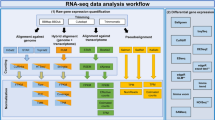
Abstract
As a revolutionary technology for life sciences, RNA-seq has many applications and the computation pipeline has also many variations. Here, we describe a protocol to perform RNA-seq data analysis where the aim is to identify differentially expressed genes in comparisons of two conditions. The protocol follows the recently published RNA-seq data analysis best practice and applies quality checkpoints throughout the analysis to ensure reliable data interpretation. It is written to help new RNA-seq users to understand the basic steps necessary to analyze an RNA-seq dataset properly. An extension of the protocol has been implemented as automated workflows in the R package ezRun, available also in the data analysis framework SUSHI, for reliable, repeatable, and easily interpretable analysis results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484
Conesa A, Madrigal P, Tarazona S et al (2016) A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol 17:13. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-0881-8
Rehrauer H, Opitz L, Tan G et al (2013) Blind spots of quantitative RNA-seq: the limits for assessing abundance, differential expression, and isoform switching. BMC Bioinformatics 14:370. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-370
Li W, Freudenberg J (2014) Mappability and rea d length. Front Genet 5:381. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00381
Zhao S, Zhang Y, Gordon W et al (2015) Comparison of stranded and non-stranded RNA-seq transcriptome profiling and investigation of gene overlap. BMC Genomics 16(1):675. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1876-7
Li S, Labaj PP, Zumbo P et al (2014) Detecting and correcting systematic variation in large-scale RNA sequencing data. Nat Biotechnol 32:888–895
Hatakeyama M, Opitz L, Russo G et al (2016) SUSHI: an exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 17:228. doi:10.1186/s12859-016-1104-8
Villarino GH, Hu Q, Manrique S et al (2016) Transcriptomic signature of the SHATTERPROOF2 expression domain reveals the meristematic nature of Arabidopsis gynoecial medial domain. Plant Physiol 171:42–61. doi:10.1104/pp.15.01845
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F et al (2013) STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29:15–21. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Wang L, Wang S, Li W (2012) RSeQC: quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 28:2184–2185. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts356
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2014) featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30:923–930. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656
Tarazona S, Furió-Tarí P, Turrà D et al (2015) Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic Acids Res 43(21):e140. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv711. gkv711
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26(1):139–140. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Robinson MD, Oshlack A (2010) A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol 11:R25. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Qi, W., Schlapbach, R., Rehrauer, H. (2017). RNA-Seq Data Analysis: From Raw Data Quality Control to Differential Expression Analysis. In: Schmidt, A. (eds) Plant Germline Development. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1669. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7286-9_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7286-9_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7285-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7286-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols