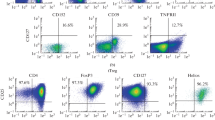
Abstract
T regulatory cells (Tregs) suppress immune responses and therefore have potential to be used in the clinic as a cellular therapy for autoimmune disease and to prevent rejection of transplanted organs. Obtaining sufficient numbers of these cells for therapeutic use is a challenge, however, since there are currently no Treg cell-specific markers, and they have a poor in vitro expansion potential. Tregs express high levels of FOXP3, a transcription factor that is critical for their function. We have shown that lentivirus-based overexpression of FOXP3 can reprogram naïve or memory human CD4+ T cells into cells which possess a phenotype and function similar to ex vivo Tregs. Here we will review the methodology involved in generating, expanding, and testing FOXP3-transduced cells and their ex vivo Treg counterparts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miyara M, Sakaguchi S (2007) Natural regulatory T cells: mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol Med 13:108–116
van Maurik A, Herber M, Wood KJ et al (2002) Cutting edge: CD4+CD25+ alloantigen specific immunoregulatory cells that can prevent CD8+ T cell-mediated graft rejection: implications for anti-CD154 immunotherapy. J Immunol 169:5401–5404
Lin CY, Graca L, Cobbold SP et al (2002) Dominant transplantation tolerance impairs CD8+ T cell function but not expansion. Nat Immunol 3:1208–1213
Lim HW, Hillsamer P, Banham AH et al (2005) Cutting edge: direct suppression of B cells by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 175:4180–4183
Maloy KJ, Antonelli LR, Lefevre M et al (2005) Cure of innate intestinal immune pathology by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Immunol Lett 97:189–192
Tiemessen MM, Jagger AL, Evans HG et al (2007) CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19446–19451
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M et al (1995) Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol 155:1151–1164
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330–336
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057–1061
Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA et al (2003) An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol 4:337–342
Tang Q, Henriksen KJ, Bi M et al (2004) In vitro-expanded antigen-specific regulatory T-cells suppress autoimmune diabetes. J Exp Med 199:1455–1465
Mottet C, Uhlig HH, Powrie F (2003) Cutting edge: cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cells. J Immunol 170:3939–3943
**a G, He J, Zhang Z et al (2006) Targeting acute allograft rejection by immunotherapy with ex vivo-expanded natural CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cells. Transplantation 82:1749–1755
Graca L, Le Moine A, Lin CY et al (2004) Donor-specific transplantation tolerance: the paradoxical behaviour of CD3+CD25+ T-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10122–10126
Taylor PA, Lees CJ, Blazar BR (2002) The infusion of ex vivo activated and expanded CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells inhibits graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood 99:3493–3499
Hoffmann P, Ermann J, Edinger M et al (2002) Donor-type CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T-cells suppress lethal acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med 196:389–399
Riley JL, June CH, Blazar BR (2009) Human T regulatory cell therapy: take a billion or so and call me in the morning. Immunity 30:656–665
Sagoo P, Lombardi G, Lechler RI (2008) Regulatory T cells as therapeutic cells. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 13:645–653
Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A et al (2009) Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 30:899–911
Ayyoub M, Deknuydt F, Raimbaud I et al (2009) Human memory FoxP3+ Tregs secrete IL-17 ex vivo and constitutively express the Th17 lineage-specific transcription factor RORγt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8635–8640
Voo KS, Wang KH, Santori FR et al (2009) Identification of IL-17-producing FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4793–4798
Allan SE, Alstad AN, Merindol N et al (2008) Generation of potent and stable human CD4+ T regulatory cells by activation-independent expression of FOXP3. Mol Ther 16:194–202
Hoffmann P, Eder R, Boeld TJ et al (2006) Only the CD45RA+ subpopulation of CD4+ CD25high T cells gives rise to homogeneous regulatory T-cell lines upon in vitro expansion. Blood 108:4260–4267
Acknowledgments
We thank Sarah E. Allan, Rosa Bacchetta, Maria Grazia Roncarolo, Mario Amendola, and Luigi Naldini for their contributions to the development of this protocol. Supported by the Roche Organ Transplant Research Foundation, CIHR (MOP-93793), and Stemcell Technologies, Inc. Core support for flow cytometry and virus production was funded by the Immunity and Infection Research Centre Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research (MSFHR) Unit. MKL holds a Canada Research Chair in Transplantation. ANM holds a Canada Vanier Scholarship, a MSFHR Junior Graduate Studentship, and a CIHR Transplantation Training Program award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
McMurchy, A.N., Levings, M.K. (2013). In Vitro Generation of Human T Regulatory Cells: Generation, Culture, and Analysis of FOXP3-Transduced T Cells. In: Helgason, C., Miller, C. (eds) Basic Cell Culture Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 946. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-128-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-128-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-127-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-128-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols