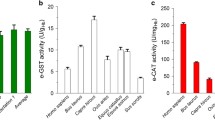
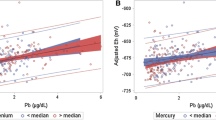
Abstract
The erythrocyte glutathione transferase (e-GST) is the most abundant GST isoenzyme in the red blood cells. This enzyme is able to inactivate numerous different toxic compounds, and many studies indicate its possible role as a biomarker in environmental toxicology since it is hyper-expressed in case of exposure to pollutants in humans as well as in animals. This chapter summarizes most of these studies, revealing also a peculiarity of this biomarker: many toxins induce hyper-expression of e-GST with consequent increased activity, but a few toxins are actually inhibitors of e-GST and cause a decrease in activity. Studies involving inhabitants, mammalians reared in polluted areas, miners, or other workers exposed to a variety of toxic chemicals, demonstrate that a simple, rapid, and inexpensive analysis of e-GST activity may provide an early alarm signal of contamination that can be verified with more traditional chemical analyses to characterize the nature of the contaminants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDNB:
-
1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- DNDGIC:
-
Dinitrosyl-diglutathionyl-iron complex
- e-GST:
-
Erythrocyte glutathione transferase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSTP1-1:
-
Glutathione transferase class P1-1
- GSTPi:
-
Glutathione transferase class P isoforms
- GSTs:
-
Glutathione transferases
- PMs:
-
Particulate matters
- RBCs:
-
Red blood cells
References
Akkam Y, Al-Taani AA, Ayasreh S, Almutairi A, Akkam N. Correlation of blood oxidative stress parameters to indoor radiofrequency radiation: a cross sectional study in Jordan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:4673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134673.
Aliko V, Qirjo M, Sula E, Morina V, Faggio C. Antioxidant defense system, immune response and erythron profile modulation in gold fish, Carassius auratus, after acute manganese treatment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018;76:101–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.02.042.
Aliya S, Reddanna P, Thyagaraju K. Does glutathione S-transferase Pi (GST-Pi) a marker protein for cancer? Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:319–27. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026036521852.
Allocati N, Masulli M, Di Ilio C, Federici L. Glutathione transferases: substrates, inhibitors and pro-drugs in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Oncogenesis. 2018;7:8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-017-0025-3.
Almutairi AM, Akkam Y, Alajmi MF, Akkam N. Effect of air pollution on glutathione S-transferase activity and total antioxidant capacity: cross sectional study in Kuwait. J Health Pollut. 2020;10:200906. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-10.27.200906.
Aly MA, Schröder P. Effect of herbicides on glutathione S-transferases in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008;15:143–9. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.02.385.
Apaydın FG, Pandır D, Kalender S, Baş H, Kalender Y. Hematoprotective effect of vitamins C and E against subchronic toxicity of bendiocarb: biochemical evidences. J Food Biochem. 2018;42:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12659.
Armstrong RN. Structure, catalytic mechanism, and evolution of the glutathione transferases. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997;10:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx960072x.
Bocedi A, Fabrini R, Bello ML, Caccuri AM, Federici G, Mannervik B, Cornish-Bowden A, Ricci G. Evolution of negative cooperativity in glutathione transferase enabled preservation of enzyme function. J Biol Chem. 2016a;291:26739–49. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.749507.
Bocedi A, Noce A, Fabrini R, Di Daniele N, Galli F, Ricci G. Erythrocyte glutathione transferase as a biomarker in kidney health and disease. In: Pateel VB, Preedy VR, editors. Biomarkers in kidney disease. Dordrecht: Springer; 2016b. p. 577–98.
Bocedi A, Fabrini R, Lai O, Alfieri L, Roncoroni C, Noce A, Pedersen JZ, Ricci G. Erythrocyte glutathione transferase: a general probe for chemical contaminations in mammals. Cell Death Discov. 2016c;2:16029. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.29.
Bocedi A, Noce A, Rovella V, Marrone G, Cattani G, Iappelli M, De Paolis P, Iaria G, Sforza D, Gallù M, Tisone G, Di Daniele N, Ricci G. Erythrocyte glutathione transferase in kidney transplantation: a probe for kidney detoxification efficiency. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:288. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0289-3.
Bocedi A, Noce A, Marrone G, Noce G, Cattani G, Gambardella G, Di Lauro M, Di Daniele N, Ricci G. Glutathione transferase P1-1 an enzyme useful in biomedicine and as biomarker in clinical practice and in environmental pollution. Nutrients. 2019;11:1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081741.
Bocedi A, Lai O, Cattani G, Roncoroni C, Gambardella G, Notari S, Tancredi F, Bitonti G, Calabrò S, Ricci G. Animal Biomonitoring for the Surveillance of Environment Affected by the Presence of Slight Contamination by β-HCH. Antioxidants. 2022;11:527. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030527.
Booth J, Boyland E, Sims P. An enzyme from rat liver catalysing conjugations with glutathione. Biochem J. 1961;79:516–24. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0790516.
Brucker N, Moro AM, Charão MF, Durgante J, Freitas F, Baierle M, Nascimento S, Gauer B, Bulcão RP, Bubols GB, Ferrari PD, Thiesen FV, Gioda A, Duarte MM, de Castro I, Saldiva PH, Garcia SC. Biomarkers of occupational exposure to air pollution, inflammation and oxidative damage in taxi drivers. Sci Total Environ. 2013;463–464:884–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.098.
Bundy JG, Sidhu JK, Rana F, Spurgeon DJ, Svendsen C, Wren JF, Stürzenbaum SR, Morgan AJ, Kille P. “Systems toxicology” approach identifies coordinated metabolic responses to copper in a terrestrial non-model invertebrate, the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. BMC Biol. 2008;6:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-6-25.
Buratti FM, Darney K, Vichi S, Turco L, Di Consiglio E, Lautz LS, Béchaux C, Dorne JCM, Testai E. Human variability in glutathione-S-transferase activities, tissue distribution and major polymorphic variants: meta-analysis and implication for chemical risk assessment. Toxicol Lett. 2021;337:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.11.007.
Burg D, Filippov DV, Hermanns R, van der Marel GA, van Boom JH, Mulder GJ. Peptidomimetic glutathione analogues as novel gammaGT stable GST inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00269-3.
Caccuri AM, Antonini G, Ascenzi P, Nicotra M, Nuccetelli M, Mazzetti AP, Federici G, Lo Bello M, Ricci G. Temperature adaptation of glutathione S-transferase P1-1. A case for homotropic regulation of substrate binding. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19276–80. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.27.19276.
Canli EG, Atli G, Canli M. Response of the antioxidant enzymes of the erythrocyte and alterations in the serum biomarkers in rats following oral administration of nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;50:145–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.02.007.
Carmagnol F, Sinet PM, Rapin J, Jerome H. Glutathione-S-transferase of human red blood cells; assay, values in normal subjects and in two pathological circumstances: hyperbilirubinemia and impaired renal function. Clin Chim Acta. 1981;117:209–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(81)90040-1.
Chatterjee A, Gupta S. The multifaceted role of glutathione S-transferases in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;433:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.06.028.
Chen H, Juchau MR. Recombinant human glutathione S-transferases catalyse enzymic isomerization of 13-cis-retinoic acid to all-trans-retinoic acid in vitro. Biochem J. 1998;336:223–6. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3360223.
Chen C, Wu C, Lu X, Yan Z, Gao J, Zhao H, Li S. Coniferyl ferulate, a strong inhibitor of glutathione S-transferase isolated from radix Angelicae sinensis, reverses multidrug resistance and downregulates P-glycoprotein. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:639083. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/639083.
Chikezie PC. Glutathione S-transferase activity in diagnostic pathology. Metabolomics. 2015;5:153. https://doi.org/10.4172/2153-0769.1000153.
de Oliveira AAF, de Oliveira TF, Dias MF, Medeiros MHG, Di Mascio P, Veras M, Lemos M, Marcourakis T, Saldiva PHN, Loureiro APM. Genotoxic and epigenotoxic effects in mice exposed to concentrated ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from São Paulo city, Brazil. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2018;15:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-018-0276-y.
Dessì M, Noce A, Dawood KF, Galli F, Taccone-Gallucci M, Fabrini R, Bocedi A, Massoud R, Fucci G, Pastore A, Manca di Villahermosa S, Zingaretti V, Federici G, Ricci G. Erythrocyte glutathione transferase: a potential new biomarker in chronic kidney diseases which correlates with plasma homocysteine. Amino Acids. 2012;43:347–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1085-x.
Dhanani S, Awasthi YC. Glutathione S-transferase isozyme composition of human tissues. In: Awasthi YC, editor. Toxicology of glutathione transferases. New York: Taylor & Francis Group; 2007. p. 321–38.
Dirr H, Reinemer P, Huber R. X-ray crystal structures of cytosolic glutathione S-transferases. Implications for protein architecture, substrate recognition and catalytic function. Eur J Biochem. 1994;220:645–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18666.x.
Dobrakowski M, Pawlas N, Hudziec E, Kozłowska A, Mikołajczyk A, Birkner E, Kasperczyk S. Glutathione, glutathione-related enzymes, and oxidative stress in individuals with subacute occupational exposure to lead. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016;45:235–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.06.008.
Dutta T, Nayak C, Bhattacharjee S. Acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase enzyme activities and their correlation with genotypic variations based on GST M1 and GST T1 loci in long term-pesticide-exposed tea garden workers of sub-Himalayan West Bengal. Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2019;11:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-019-0389-1.
Eaton DL, Bammler TK. Concise review of the glutathione S-transferases and their significance to toxicology. Toxicol Sci. 1999;49:156–64. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/49.2.156.
Ebokaiwe AP, Omaka ON, Okorie U, Oje O, Egedeigwe C, Ekwe A, Nnaji NJ. Assessment of heavy metals around Abakaliki metropolis and potential bioaccumulation and biochemical effects on the liver, kidney, and erythrocyte of rats. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J. 2018;24:1233–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1410695.
Edwards R, Dixon DP, Walbot V. Plant glutathione S-transferases: enzymes with multiple functions in sickness and in health. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5:193–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01601-0.
Enayati AA, Ranson H, Hemingway J. Insect glutathione transferases and insecticide resistance. Insect Mol Biol. 2005;14:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.2004.00529.x.
Espín S, Martínez-López E, Jiménez P, María-Mojica P, García-Fernández AJ. Effects of heavy metals on biomarkers for oxidative stress in Griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus). Environ Res. 2014a;129:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.11.008.
Espín S, Martínez-López E, León-Ortega M, Martínez JE, García-Fernández AJ. Oxidative stress biomarkers in Eurasian eagle owls (Bubo bubo) in three different scenarios of heavy metal exposure. Environ Res. 2014b;131:134–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.03.015.
Fabrini R, De Luca A, Stella L, Mei G, Orioni B, Ciccone S, Federici G, Lo Bello M, Ricci G. Monomer-dimer equilibrium in glutathione transferases: a critical re-examination. Biochemistry. 2009;48:10473–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901238t.
Fabrini R, Bocedi A, Massoud R, Federici G, Ricci G. Spectrophotometric assay for serum glutathione transferase: a re-examination. Clin Biochem. 2012a;45:668–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.02.017.
Fabrini R, Bocedi A, Del Grosso E, Morici L, Federici G, Palleschi A, Ricci G. Erythrocyte glutathione transferase: a novel biomarker to check environmental pollution hazardous for humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012b;426:71–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.037.
Fabrini R, Bocedi A, Camerini S, Fusetti M, Ottaviani F, Passali FM, Topazio D, Iavarone F, Francia I, Castagnola M, Ricci G. Inactivation of human salivary glutathione transferase P1-1 by hypothiocyanite: a post-translational control system in search of a role. PLoS One. 2014;9:e112797. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112797.
Galli F, Rovidati S, Benedetti S, Buoncristiani U, Covarelli C, Floridi A, Canestrari F. Overexpression of erythrocyte glutathione S-transferase in uremia and dialysis. Clin Chem. 1999;45:1781–8.
Gonçalves AMM, Rocha CP, Marques JC, Gonçalves FJM. Enzymes as useful biomarkers to assess the response of freshwater communities to pesticide exposure – a review. Ecol Indic. 2021;122:107303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107303.
Habdous M, Vincent-Viry M, Visvikis S, Siest G. Rapid spectrophotometric method for serum glutathione S-transferases activity. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;326:131–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-8981(02)00329-7.
Habig WH, Jakoby WB. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77053-8.
Hayes JD, Pulford DJ. The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;30:445–600. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409239509083491.
Hayes JD, Flanagan JU, Jowsey IR. Glutathione transferases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:51–88. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.095857.
Hellou J, Ross NW, Moon TW. Glutathione, glutathione S-transferase, and glutathione conjugates, complementary markers of oxidative stress in aquatic biota. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2012;19:2007–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0909-x.
Higgins LG, Hayes JD. Mechanisms of induction of cytosolic and microsomal glutathione transferase (GST) genes by xenobiotics and pro-inflammatory agents. Drug Metab Rev. 2011;43:92–137. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602532.2011.567391.
Kilpikari I, Savolainen H. Decreased erythrocyte glutathione S-transferase activity in rubber workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1984;53:299–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380668.
Kural C, Kaya Kocdogan A, Şimşek GG, Oğuztüzün S, Kaygın P, Yılmaz I, Bayram T, Izci Y. Glutathione S-transferases and cytochrome P450 enzyme expression in patients with intracranial tumors: preliminary report of 55 patients. Med Princ Pract. 2019;28:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1159/000494496.
Kurata M, Suzuki M, Agar NS. Antioxidant systems and erythrocyte life-span in mammals. Comp Biochem Physiol B Comp Biochem. 1993;106:477–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(93)90121-k.
Lee WH, Joshi P, Wen R. Glutathione S-transferase pi isoform (GSTP1) expression in murine retina increases with developmental maturity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;801:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3209-8_4.
Li T, Liu G, Li H, Yang X, **g Y, Zhao G. The synthesis of ethacrynic acid thiazole derivatives as glutathione S-transferase pi inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20:2316–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.02.011.
Lo Bello M, Parker MW, Desideri A, Polticelli F, Falconi M, Del Boccio G, Pennelli A, Federici G, Ricci G. Peculiar spectroscopic and kinetic properties of Cys-47 in human placental glutathione transferase. Evidence for an atypical thiolate ion pair near the active site. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:19033–8.
Mahadevan D, Sutton GR. Ezatiostat hydrochloride for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24:725–33. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2015.1021003.
Oakley A. Glutathione transferases: a structural perspective. Drug Metab Rev. 2011;43:138–51. https://doi.org/10.3109/03602532.2011.558093.
Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Asenuga ER, Afolabi JM, Adejumobi OA, Adedapo AA, Yakubu MA. Effect of arsenic acid withdrawal on hepatotoxicity and disruption of erythrocyte antioxidant defense system. Toxicol Rep. 2017;4:521–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.09.006.
Parker LJ, Bocedi A, Ascher DB, Aitken JB, Harris HH, Lo Bello M, Ricci G, Morton CJ, Parker MW. Glutathione transferase P1-1 as an arsenic drug-sequestering enzyme. Protein Sci. 2017;26:317–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3084.
Possamai FP, Júnior SÁ, Parisotto EB, Moratelli AM, Inácio DB, Garlet TR, Dal-Pizzol F, Filho DW. Antioxidant intervention compensates oxidative stress in blood of subjects exposed to emissions from a coal electric-power plant in South Brazil. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;30:175–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2010.05.006.
Primavera A, Fustinoni S, Biroccio A, Ballerini S, Urbani A, Bernardini S, Federici G, Capucci E, Manno M, Lo Bello M. Glutathione transferases and glutathionylated hemoglobin in workers exposed to low doses of 1,3-butadiene. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2008;17:3004–12. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0443.
Raza A, Galili N, Smith S, Godwin J, Lancet J, Melchert M, Jones M, Keck JG, Meng L, Brown GL, List A. Phase 1 multicenter dose-escalation study of ezatiostat hydrochloride (TLK199 tablets), a novel glutathione analog prodrug, in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 2009;113:6533–40. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-01-176032.
Ricci G, Caccuri AM, Bello ML, Pastore A, Piemonte F, Federici G. Colorimetric and fluorometric assays of glutathione transferase based on 7-chloro-4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole. Anal Biochem. 1994;218:463–5. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1994.1209.
Ricci G, De Maria F, Antonini G, Turella P, Bullo A, Stella L, Filomeni G, Federici G, Caccuri AM. 7-Nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole derivatives, a new class of suicide inhibitors for glutathione S-transferases. Mechanism of action of potential anticancer drugs. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26397–405. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M503295200.
Rotili D, De Luca A, Tarantino D, Pezzola S, Forgione M, Morozzo Della Rocca B, Falconi M, Mai A, Caccuri AM. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of new cytotoxic agents targeting human glutathione-S-transferases. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;89:156–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.033.
Rotimi OA, Rotimi SO, Oluwafemi F, Ademuyiwa O, Balogun EA. Oxidative stress in extrahepatic tissues of rats co-exposed to aflatoxin B1 and low protein diet. Toxicol Res. 2018;34:211–20. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2018.34.3.211.
Rowe JD, Nieves E, Listowsky I. Subunit diversity and tissue distribution of human glutathione S-transferases: interpretations based on electrospray ionization-MS and peptide sequence-specific antisera. Biochem J. 1997;325:481–6. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3250481.
Sachdeva S, Kushwaha P, Flora SJ. Effects of sodium tungstate on oxidative stress enzymes in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2013;23:519–27. https://doi.org/10.3109/15376516.2013.787132.
Saint-Denis M, Narbonne JF, Arnaud C, Ribera D. Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil, effects of lead acetate. Soil Biol Biochem. 2001;33:395–404.
Salinas AE, Wong MG. Glutathione S-transferases – a review. Curr Med Chem. 1999;6:279–309.
Sawers L, Ferguson MJ, Ihrig BR, Young HC, Chakravarty P, Wolf CR, Smith G. Glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) directly influences platinum drug chemosensitivity in ovarian tumour cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:1150–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.386.
Schins RPF, Keman S, Borm PJA. Blood antioxidant status in coal dust induced respiratory disorders: a longitudinal evaluation of multiple biomarkers. Biomarkers. 1997;2:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/135475097231968.
Sharma RK, Upadhyay G, Siddiqi NJ, Sharma B. Pesticides-induced biochemical alterations in occupational North Indian suburban population. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013;32:1213–27. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327112474835.
Sheehan D, Meade G, Foley VM, Dowd CA. Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem J. 2001;360:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3600001.
Sluis-Cremer N, Naidoo N, Dirr H. Class-pi glutathione S-transferase is unable to regain its native conformation after oxidative inactivation by hydrogen peroxide. Eur J Biochem. 1996;242:301–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0301r.x.
Stott WT, Gollapudi BB, Rao KS. Mammalian toxicity of 1,3-dichloropropene. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2001;168:1–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0143-1_1.
Temel Y, Taysi MŞ. The effect of mercury chloride and boric acid on rat erythrocyte enzymes. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;191:177–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1601-x.
Terrier P, Townsend AJ, Coindre JM, Triche TJ, Cowan KH. An immunohistochemical study of pi class glutathione S-transferase expression in normal human tissue. Am J Pathol. 1990;137:845–53.
Tew KD, Ronai Z. GST function in drug and stress response. Drug Resist Updat. 1999;3:143–7. https://doi.org/10.1054/drup.1999.0086.
Tuluce Y, Ozkol H, Koyuncu I, Ine H. Increased occupational coal dust toxicity in blood of central heating system workers. Toxicol Ind Health. 2011;27:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710381889.
Türkan F, Huyut Z, Demir Y, Ertaş F, Beydemir Ş. The effects of some cephalosporins on acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase: an in vivo and in vitro study. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2019;125:235–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2018.1452037.
Wilce MC, Parker MW. Structure and function of glutathione S-transferases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1205:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4838(94)90086-8.
Wilhelm Filho D, Avila S Jr, Possamai FP, Parisotto EB, Moratelli AM, Garlet TR, Inácio DB, Torres MA, Colepicolo P, Dal-Pizzol F. Antioxidant therapy attenuates oxidative stress in the blood of subjects exposed to occupational airborne contamination from coal mining extraction and incineration of hospital residues. Ecotoxicology. 2010;19:1193–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0503-2.
Yaman T, Yener Z, Celik I. Histopathological and biochemical investigations of protective role of honey in rats with experimental aflatoxicosis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:232. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1217-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Bocedi, A., Gambardella, G., Cattani, G., Notari, S., Pedersen, J.Z., Ricci, G. (2022). Erythrocyte Glutathione Transferase P1-1 as a Biomarker in Environmental Toxicology: A New Narrative. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Rajendram, R. (eds) Biomarkers in Toxicology. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_25-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_25-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87225-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87225-0
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences