Abstract
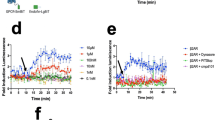
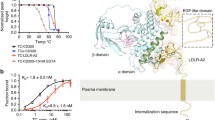
STRA6 is a multitransmembrane domain protein that was recently identified as the cell-surface receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP), the vitamin A carrier protein in the blood. STRA6 binds to RBP with high affinity and mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A from RBP. It is not homologous to any known receptors, transporters, and channels, and it represents a new class of membrane transport protein. Consistent with the diverse physiological functions of vitamin A, STRA6 is widely expressed in diverse adult organs and throughout embryonic development. Mutations in human STRA6 that abolish its vitamin A uptake activity cause severe pathological phenotypes in many human organs including the eye, brain, lung, and heart. This chapter describes functional assays for STRA6 in live cells and on cellular membranes. These assays can be employed to study the mechanism of this new membrane transport mechanism and its roles in the physiology and pathology of many organs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomhoff, R. (1994) Overview of vitamin A metabolism and function. In: Blomhoff, R. (ed.), Vitamin A in Health and Disease, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, Hong Kong, pp. 1–35.
Ross, A.C., Gardner, E.M. (1994) The function of vitamin A in cellular growth and differentiation, and its roles during pregnancy and lactation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 352, 187–200.
Napoli, J.L. (1996) Biochemical pathways of retinoid transport, metabolism, and signal transduction. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 80, S52–S62.
Evans, R.M. (1994) The molecular basis of signaling by vitamin A and its metabolites. Harvey Lect. 90, 105–117.
Chambon, P. (1996) A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 10, 940–954.
Maden, M. (1994) Role of retinoids in embryonic development. In: Blomhoff, R. (ed.), Vitamin A in Health and Disease, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, Hong Kong.
Duester, G. (2008) Retinoic acid synthesis and signaling during early organogenesis. Cell 134, 921–931.
Drager, U.C. (2006) Retinoic acid signaling in the functioning brain. Sci STKE 2006, pe10.
Blomhoff, H.K., Smeland, E.B. (1994) Role of retinoids in normal hematopoiesis and the immune system. In: Blomhoff, R. (ed.), Vitamin A in Health and Disease, Marcel Dekker, Inc., pp. 451–484
Stephensen, C.B. (2001) Vitamin A, infection, and immune function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 21, 167–192.
Chung, S.S., Wolgemuth, D.J. (2004) Role of retinoid signaling in the regulation of spermatogenesis. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 105, 189–202.
Wolbach, S.R., Howe, P.R. (1925) Tissue change following deprivation of fat-soluble A vitamin. J. Exp. Med. 42, 753–777.
Biesalski, H.K. (2003) The significance of vitamin A for the development and function of the lung. Forum Nutr. 56, 37–40.
Vahlquist, A. (1994) Role of retinoids in normal and diseased skin. In: Blomhoff, R. (ed.), Vitamin A in Health and Disease, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, Hong Kong, pp 365–424.
Chen, N., Onisko, B., Napoli, J.L. (2008) The nuclear transcription factor RARalpha associates with neuronal RNA granules and suppresses translation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 20841–20847.
Aoto, J., Nam, C.I., Poon, M.M., Ting, P., Chen, L. (2008) Synaptic signaling by all-trans retinoic acid in homeostatic synaptic plasticity. Neuron 60, 308–320.
Travis, G.H., Golczak, M., Moise, A.R., Palczewski, K. (2007) Diseases caused by defects in the visual cycle: Retinoids as potential therapeutic agents. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47, 469–512.
Ziouzenkova, O., Orasanu, G., Sharlach, M., Akiyama, T.E., Berger, J.P., Viereck, J., Hamilton, J.A., Tang, G., Dolnikowski, G.G., Vogel, S., Duester, G., Plutzky, J. (2007) Retinaldehyde represses adipogenesis and diet-induced obesity. Nat. Med. 13, 695–702.
Buck, J., Myc, A., Garbe, A., Cathomas, G. (1991) Differences in the action and metabolism between retinol and retinoic acid in B lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 115, 851–859.
Chen, Y., Derguini, F., Buck, J. (1997) Vitamin A in serum is a survival factor for fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10205–10208.
Baleato, R.M., Aitken, R.J., Roman, S.D. (2005) Vitamin A regulation of BMP4 expression in the male germ line. Dev. Biol. 286, 78–90.
Chen, L., Khillan, J.S. (2008) Promotion of feeder-independent self-renewal of embryonic stem cells by retinol (vitamin A). Stem Cells 26, 1858–1864.
Blomhoff, R., Green, M.H., Berg, T., Norum, K.R. (1990) Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science 250, 399–404.
Newcomer, M.E., Ong, D.E. (2000) Plasma retinol binding protein: Structure and function of the prototypic lipocalin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1482, 57–64.
Zanotti, G., Berni, R. (2004) Plasma retinol-binding protein: Structure and interactions with retinol, retinoids, and transthyretin. Vitam. Horm. 69, 271–295.
Quadro, L., Hamberger, L., Gottesman, M.E., Wang, F., Colantuoni, V., Blaner, W.S., Mendelsohn, C.L. (2005) Pathways of vitamin A delivery to the embryo: Insights from a new tunable model of embryonic vitamin A deficiency. Endocrinology 146, 4479–4490.
Bok, D., Heller, J. (1976) Transport of retinol from the blood to the retina: An autoradiographic study of the pigment epithelial cell surface receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein. Exp. Eye Res. 22, 395–402.
Heller, J. (1975) Interactions of plasma retinol-binding protein with its receptor. Specific binding of bovine and human retinol-binding protein to pigment epithelium cells from bovine eyes. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 3613–3619.
Heller, J., Bok, D. (1976) Transport of retinol from the blood to the retina: Involvement of high molecular weight lipoproteins as intracellular carriers. Exp. Eye Res. 22, 403–410.
Rask, L., Peterson, P.A. (1976) In vitro uptake of vitamin A from the retinol-binding plasma protein to mucosal epithelial cells from the monkey's small intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 6360–6366.
Maraini, G., Gozzoli, F. (1975) Binding of retinol to isolated retinal pigment epithelium in the presence and absence of retinol-binding protein. Invest. Ophthalmol. 14, 785–787.
Chen, C.C., Heller, J. (1977) Uptake of retinol and retinoic acid from serum retinol-binding protein by retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 5216–5221.
Sivaprasadarao, A., Findlay, J.B. (1988) The interaction of retinol-binding protein with its plasma-membrane receptor. Biochem. J. 255, 561–569.
Smeland, S., Bjerknes, T., Malaba, L., Eskild, W., Norum, K.R., Blomhoff, R. (1995) Tissue distribution of the receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein. Biochem. J. 305(Pt 2), 419–424.
Sivaprasadarao, A., Boudjelal, M., Findlay, J.B. (1994) Solubilization and purification of the retinol-binding protein receptor from human placental membranes. Biochem. J. 302(Pt 1), 245–251.
MacDonald, P.N., Bok, D., Ong, D.E. (1990) Localization of cellular retinol-binding protein and retinol-binding protein in cells comprising the blood-brain barrier of rat and human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4265–4269.
Shingleton, J.L., Skinner, M.K., Ong, D.E. (1989) Characteristics of retinol accumulation from serum retinol-binding protein by cultured Sertoli cells, Biochemistry 28, 9641–9647.
Bishop, P.D., Griswold, M.D. (1987) Uptake and metabolism of retinol in cultured Sertoli cells: Evidence for a kinetic model. Biochemistry 26, 7511–7518.
Bhat, M.K., Cama, H.R. (1979) Gonadal cell surface receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein. A method for its radioassay and studies on its level during spermatogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 587, 273–281.
Davis, J.T., Ong, D.E. (1995) Retinol processing by the peritubular cell from rat testis. Biol. Reprod. 52, 356–364.
Hagen, E., Myhre, A.M., Smeland, S., Halvorsen, B., Norum, K.R., Blomhoff, R. (1999) Uptake of vitamin A in macrophages from physiologic transport proteins: Role of retinol-binding protein and chylomicron remnants. J. Nutr. Biochem. 10, 345–352.
Torma, H., Vahlquist, A. (1984) Vitamin A uptake by human skin in vitro. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 276, 390–395.
Buck, J., Ritter, G., Dannecker, L., Katta, V., Cohen, S.L., Chait, B.T., Hammerling, U. (1990) Retinol is essential for growth of activated human B cells. J. Exp. Med. 171, 1613–1624.
Kawaguchi, R., Yu, J., Honda, J., Hu, J., Whitelegge, J., **, P., Wiita, P., Bok, D., Sun, H. (2007) A membrane receptor for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A. Science 315, 820–825.
Bouillet, P., Sapin, V., Chazaud, C., Messaddeq, N., Decimo, D., Dolle, P., Chambon, P. (1997) Developmental expression pattern of Stra6, a retinoic acid-responsive gene encoding a new type of membrane protein. Mech. Dev. 63, 173–186.
Szeto, W., Jiang, W., Tice, D.A., Rubinfeld, B., Hollingshead, P.G., Fong, S.E., Dugger, D.L., Pham, T., Yansura, D.G., Wong, T.A., Grimaldi, J.C., Corpuz, R.T., Singh, J.S., Frantz, G.D., Devaux, B., Crowley, C.W., Schwall, R.H., Eberhard, D.A., Rastelli, L., Polakis, P., Pennica, D. (2001) Overexpression of the retinoic acid-responsive gene Stra6 in human cancers and its synergistic induction by Wnt-1 and retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 61, 4197–4205.
Pasutto, F., Sticht, H., Hammersen, G., Gillessen-Kaesbach, G., Fitzpatrick, D.R., Nurnberg, G., Brasch, F., Schirmer-Zimmermann, H., Tolmie, J.L., Chitayat, D., Houge, G., Fernandez-Martinez, L., Keating, S., Mortier, G., Hennekam, R.C., von der Wense, A., Slavotinek, A., Meinecke, P., Bitoun, P., Becker, C., Nurnberg, P., Reis, A., Rauch, A. (2007) Mutations in STRA6 cause a broad spectrum of malformations including anophthalmia, congenital heart defects, diaphragmatic hernia, alveolar capillary dysplasia, lung hypoplasia, and mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 550–560.
Golzio, C., Martinovic-Bouriel, J., Thomas, S., Mougou-Zrelli, S., Grattagliano-Bessieres, B., Bonniere, M., Delahaye, S., Munnich, A., Encha-Razavi, F., Lyonnet, S., Vekemans, M., Attie-Bitach, T., Etchevers, H.C. (2007) Matthew-Wood syndrome is caused by truncating mutations in the retinol-binding protein receptor gene STRA6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 1179–1187.
Kawaguchi, R., Yu, J., Wiita, P., Honda, J., Sun, H. (2008) An essential ligand-binding domain in the membrane receptor for retinol-binding protein revealed by large-scale mutagenesis and a human polymorphism. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 15160–15168.
Kawaguchi, R., Yu, J., Wiita, P., Ter-Stepanian, M., Sun, H. (2008) Map** the membrane topology and extracellular ligand binding domains of the retinol binding protein receptor. Biochemistry 47, 5387–5395.
Flanagan, J.G., Cheng, H.J. (2000) Alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins for molecular characterization and cloning of receptors and their ligands. Methods Enzymol. 327, 198–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kawaguchi, R., Sun, H. (2010). Techniques to Study Specific Cell-Surface Receptor-Mediated Cellular Vitamin A Uptake. In: Sun, H., Travis, G. (eds) Retinoids. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 652. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-325-1_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-325-1_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-60327-324-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-60327-325-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols