Abstract
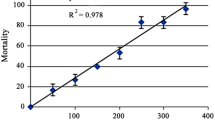
Cyantraniliprole can effectively control lepidopteran pests and has been used all over the world. In general, the risk of cyantraniliprole seems low for fish, but the toxicity selectivity among different fish species was not clear. Here, we present the methods for the acute toxicity and chronic effects of cyantraniliprole by using juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Based on this test, 96 h LC50 of cyantraniliprole to tilapia was 38.0 mg/L. After exposed for 28 days, specific growth rates of the blank control, solution control, and the treatments of 0.037, 0.37 and 3.7 mg/L of cyantraniliprole were 1.14, 0.95, 0.93, 0.82, and 0.70% per day, respectively. The results of micronucleus experiment and single cell gel electrophoresis showed that cyantraniliprole damaged DNA in liver cells of tilapia larvae. Quantitative PCR results showed that cyantraniliprole could induce the upregulation of Rpa 3 that is responsible for the DNA repair. The significant downregulation of Chk 2 gene was related to p53 pathway. It is therefore proposed that cyantraniliprole causes DNA damage in liver cells of tilapia and activates DNA damage and repair pathways.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parolini M, Magni S, Castiglioni S, Binelli A (2016) Genotoxic effects induced by the exposure to an environmental mixture of illicit drugs to the zebra mussel. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:26–30
Alleva R, Manzella N, Gaetani S, Ciarapica V, Bracci M, Caboni MF, Pasini F, Monaco F, Amati M, Borghi B, Tomasetti M (2016) Organic honey supplementation reverses pesticide-induced genotoxicity by modulating DNA damage response. Mol Nutr Food Res 60:2243–2255
Želježić D, Mladinić M, Žunec S, Lucić Vrdoljak A, Kašuba V, Tariba B, Živković T, Marjanović AM, Pavičić I, Milić M, Rozgaj R, Kopjar N (2016) Cytotoxic, genotoxic and biochemical markers of insecticide toxicity evaluated in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and an HepG2 cell line. Food Chem Toxicol 96:90–106
Li D, Huang Q, Lu M, Zhang L, Yang Z, Zong M, Tao L (2015) The organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos confers its genotoxic effects by inducing DNA damage and cell apoptosis. Chemosphere 135:387–393
Horibe A, Odashima S, Hamasuna N, Morita T, Hayashi M (2018) Weight of contribution of in vitro chromosomal aberration assay for evaluation of pesticides: experience of risk assessment at the food safety Commission of Japan. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 95:133–141
Yoshida M, McGregor D (2013) First draft prepared by Midori Yoshida1 and Douglas McGregor2 division of pathology. National Institute of Health Sciences, Tokyo, Japan
Wang M, Lu M (2016) Tilapia polyculture: a global review. Aquac Res 47:2363–2374
Chen L, Jiang X, Feng H, Shi H, Sun L, Tao W, ** Q, Wang D (2016) Simultaneous exposure to estrogen and androgen resulted in feminization and endocrine disruption. J Endocrinol 228:205–218
Stickney RR (1986) Tilapia tolerance of saline waters: a review. Prog Fish-Cult 48:161–167
Tiwari S, Stelinski LL (2013) Effects of cyantraniliprole, a novel anthranilic diamide insecticide, against Asian citrus psyllid under laboratory and field conditions. Pest Manag Sci 69:1066–1072
Moreno I, Belando A, Grávalos C, Bielza P (2018) Baseline susceptibility of Mediterranean strains of Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Westwood) to cyantraniliprole. Pest Manag Sci 74:1552–1557
Zhang R, Jang EB, He S, Chen J (2015) Lethal and sublethal effects of cyantraniliprole on Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Manag Sci 71:250–256
Xu C, Ding J, Zhao Y, Luo J, Mu W, Zhang Z (2017) Cyantraniliprole at sublethal dosages negatively affects the Development, reproduction, and nutrient utilization of Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J Econ Entomol 110:230–238
Zhang Z, Xu C, Ding J, Zhao Y, Lin J, Liu F, Mu W (2019) Cyantraniliprole seed treatment efficiency against Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and residue concentrations in corn plants and soil. Pest Manag Sci 75:1464–1472
Sharma AK, Zimmerman WT, Singles SK, Malekani K, Swain S, Ryan D, McQuorcodale G, Wardrope L (2014) Photolysis of chlorantraniliprole and cyantraniliprole in water and soil: verification of degradation pathways via kinetics modeling. J Agric Food Chem 62:6577–6584
Authority EFS (2014) Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance cyantraniliprole. EFSA Journal 12:3814
Lindahl T, Wood RD (1999) Quality control by. DNA Repair 286:1897–1905
Hayashi M (2016) The micronucleus test-most widely used in vivo genotoxicity test. Gene Environ 38:18
Glei M, Schneider T, Schlörmann W (2016) Comet assay: an essential tool in toxicological research. Arch Toxicol 90:2315–2336
Pei DS, Strauss PR (2013) Zebrafish as a model system to study DNA damage and repair. Mutat Res 743-744:151–159
Chen HY (2017) Hepatotoxicity of commonly used organophosphate flame retardants in Aebraflsh (Danio rerio) School of the Environment. Nan**g University, Nan**g, Jiangsu, China
Development, O. f. E. C.-o. a. (1992) Test no. 203: fish, acute toxicity test. OECD Guidel. Test. Chem. 1, 1e10 (10)
El-Harbawi M (2014) Toxicity measurement of imidazolium ionic liquids using acute toxicity test. Procedia Chem 9:40–52
Thomas P, Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2009) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Protoc 4:825–837
Lorenzo Y, Costa S, Collins AR, Azqueta A (2013) The comet assay, DNA damage, DNA repair and cytotoxicity: hedgehogs are not always dead. Mutagenesis 28:427–432
Jordon-Thaden IE, Chanderbali AS, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis DE (2015) Modified CTAB and TRIzol protocols improve RNA extraction from chemically complex Embryophyta. Appl Plant Sci 3:apps.1400105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Fan, Y., Xu, C., Miao, W. (2021). DNA Damage in Liver Cells of the Tilapia Fish Oreochromis mossambicus Larva Induced by the Insecticide Cyantraniliprole at Sublethal Doses During Chronic Exposure. In: Pan, X., Zhang, B. (eds) Environmental Toxicology and Toxicogenomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2326. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1514-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1514-0_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1513-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1514-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols