancer of zeste 2...

-
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine alleviates pressure overload-induced myocardial remodeling in mice via inhibiting CaM-JNK/p38 signaling pathway
Apoptosis plays a critical role in the development of heart failure, and sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) is a bioactive sphingolipid naturally...

-
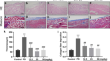
Silymarin ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is the mainstay of treatment for renal failure replacement therapy. Although PD has greatly improved the quality of life of...
-
Nr4a1 promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating the p38 MAPK phosphorylation
BackgroundRenal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) is a common pathway to end-stage renal disease regardless of the initial etiology. Currently, the...

