Abstract
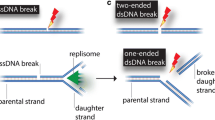
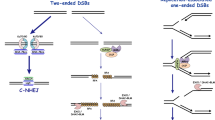
A large number of studies suggests that double-strand breaks (DSBs) induced in DNA by ionizing radiation or chemical agents are critical lesions, which if unrepaired or misrepaired may kill a cell, or cause its transformation to a cancer cell. Cells have developed efficient repair mechanisms to remove DSBs and restore integrity to their DNA. Despite the potential importance of DSBs in cell killing and transformation, relatively little is known regarding DSB repair mechanisms and the enzymes involved. However, characterization of these processes is crucial for a complete understanding of the consequences of exposure to agents, inducing DSBs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedberg, E. C., Walker, G. C., and Siede, W. (1995) DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Derbyshire, M. K., Epstein, L. H., Young, C. S. H., Munz, P. L., and Fishel, R. (1994) Nonhomologous recombination in human cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 156–169.
Fairman, M. P., Johnson, A. P., and Thacker, J. (1992) Multiple components are involved in the efficient joining of double stranded DNA breaks in human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 4145–4152.
Nicolas, A. L. and Young, C. S. H. (1994) Characterization of DNA end joining in a mammalian cell nuclear extract: Junction formation is accompanied by nucleotide loss, which is limited and uniform but not site specific. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 170–180.
North, P., Ganesh, A., and Thacker, J. (1990) The rejoining of double-strand breaks in DNA by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6205–6210.
Pfeiffer, P. and Vielmetter, W. (1988) Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 907–924.
Cheong, N. and Iliakis, G. (1997) In vitro rejoining of double strand breaks induced in cellular DNA by bleomycin and restriction endonucleases. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 71, 365–375.
Cheong, N., Okayasu, R., Shah, S., Ganguly, T., Mammen, P., and Iliakis, G. (1996) In vitro rejoining of double-strand breaks in cellular DNA by factors present in extracts of HeLa cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 69, 665–677.
Ganguly, T. and Iliakis, G. (1995) aA cell-free assay using cytoplasmic cell extract to study rejoining of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in human cell nuclei. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 68, 447–457.
Nevaldine, B., Longo, J. A., Vilenchik, M., King, G. A., and Hahn, P. J. (1994) Induction and repair of DNA double-strand breaks in the same dose range as the shoulder of the survival curve. Radiat. Res. 140, 161–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Humana Press Inc.
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Iliakis, G., Cheong, N. (1999). In Vitro Rejoining of Double-Strand Breaks in Genomic DNA. In: Henderson, D.S. (eds) DNA Repair Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 113. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-675-4:473
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-675-4:473
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-0-89603-802-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-59259-675-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols