Abstract
Survival has been considered the cornerstone for clinical outcome evaluation in critically ill patients admitted to intensive care unit (ICU). There is evidence that ICU survivors commonly show impairments in long-term outcomes such as quality of life (QoL) considering them as the most relevant ones. In the last years, the concept of patient-important outcomes has been introduced and increasingly reported in peer-reviewed publications. In the present systematic review, we evaluated how many randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were conducted on critically ill patients and reporting a benefit on survival reported also data on QoL. All RCTs investigating nonsurgical interventions that significantly reduced mortality in critically ill patients were searched on MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus and Embase from inception until August 2021. In a second stage, for all the included studies, the outcome QoL was investigated. The primary outcome was to evaluate how many RCTs analyzing interventions reducing mortality reported also data on QoL. The secondary endpoint was to investigate if QoL resulted improved, worsened or not modified. Data on QoL were reported as evaluated outcome in 7 of the 239 studies (2.9%). The tools to evaluate QoL and QoL time points were heterogeneous. Four interventions showed a significant impact on QoL: Two interventions improved survival and QoL (pravastatin in subarachnoid hemorrhage, dexmedetomidine in elderly patients after noncardiac surgery), while two interventions reduced mortality but negatively influenced QoL (caloric restriction in patients with refeeding syndrome and systematic ICU admission in elderly patients). In conclusion, only a minority of RCTs in which an intervention demonstrated to affect mortality in critically ill patients reported also data on QoL. Future research in critical care should include patient-important outcomes like QoL besides mortality. Data on this topic should be collected in conformity with PROs statement and core outcome sets to guarantee quality and comparability of results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In the last 50 years, the number of patients admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) has increased [1, 2]. This is particularly true after the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic [3]. At the same time, new technologies and improvements in critical care have positively influenced survival after ICU admission [4,5,6].
Survival is easy and reliable to be collected, and it has been traditionally considered as the most important outcome to be improved in ICU, both by clinicians and by researchers [7]; accordingly, the identification and implementation of the interventions improving survival in ICU is a crucial task investigated in many randomized control trials (RCTs) and systematic reviews [8,9,10].
Recently, the concept of patient-important (or patient-centered) outcomes, including long-term quality of life (QoL), functional, cognitive and mental health outcomes, has been introduced, to consider patients’ feelings and values in a holistic and comprehensive perspective [7, 11,12,13]. Moreover, there is evidence that patients discharged from ICU consider survival as one of the less important outcomes, while physical, cognitive and mental outcomes and the ability to return to work are perceived as the most relevant [7, 13]. ICU survivors commonly show impaired QoL [14, 15], defined from World Health Organization as “individual perceptions of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns” [16, 17]. Patient-important outcomes in ICU survivors have been increasingly reported in peer-reviewed publications in the last years, even if using heterogeneous instruments [18]. In the present systematic review, we evaluated how many randomized controlled studies were conducted on critically ill patients and reporting a benefit on survival also reported data on the treatment effect on QoL.
Material and methods
In a first stage, all published RCTs investigating nonsurgical interventions that reduced mortality in critically ill patients were identified on MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus and Embase. There was no time limit, and the date of last update was August 31, 2021. The full MEDLINE/PubMed search strategy was already published [8, 9] and is available in the Additional files (Additional file 1). We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Metaanalyses (PRISMA) guidelines and PRISMA checklist is included in Additional file 1 (Additional Table 1).
Inclusion criteria for the selected papers were: (1) be published in a peer-reviewed journal, (2) be classifiable as RCT, (3) investigating nonsurgical interventions (drug, technique or strategy), (4) involve critically ill patients, and (5) interventions should significantly reduce mortality.
Exclusion criteria were: (1) not RCTs (observational studies, quasi-randomized studies), (2) nonsignificant reduction in mortality before statistical adjustments, or reduction only in subgroups, (3) classification as surgical procedure, and (4) intraoperative intervention.
The definition of “critically ill patient” was determined by the presence of acute failure of at least 1 organ, ICU admission, or emergent treatment.
Only landmark mortality (evaluated at a specific time point), obtained without adjustment for baseline characteristics, was considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
In a second stage, all the studies identified in the first stage were then screened by two independent reviewers to identify the presence of the outcome “quality of life,” according to the World Health Organization definition of QoL [16, 17].
Full-text articles were downloaded when the abstract lacked information and data on QoL were extracted in addition to those on mortality. The following data were collected: QoL p value, number of patients included in QoL analysis, QoL score or scale used, QoL time point, time frame and baseline, how QoL questionnaires were administered, and if the intervention of a proxy was admitted. Data were independently retrieved from the selected articles by two reviewers. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus or by a third reviewer.
Results
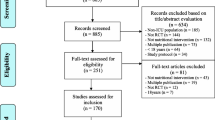
We identified 239 RCTs performed in critically ill patients reporting a statistically significant reduction in mortality. Among these, 18 studies reported data on QoL and were initially selected. After checking the full texts, 11 articles were excluded for inadequacy of the QoL scores used. Seven out of 239 (2.9%) RCTs were included in final analysis [19,20,21,22,23,24,25], with an overall population of 7,696 patients (Tables 1, 2). The whole process of study selection is described in Fig. 1. Five studies were multicenter [20,21,22,23, 25] and three were multinational [20, 22, 23]. The longest follow-up with significant effect on mortality differed between studies and ranged between 7 days and 2 years. The outcome “quality of life” was reported for 5396 patients. Other 2214 patients died, and 86 patients were lost to follow-up before data on QoL were collected.
The instruments used to assess QoL differed between included studies: Two studies used the Short Form 36 questionnaire (SF 36) [19, 20], one study used the Short Form 12 (SF 12) [21], one study used the World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF) [24], three studies applied Euro Quality of Life questionnaires in different forms: EQ 5D 5L, EQ VAS and EQ HUS [22, 23, 25]. One study treating severe stroke also used the specific Stroke Impact Scale in addition to the EQ VAS [22]. Only two of seven studies reported how the questionnaires were administered to patients: by telephone (one study) [24] or direct interview (one study) [19]. The longest follow-up for assessment of QoL was 3 months for two studies [20, 23], 6 months for three studies [19, 21, 25] and 3 years in one study [24]. In one study, the length of follow-up was not specified [22]. Patients’ baseline QoL was registered only in one study [25].
Four interventions showed a significant impact on QoL beside that on survival [19,20,21, 24]. Of these, two interventions consensually improved survival and QoL [19, 24], while two interventions reduced mortality but negatively influenced QoL [20, 21]. Three interventions did not significantly affect QoL [22, 23, 25]. Pravastatin in subarachnoid hemorrhage and dexmedetomidine in elderly patients admitted to the ICU after noncardiac surgery were effective both in reducing mortality and in improving QoL [19, 24]. Of the two interventions with opposite effects on survival and QoL, caloric restriction improved overall survival in patients with refeeding syndrome but had a negative effect on QoL in the general health domain of SF 36 questionnaire (p 0.014) [20]; the systematic ICU admission of elderly patients in place of usual triage improved survival but reduced QoL, specifically in mental aspects of QoL evaluated with SF 12 questionnaire (p < 0.01) [21].
Discussion
The present study is the first to evaluate the impact on QoL of the interventions which showed a significant effect on survival in critically ill patients. We found that: (1) only 7 (2.9%) studies assessed QoL among the 239 RCTs reporting a significant effect on survival; (2) interventions improving survival can have not only a positive or null but also a negative effect on QoL.
Our findings raise the ethical need to establish if the improvement in survival outweighs the negative effect on QoL. Ideally, the single patient should be the judge: Therapeutic decisions should be shared with every patient, or, when not feasible, with his/her family and loved ones, addressing the expected impact of interventions not only on survival but also on QoL.
ICU survivors suffer from medium- and long-term impairments in mental health, cognition and physical function, because of premorbid conditions, severity of the acute illness and complications associated with treatments during the ICU stay [13, 26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. Only in 2010, the set of all these impairments was defined “Post-Intensive Care Syndrome” [6, 34, 35]. Implications of PICS are multidimensional and touch not only patients but also caregivers and society [36]. For all these aspects described above, long-term QoL is compromised among ICU survivors when compared with general population [14, 15].
Recent publications established the importance of a “patient-centered” approach in evaluating the impact of critical illness, and the relevance of considering also “patient-oriented” outcomes (besides “disease-oriented” outcomes) when conducting or evaluating a study [37,38,39]. Despite this, Gaudry et al. (in a study not focused on RCTs in which a significant effect on survival was present, in contrast to our study) found that only 10% of 112 RCTs published in 2013 including critically ill patients recorded at least one QoL functional/cognitive/neurological outcome assessed after ICU discharge [12].
In a review on post-discharge ICU outcomes, Dinglas et al. [7] pointed out that the heterogeneity in outcomes assessment may represent a major limitation of research in this field, making difficult the comparison across studies and metanalyses. Several proposals have been published to standardize QoL score systems and time to follow up. In 2018, an evidence-based extension of the SPIRIT 2013 statement was published. The aim was to identify additional patient-reported outcomes (PRO) items recommended for inclusion in clinical trial protocols (extensions) and to adapt the existing SPIRIT 2013 statement specifically as applied to PROs [40]. Moreover, completed core outcome sets already exist for studies on critical illness, which include QoL evaluation [41]. Assessment of QoL requires a multidimensional approach that includes “individual’s perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, and standards” [16, 17]. As such, QoL assessment requires multiple measures to fully consider subjectivity and multidimensionality, and it is of paramount importance that only validated instruments such as SF-36 or EQ-5D are used [42]. Despite this, at present, great variety persists in studies analyzing QoL [39, 41, 43].
In our work, even if EQ 5D 5L and SF 36 were the mainly applied scores, other scores or variants of these two were used in 4 out of the 7 included studies [21,22,23,24]. In addition, there were a variety of different time points for the follow-up.
In the present systematic review, we found that only two interventions showed a significant positive influence on both survival and QoL: pravastatin in subarachnoid hemorrhage [19] and dexmedetomidine in ICU after noncardiac surgery in patients aged more than 65 years old [24]. At the same time, it is important to note that other interventions, in particular caloric restriction in patients with refeeding syndrome [20] and systematic ICU admission of elderly patients arriving to the emergency department [21], can improve survival after critical illness, but reduce QoL at, respectively, 3 and 6 months. These findings may be also attributable to the fact that more patients in the treatment groups survived and could be assessed at follow-up for longer periods. Moreover, in those two studies the observed statistically significant difference in QoL was limited to one single QoL domain (RAND-36 general health in Doig [20] and SF-12 mental component score in Guidet [21]) and it was not considered to reach the minimum clinically relevant difference by the authors.
Even if the interest on this topic is growing, our review shows that to the present day little information is available on QoL after ICU discharge and this information is difficult to interpret because of the absence of standardization of data collection in this field.
Several barriers can explain the very limited exploration of QoL in ICU survivors: Long-term follow-up of survivors requires human and logistical resources, increasing the costs of a study [12]. Lengthy questionnaires can be required, but they are time-consuming, and this often increases the percentage of non-respondents [12]. Moreover, cognitive and communication difficulties and the need for trained interviewers are further limitations to inclusion of long-term QoL data in studies [12, 44].
Nevertheless, our review suggests that patients’ priorities are fundamental in daily clinical practice and in choosing the appropriate treatments, as patients could refuse a treatment with the potential of improving survival but significantly worsening the QoL, eventually preferring a treatment aiming at improving the quality of dying [12]. Thus, future research in critical care should aim to investigate effects of interventions on QoL in conformity with PRO statement and core outcome sets [40, 41].
Our study has some limitations. First, the included studies were markedly heterogeneous in their background: Different numbers of centers and patients, methods of QoL assessment and particularly the use of a phone or direct interview questionnaires make hard to compare the results. Second, we excluded all the non-RCTs and all the RCTs with nonsignificant effect on mortality, and then we did not evaluate all the studies reporting positive or negative effects on QoL. Third, we focused on the outcome “quality of life” according to a precise definition [16, 17], excluding other long-term outcomes and patient-important outcomes. We aimed to restrict to an outcome which was multidimensional and directly connected with patients’ self-perception of life, because patient involvement was of primary interest in our study.
Conclusion
A minority of RCTs in which an intervention demonstrated to affect mortality in critically ill patients reported also data on QoL. Future research in critical care should include patient-important outcomes like QoL besides mortality. Data on this topic should be collected in conformity with PROs statement and core outcome sets to guarantee quality and comparability of results.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled trials
- PICS:
-
Post-intensive care syndrome
- SF-36 = RAND-36:
-
Short Form 36
- SF-12:
-
Short Form 12
- WHOQOL-BREF:
-
World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF
- EQ 5D 5L:
-
EuroQoL 5D 5L
- EQ VAS:
-
EuroQoL Visual Analogue Scale
- EQ HUS:
-
EuroQoL Health Utility Score
- SPIRIT:
-
Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials
- PROs:
-
Patient-reported outcomes
References
Halpern NA, Pastores SM. Critical care medicine in the United States 2000–2005: an analysis of bed numbers, occupancy rates, payer mix, and costs. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:65–71.
Zimmerman JE, Kramer AA, Knaus WA. Changes in hospital mortality for United States intensive care unit admissions from 1988 to 2012. Crit Care. 2013;17:R81.
Grasselli G, Greco M, Zanella A, Albano G, Antonelli M, Bellani G, et al.; COVID-19 Lombardy ICU Network. Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(10):1345–1355.
Spragg RG, Bernard GR, Checkley W, Curtis JR, Gajic O, Guyatt G, et al. Beyond mortality: future clinical research in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:1121–7.
Wunsch H, Linde-Zwirble WT, Angus DC, Hartman ME, Milbrandt EB, Kahn JM. The epidemiology of mechanical ventilation use in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:1947–53.
Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, Hopkins RO, Weinert C, Wunsch H, et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(2):502–9.
Dinglas VD, Faraone LN, Needham DM. Understanding patient-important outcomes after critical illness: a synthesis of recent qualitative, empirical, and consensus-related studies. CurrOpin Crit Care. 2018;24(5):401–9.
Sartini C, Lomivorotov V, Pieri M, Lopez-Delgado JC, Baiardo Redaelli M, Hajjar L, et al. A systematic review and international web-based survey of randomized controlled trials in the perioperative and critical care setting: interventions reducing mortality. J CardiothoracVascAnesth. 2019;33(5):1430–9.
Landoni G, Comis M, Conte M, Finco G, Mucchetti M, Paternoster G, et al. Mortality in multicenter critical care trials: an analysis of interventions with a significant effect. Crit Care Med. 2015;43(8):1559–68.
Baiardo Redaelli M, Landoni G, Di Sanzo S, Frassoni S, Sartini C, Cabrini L, et al. Interventions affecting mortality in critically ill and perioperative patients: a systematic review of contemporary trials. J Crit Care. 2017;41:107–11.
Weldring T, Smith SM. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs). Health Serv Insights. 2013;4(6):61–8.
Gaudry S, Messika J, Ricard JD, Guillo S, Pasquet B, Dubief E, et al. Patient-important outcomes in randomized controlled trials in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Ann Intensive Care. 2017;7(1):28.
Gajic O, Ahmad SR, Wilson ME, Kaufman DA. Outcomes of critical illness: what is meaningful? CurrOpin Crit Care. 2018;24:394–400.
Cuthbertson BH, Roughton S, Jenkinson D, Maclennan G, Vale L. Quality of life in the five years after intensive care: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2010;14:R6.
Dowdy DW, Eid MP, Sedrakyan A, Mendez-Tellez PA, Pronovost PJ, Herridge MS, Needham DM. Quality of life in adult survivors of critical illness: a systematic review of the literature. Intensive Care Med. 2005;31:611–20.
World Health Organization. WHOQOL Study Protocol (MNH/PSF/93.9). Geneva: WHO; 1993.
WHOQOL Group. Development of the WHO-QOL: rationale and current status. Int J Ment Health. 1994;23:24.
Turnbull AE, Rabiee A, Davis WE, Nasser MF, Venna VR, Lolitha R, et al. Outcome measurement in ICU. Survivorship research from 1970 to 2013: a sco** review of 425 publications. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:1267–77.
Tseng MY, Hutchinson PJ, Czosnyka M, Richards H, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ. Effects of acute pravastatin treatment on intensity of rescue therapy, length of inpatient stay, and 6-month outcome in patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2007;38(5):1545–50.
Doig GS, Simpson F, Heighes PT, Bellomo R, Chesher D, Caterson ID, et al.; Refeeding Syndrome Trial Investigators Group. Restricted versus continued standard caloric intake during the management of refeeding syndrome in critically ill adults: a randomised, parallel-group, multicentre, single-blind controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(12):943–52
Guidet B, Leblanc G, Simon T, Woimant M, Quenot JP, Ganansia O, et al.; ICE-CUB 2 Study Network. Effect of systematic Intensive Care Unit triage on long-term mortality among critically ill elderly patients in France: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(15):1450–9
Hanley DF, Lane K, McBee N, Ziai W, Tuhrim S, Lees KR, et al.; CLEAR III Investigators. Thrombolytic removal of intraventricular haemorrhage in treatment of severe stroke: results of the randomised, multicentre, multiregion, placebo controlled CLEAR III trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):603–11.
Sprigg N, Flaherty K, Appleton JP, Al-Shahi Salman R, Bereczki D, Beridze M, et al.; TICH-2 Investigators. Tranexamic acid for hyperacute primary Intra Cerebral Haemorrhage (TICH-2): an international randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 superiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10135):2107–15.
Zhang DF, Su X, Meng ZT, Li HL, Wang DX, Li X-Y, et al. Impact of dexmedetomidine on long-term outcomes after noncardiac surgery in elderly: 3-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2019;270(2):356–63.
Parke RL, Gilder E, Gillham MJ, Walker LJC, Bailey MJ, McGuinness SP; Fluids After Bypass Study Investigators. A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial of a conservative fluid management strategy compared with usual care in participants after cardiac surgery: the fluids after bypass study. Crit Care Med. 2021;49(3):449–61.
Robinson KA, Davis WE, Dinglas VD, Mendez-Tellez PA, Rabiee A, Sukrithan V, et al. A systematic review finds limited data on measurement properties of instruments measuring outcomes in adult intensive care unit survivors. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;82:37–46.
Prescott HC, Iwashyna TJ, Blackwood B, Calandra T, Chlan LL, Choong K, et al. Understanding and enhancing sepsis survivorship. Priorities for research and practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:972–81.
Pfoh ER, Wozniak AW, Colantuoni E, Dinglas VD, Mendez-Tellez PA, Shanholtz C, et al. Physical declines occurring after hospital discharge in ARDS survivors: a 5-year longitudinal study. IntensiveCare Med. 2016;42:1557–66.
Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matte A, Tomlinson G, Diaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1293–304.
Fan E, Dowdy DW, Colantuoni E, Mendez-Tellez PA, Sevransky JE, Shanholtz C, et al. Physical complications in acute lung injury survivors: a two-year longitudinal prospective study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:849–59.
Nikayin S, Rabiee A, Hashem MD, Huang M, Bienvenu OJ, Turnbull AE, Needham DM. Anxiety symptoms in survivors of critical illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2016;43:23–9.
Parker AM, Sricharoenchai T, Raparla S, Schneck KW, Bienvenu OJ, Needham DM. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in critical illness survivors: a meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:1121–9.
Rabiee A, Nikayin S, Hashem MD, Huang M, Dinglas VD, Bienvenu OJ, et al. Depressive symptoms after critical illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:1744–53.
Morgan A. Long-term outcomes from critical care. Surgery (Oxf). 2021;39(1):53–7.
Fontela PC, Abdala FANB, Forgiarini SGI, Forgiarini LA Jr. Quality of life in survivors after a period of hospitalization in the intensive care unit: a systematic review. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):496–507.
Griffiths J, Hatch RA, Bishop J, Morgan K, Jenkinson C, Cuthbertson BH, Brett SJ. An exploration of social and economic outcome and associated health-related quality of life after critical illness in general intensive care unit survivors: a 12- month follow-up study. Crit Care. 2013;17:R100.
Rylander C. Historic review of long-term outcomes research. CurrOpin Crit Care. 2019;25(5):523–9.
Hashem MD, Nallagangula A, Nalamalapu S, Nunna K, Nausran U, Robinson KA, et al. Patient outcomes after critical illness: a systematic review of qualitative studies following hospital discharge. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):345.
de Grooth HJ, Parienti JJ, Oudemans-van Straaten HM. Should we rely on trials with disease- rather than patient-oriented endpoints? Intensive Care Med. 2018;44(4):464–6.
Calvert M, Kyte D, Mercieca-Bebber R, Slade A, Chan AW, King MT, et al. Guidelines for inclusion of patient-reported outcomes in clinical trial protocols: the SPIRIT-PRO extension. JAMA. 2018;319(5):483–94.
Dinglas VD, Cherukuri SPS, Needham DM. Core outcomes sets for studies evaluating critical illness and patient recovery. CurrOpin Crit Care. 2020;26(5):489–549.
Pequeno NPF, Cabral NLA, Marchioni DM, Lima SCVC, Lyra CO. Quality of life assessment instruments for adults: a systematic review of population-based studies. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):208.
Spies CD, Krampe H, Paul N, Denke C, Kiselev J, Piper SK, et al. Instruments to measure outcomes of post-intensive care syndrome in outpatient care settings—results of an expert consensus and feasibility field test. J Intensive Care Soc. 2021;22(2):159–74.
Wysham NG, Abernethy AP, Cox CE. Setting the vision: applied patient reported outcomes and smart, connected digital healthcare systems to improve patient-centered outcomes prediction in critical illness. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014;20(5):566–72.
Funding
The study was supported by departmental funds only.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GL, CM, NM and CS searched electronically for pertinent studies from inception until August 31, 2021, supervised by LC and AZ. OP and AO selected studies for the QoL analysis, extracted data into standardized collection forms and created tables for the evidence and outcomes. Discrepancies were resolved, and the whole process was supervised by LC, PP and NL. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
. Additional File 1 - Search string. Additional Table 1 - PRISMA 2020 Checklist
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Pallanch, O., Ortalda, A., Pelosi, P. et al. Effects on health-related quality of life of interventions affecting survival in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Crit Care 26, 126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-022-03993-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-022-03993-3