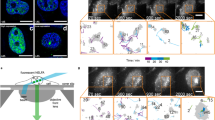
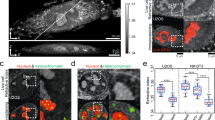
Abstract
The polycomb group (PcG) proteins play a central role in the maintenance of a repressive state of gene expression. Recent findings demonstrate that PcG components are organized into nuclear condensates, contributing to the resha** of chromatin architecture in physiological and pathological conditions, thus affecting the nuclear mechanics. In this context, direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) provides an effective tool to achieve a detailed characterization of PcG condensates by visualizing them at a nanometric level. Furthermore, by analyzing dSTORM datasets with cluster analysis algorithms, quantitative information can be yielded regarding protein numbers, grou**, and spatial organization. Here, we describe how to set up a dSTORM experiment and perform the data analysis to study PcG complexes’ components in adhesion cells quantitatively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kundu S, Ji F, Sunwoo H, Jain G, Lee JT, Sadreyev RI, Dekker J, Kingston RE (2017) Polycomb repressive complex 1 generates discrete compacted domains that change during differentiation. Mol Cell 65(3):432–446 e435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.01.009
Fasciani A, D'Annunzio S, Poli V, Fagnocchi L, Beyes S, Michelatti D, Corazza F, Antonelli L, Gregoretti F, Oliva G, Belli R, Peroni D, Domenici E, Zambrano S, Intartaglia D, Settembre C, Conte I, Testi C, Vergyris P, Ruocco G, Zippo A (2020) MLL4-associated condensates counterbalance Polycomb-mediated nuclear mechanical stress in Kabuki syndrome. Nat Genet 52(12):1397–1411. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00724-8
Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang X (2006) Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat Methods 3(10):793–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth929
Magrassi R, Scalisi S, Cella Zanacchi F (2019) Single-molecule localization to study cytoskeletal structures, membrane complexes, and mechanosensors. Biophys Rev 11(5):745–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00595-2
Nicovich PR, Owen DM, Gaus K (2017) Turning single-molecule localization microscopy into a quantitative bioanalytical tool. Nat Protoc 12(3):453–460. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.166
Khater IM, Nabi IR, Hamarneh G (2020) A review of super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy cluster analysis and quantification methods. Patterns 1(3):100038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2020.100038
Wu YL, Tschanz A, Krupnik L, Ries J (2020) Quantitative data analysis in single-molecule localization microscopy. Trends Cell Biol 30(11):837–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2020.07.005
Endesfelder U, Malkusch S, Fricke F, Heilemann M (2014) A simple method to estimate the average localization precision of a single-molecule localization microscopy experiment. Histochem Cell Biol 141(6):629–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1192-3
Owen DM, Rentero C, Rossy J, Magenau A, Williamson D, Rodriguez M, Gaus K (2010) PALM imaging and cluster analysis of protein heterogeneity at the cell surface. J Biophotonics 3(7):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.200900089
Kiskowski MA, Hancock JF, Kenworthy AK (2009) On the use of Ripley's K-function and its derivatives to analyze domain size. Biophys J 97(4):1095–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2009.05.039
Lagache T, Lang G, Sauvonnet N, Olivo-Marin JC (2013) Analysis of the spatial organization of molecules with robust statistics. PLoS One 8(12):e80914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080914
Sengupta P, Jovanovic-Talisman T, Skoko D, Renz M, Veatch SL, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2011) Probing protein heterogeneity in the plasma membrane using PALM and pair correlation analysis. Nat Methods 8(11):969–975. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1704
Schnitzbauer J, Wang Y, Zhao S, Bakalar M, Nuwal T, Chen B, Huang B (2018) Correlation analysis framework for localization-based superresolution microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(13):3219–3224. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1711314115
Sengupta P, Jovanovic-Talisman T, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2013) Quantifying spatial organization in point-localization superresolution images using pair correlation analysis. Nat Protoc 8(2):345–354. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.005
Gao J, Wang F, Liu Y, Cai M, Xu H, Jiang J, Wang H (2015) Revealing the cellular localization of STAT1 during the cell cycle by super-resolution imaging. Sci Rep 5:9045. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09045
Pereira CF, Rossy J, Owen DM, Mak J, Gaus K (2012) HIV taken by STORM: super-resolution fluorescence microscopy of a viral infection. Virol J 9:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-9-84
Andronov L, Orlov I, Lutz Y, Vonesch JL, Klaholz BP (2016) ClusterViSu, a method for clustering of protein complexes by Voronoi tessellation in super-resolution microscopy. Sci Rep 6:24084. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24084
Endesfelder U, Finan K, Holden SJ, Cook PR, Kapanidis AN, Heilemann M (2013) Multiscale spatial organization of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli. Biophys J 105(1):172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2013.05.048
Mazouchi A, Milstein JN (2016) Fast optimized cluster algorithm for localizations (FOCAL): a spatial cluster analysis for super-resolved microscopy. Bioinformatics 32(5):747–754. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv630
Pike JA, Khan AO, Pallini C, Thomas SG, Mund M, Ries J, Poulter NS, Styles IB (2020) Topological data analysis quantifies biological nanostructure from single molecule localization microscopy. Bioinformatics 36(5):1614–1621. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz788
Levet F, Hosy E, Kechkar A, Butler C, Beghin A, Choquet D, Sibarita JB (2015) SR-Tesseler: a method to segment and quantify localization-based super-resolution microscopy data. Nat Methods 12(11):1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3579
Griffie J, Shannon M, Bromley CL, Boelen L, Burn GL, Williamson DJ, Heard NA, Cope AP, Owen DM, Rubin-Delanchy P (2016) A Bayesian cluster analysis method for single-molecule localization microscopy data. Nat Protoc 11(12):2499–2514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.149
Williamson DJ, Burn GL, Simoncelli S, Griffie J, Peters R, Davis DM, Owen DM (2020) Machine learning for cluster analysis of localization microscopy data. Nat Commun 11(1):1493. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15293-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Scalisi, S., Ahmad, A., D’Annunzio, S., Rousseau, D., Zippo, A. (2023). Quantitative Analysis of PcG-Associated Condensates by Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM). In: Lanzuolo, C., Marasca, F. (eds) Polycomb Group Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2655. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3143-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3143-0_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3142-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3143-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols