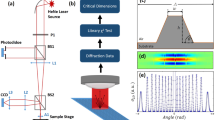
Abstract
This chapter describes in-process measurement of subwavelength structures. Especially, from the viewpoint of affinity with in-process measurement, this chapter focuses on optical measurement, which provides in-process evaluation of engineering microstructure surfaces beyond the diffraction limit. First, application of optical super-resolution using structured light illumination to semiconductor patterns inspection is shown. Second, a new type of optical depth measurement of subwavelength microgrooves using an interference measuring method, which can measure the depth of microgrooves, with widths less than the diffraction limit, is described. Third, as an example of application of near-field optics for in-process measurement for quality of subwavelength structures, nano-thickness inspection of residual layer thickness during nanoimprint lithography is demonstrated. Through concrete examples, the possibility of an optical measurement method for the in-process measurement of subwavelength structures is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigouy L, Lahrech A, GrÃsillon S, Cory H, Boccara AC, Rivoal JC (1999) Polarization effects in Apertureless scanning near-field optical microscopy: an experimental study. Opt Lett 24(4):187–189
Balla T, Spearing SM, Monk A (2008) An assessment of the process capabilities of nanoimprint lithography. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:174001–174010
Bruzzone AAG, Costa HL, Lonardo PM, Lucca DA (2008) Advances in engineered surfaces for functional performance. Ann CIRP 57(2):750–769
Calaon M, Hansen HN, Tosello G, Garnaes J, Norregaard J, Li W (2015) Microfluidic chip designs process optimization and dimensional quality control. Microsyst Technol 21:561–570
Chou SY, Krauss PR, Renstom PJ (1996) Nanoimprint lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 14:4129–4133
de Groot P, de Lega XC, Liesener J, Darwin M (2008) Metrology of optically-unresolved features using interferometric surface profiling and RCWA modeling. Opt Exp 16(6):3970–3975
Gao P, Pedrini G, Osten W (2013) Structured illumination for resolution enhancement and autofocusing in digital holographic microscopy. Opt Lett 38(8):1328–1330
Gass J, Dakoff A, Kim MK (2003) Phase imaging without 2π ambiguity by multiwavelength digital holography. Opt Lett 28(13):1141–1143
Gustafsson MGL (2000) Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J Microsc 198(2):82–87
Hansen HN, Carneiro K, Haitjema H, De Chiffre L (2006) Dimensional micro and nano metrology. Ann CIRP 55(2):721–743
Ho YL, Portela A, Lee Y, Maeda E, Tabata H, Delaunay JJ (2014) Hollow Plasmonic U-Cavites with high-aspect-ratio nanofins sustaining strong optical vortices for light trap** and sensing. Adv Opt Mater 2(6):522–528
Kawata S, Inouye Y (1995) Scanning probe optical microscopy using a metallic probe tip. Ultramicroscopy 57:313–317
Kudo R, Usuki S, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2009) Fundamental verification for 2-dimensional super-resolution optical inspection for semiconductor defects by using standing wave illumination shift. Proceedings of IMEKO world congress, Lisbon, TC2
Kudo R, Usuki S, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2011) Experimental analysis of influence of error on super-resolution optical inspection using standing wave illumination. Proceedings of the 10th international symposium of measurement technology and intelligent instruments, A5–4, Daejeon, pp 1–6
Lee H (2005) Effect of imprinting pressure on residual layer thickness in ultraviolet nanoimprint lithography. J Vac Sci Technol 23(3):1102–1106
Lehmann P, Niehues J, Tereschenko S (2014) 3-D optical interference microscopy at the lateral resolution. Int J Optomechtron 8(4):231–234
Lucy LB (1974) An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions. Astron J 79:745–754
Mico V, Zalevsky Z, Garcia-Martinez P, Garcia J (2006) Superresolved imaging in digital holography by superposition of tilted wavefronts. Appl Opt 45(5):822–828
Nishioka H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2006) A super-resolution microscopy with standing evanescent light and image reconstruction method. Proceedings of IMEKO world congress, Rio de Janeiro, TC2
Peng KQ, Wang X, Li L, Wu XL, Lee ST (2010) High-performance silicon Nanohole solar cells. Am Chem Soc 132(20):6872–6873
Takahashi S (2015) The gap between observation with light and geometric measurement. J Jpn Soc Mech Eng 118(1161):14–17
Takahashi S, Okada S, Nishioka H, Usuki S, Takamasu K (2008) Theoretical and numerical analysis of lateral resolution improvement characteristics for fluorescence microscopy using standing evanescent light with image retrieval. Meas Sci Technol 19:084006
Takahashi S, Ikeda Y, Takamasu K (2013) Study on nano thickness inspection for residual layer of nanoimprint lithography using near-field optical enhancement of metal tip. CIRP Ann 62(1):527–530
Takahashi S, ** C, Ye S, Michihata M, Takamasu K (2017) Theoretical analyses of in-process depth measurements of fine microgrooves based on near-field optical response. CIRP Ann 66(1):503–506
Usuki S, Nishioka H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2006) Development of super-resolution optical inspection system for semiconductor defects using standing wave illumination shift. Proceedings of SPIE 6375, Boston, 637508
Usuki S, Nishioka H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2008) Super-resolution optical measurement for ultra-precision machined surface defects by using structured light illumination shift (1st report): theoretical verification of resolution property. J Jpn Soc Precis Eng 74(5):498–503
Usuki S, Nishioka H, Takahashi S, Takamasu K (2010) Experimental verification of super-resolution optical inspection for semiconductor defect using standing wave illumination shift. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 46(9–12):863–875
Wingerden J, Frankena HJ, Smorenburg C (1991) Liner approximation for measurement errors in phase shifting interferometry. Appl Phys 30(19):2718–2729
Yuan C, Zhai H, Liu H (2008) Angular multiplexing in pulsed digital holography for aperture synthesis. Opt Lett 33(20):2356–2358
Yuan C, Situ G, Pedrini G, Ma J, Osten W (2011) Resolution improvement in digital holography by angular and polarization multiplexing. Appl Opt 50(7):B6–b11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Takahashi, S. (2019). In-Process Measurement of Subwavelength Structures. In: Gao, W. (eds) Metrology. Precision Manufacturing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4912-5_15-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4912-5_15-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4912-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4912-5
eBook Packages: Springer Reference EngineeringReference Module Computer Science and Engineering