Abstract
This review focuses on mechanical ventilation strategies that allow unsupported spontaneous breathing activity in any phase of the ventilatory cycle. By allowing patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome to breathe spontaneously, one can expect improvements in gas exchange and systemic blood flow, based on findings from both experimental and clinical trials. In addition, by increasing end-expiratory lung volume, as occurs when using biphasic positive airway pressure or airway pressure release ventilation, recruitment of collapsed or consolidated lung is likely to occur, especially in juxtadiaphragmatic lung legions. Traditional approaches to mechanical ventilatory support of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome require adaptation of the patient to the mechanical ventilator using heavy sedation and even muscle relaxation. Recent investigations have questioned the utility of sedation, muscle paralysis and mechanical control of ventilation. Furthermore, evidence exists that lowering sedation levels will decrease the duration of mechanical ventilatory support, length of stay in the intensive care unit, and overall costs of hospitalization. Based on currently available data, we suggest considering the use of techniques of mechanical ventilatory support that maintain, rather than suppress, spontaneous ventilatory effort, especially in patients with severe pulmonary dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Partial ventilatory support is commonly used, not only to wean patients from mechanical ventilation but also to provide stable ventilatory assistance to a desired degree. Conventional partial ventilatory support modalities either provide ventilatory assistance to every inspiratory effort and modulate the tidal volume (VT) of the patient (e.g. pressure support ventilation [PSV] [1] and pressure assisted ventilation [2]) or modulate minute ventilation by periodically adding mechanical insufflations to unsupported spontaneous breathing (e.g. intermittent mandatory ventilation [IMV] [3]). In contrast, biphasic positive airway pressure (BiPAP) [4] and airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) [5] allow unrestricted spontaneous breathing in any phase of the mechanical cycle.
The principles of airway pressure release ventilation and biphasic positive airway pressure
APRV and BiPAP ventilate by time-cycled switching between two pressure levels in a high flow or demand valve continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) circuit, and therefore they allow unrestricted spontaneous breathing in any phase of the mechanical ventilator cycle [4, 5]. The degree of ventilatory support is determined by the duration of both CPAP levels and VT during APRV/BiPAP [4, 5]. VT depends mainly on respiratory compliance and the difference between the CPAP levels. BiPAP is identical to APRV except that no restrictions are imposed on the duration of the low CPAP level (release pressure) [5]. Based on the initial description, APRV uses a duration of low CPAP (release time) that is equal to or less than 1.5 s.
Asynchronous interference between spontaneous and mechanical ventilation may increase the work of breathing and reduce effective ventilatory support during APRV/BiPAP [6]. Synchronization of switching between the two CPAP levels to spontaneous inspiration or expiration has been incorporated into commercially available demand valve APRV/BiPAP circuits in order to avoid asynchronous interference between spontaneous and mechanical breaths. Because patient triggered mechanical cycles during IMV have not been demonstrated to be advantageous for the patient, there is no reason why this should be different for APRV/BiPAP [6]. When spontaneous breathing is absent, APRV/BiPAP is not different from conventional pressure controlled, time cycled mechanical ventilation (PCV) [4, 5].
Commercially available ventilators frequently offer combinations of APRV/BiPAP with PSV or automatic tube compensation (ATC). Only the combination of APRV/BiPAP with ATC in order to compensate for the resistance of the endotracheal tube, at least partly, has been shown to confer benefit in treatment of selected patients [7]. However, the observed decrease in inspiratory muscle load was associated with higher pressure support levels when adding ATC during APRV/BiPAP. In contrast, it remains doubtful whether the positive effects of different modalities of ventilation are additive when they are simply combined [8]. Thus, it cannot be ruled out that proven physiological effects of unassisted spontaneous breathing during APRV/BiPAP may be attenuated or even eliminated when each detected spontaneous breathing effort is assisted with PSV during APRV/BiPAP.
Setting ventilation pressures and tidal volumes during airway pressure release ventilation/biphasic positive airway pressure
Mechanical ventilation with positive end-expiratory airway pressure titrated above the lower inflection pressure of a static pressure–volume curve and low VT has been suggested to prevent tidal alveolar collapse at end-expiration and overdistension of lung units at end-inspiration during acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [9]. This lung protective ventilatory strategy has been found to improve lung compliance, venous admixture, and arterial oxygen tension without causing cardiovascular impairment in ARDS [9]. Mechanical ventilation using a VT of not more than 6 ml/kg ideal body weight has been shown to improve outcome in patients with ARDS [9, 10]. Based on these results, CPAP levels during APRV/BiPAP should be titrated to prevent end-expiratory alveolar collapse and tidal alveolar overdistension [9, 10]. When CPAP levels during APRV/BiPAP were adjusted according to a lung protective ventilatory strategy, the occurrence of spontaneous breathing improved cardiorespiratory function without affecting total oxygen consumption because of the work of breathing in patients with ARDS [11].
Moreover, pulmonary compliance in this range of airway pressures should be greatest, thus reducing the transpulmonary pressure required for normal tidal breathing and hence reducing the elastic work of breathing [12]. Because APRV and BiPAP do not provide ventilatory assistance to every inspiratory effort, the use of proper CPAP levels is required to allow efficient ventilation with minimal work of breathing during unsupported spontaneous breaths.
Analgesia and sedation during airway pressure release ventilation/biphasic positive airway pressure
Apart from ensuring sufficient pain relief and anxiolysis, analgesia and sedation are used to adapt the patient to mechanical ventilation [13, 14]. The level of analgesia and sedation required during controlled mechanical ventilation (CMV) is equivalent to a Ramsay score of between 4 and 5 (i.e. a deeply sedated patient who is unable to respond when spoken to and has no sensation of pain). During partial ventilatory support a Ramsay score between 2 and 3 can be targeted (i.e. an awake, responsive and cooperative patient). In a study conducted in about 600 post-cardiac-surgery patients [15] and in another study of patients with multiple injuries [16], maintaining spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP led to significantly lower consumption of analgesics and sedatives as compared with the initial use of CMV followed by weaning with partial ventilatory support. Clearly, the higher doses of analgesics and sedatives used exclusively to adapt patients to CMV required higher doses of vasopressors and positive inotropes to maintain stability of cardiovascular function [16].
Benefits of maintained spontaneous breathing during airway pressure release ventilation/biphasic positive airway pressure
Pulmonary gas exchange
Computed tomography (CT) of patients with ARDS has been used to identify radiographic densities corresponding to alveolar collapse that is localized primarily in the dependent lung regions, correlating with intrapulmonary shunting [17]. Formation of radiographic densities has been attributed to alveolar collapse caused by superimposed pressure on the lung and a cephalad shift of the diaphragm that is most evident in dependent lung areas during mechanical ventilation [18]. Persisting spontaneous breathing has been considered to improve the distribution of ventilation to dependent lung areas and thereby ventilation/perfusion (VA/Q) matching, presumably by diaphragmatic contraction opposing alveolar compression [11, 19]. This concept is supported by CT observations in anaesthetized patients demonstrating that contractions in the diaphragm induced by phrenic nerve stimulation favour distribution of ventilation to dependent, well perfused lung areas and decrease atelectasis formation [20].
Spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP in experimentally induced lung injury was associated with less atelectasis formation in end-expiratory spiral CT of the whole lungs and in scans above the diaphragm (Fig. 1) [21]. Although other inspiratory muscles may also contribute to improvement in aeration during spontaneous breathing, the craniocaudal gradient in aeration, aeration differences, and the marked differences in aeration in regions close to the diaphragm between APRV/BiPAP with and without spontaneous breathing suggest a predominant role played by diaphragmatic contractions in the observed aeration differences [21]. These experimental findings are supported by observations using electro-impedance tomography to estimate regional ventilation in patients with ARDS, which demonstrated better ventilation in dependent regions during spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP (Fig. 2). Experimental data suggest that recruitment of dependent lung areas may be caused essentially by an increase in transpulmonary pressure due to the decrease in pleural pressure with spontaneous breathing during APRV/BiPAP [22].
Electro-impedance tomography used to estimate regional ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome during continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)/biphasic positive airway pressure (BiPAP) with and without spontaneous breathing. Spontaneous breathing with CPAP is associated with better ventilation in the dependent well perfused lung regions. Spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP is associated with better ventilation in the dependent well perfused lung regions and the anterior lung areas. When spontaneous breathing during APRV/BiPAP is abolished, mechanical ventilation is directed entirely to the less well perfused, nondependent anterior lung areas. PCV, pressure-controlled ventilation.
In patients with ARDS, APRV/BiPAP with spontaneous breathing of 10–30% of the total minute ventilation accounted for an improvement in VA/Q matching and arterial oxygenation (Fig. 3) [11]. Increase in arterial oxygenation in conjunction with greater pulmonary compliance indicates recruitment of previously nonventilated lung areas. Clinical studies in patients with ARDS show that spontaneous breathing during APRV/BiPAP does not necessarily lead to instant improvement in gas exchange, but rather to a continuous improvement in oxygenation over 24 hours after the start of spontaneous breathing [23].
Spontaneous breathing during airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)/biphasic positive airway pressure (BiPAP) accounted for a decrease in blood flow to shunt units (ventilation/perfusion [VA/Q] < 0.005) and an increase in perfusion of normal VA/Q units (0.1 < VA/Q < 10), without creating low VA/Q areas (0.05 < VA/Q < 0.1). Pressure support ventilation had no effect on pulmonary blood flow distribution when compared with controlled mechanical ventilation (APRV/BiPAP without spontaneous breathing).
Assisted inspiration with PSV did not produce significant improvement in intrapulmonary shunt, VA/Q matching, or gas exchange when compared with CMV in a previous study [11]. This is in agreement with observations demonstrating comparable gas exchange in patients with acute lung injury during CMV and PSV [24]. Apparently, spontaneous contribution on a mechanically assisted breath was not sufficient to counteract VA/Q maldistribution of positive pressure lung insufflations. One possible explanation might be that inspiration is terminated by the decrease in gas flow at the end of inspiration during PSV [1], which may reduce ventilation in areas of the lung with a slow time constant.
In patients at risk for develo** ARDS, maintained spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP resulted in lower venous admixture and better arterial blood oxygenation over an observation period of more than 10 days as compared with CMV with subsequent weaning [16]. These findings show that, even in patients requiring ventilatory support, maintained spontaneous breathing can counteract progressive deterioration in pulmonary gas exchange.
Cardiovascular effects
Positive pressure ventilation increases intrathoracic pressure, which in turn reduces venous return to the heart [25]. In normovolaemic and hypovolaemic patients, this produces reduction in right and left ventricular filling and results in decreased stroke volume, cardiac output and oxygen delivery (DO2). Reducing mechanical ventilation to a level that provides adequate support for existing spontaneous breathing should help to reduce the cardiovascular side effects of ventilatory support [26]. This concept is supported by studies of anaesthetized animals with haemorrhagic shock, which demonstrated that contractions of the diaphragm induced by phrenic nerve stimulation favour preload and cardiac output [27].
A transient decrease in intrathoracic pressure resulting from maintained spontaneous breathing of 10–40% of total minute ventilation during APRV/BiPAP promotes venous return to the heart and right and left ventricular filling, thereby increasing cardiac output and DO2 [11]. Simultaneous elevations in right ventricular end-diastolic volume and cardiac index occurred during spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP, which indicates improved venous return to the heart [11]. In addition, outflow from the right ventricle, which depends mainly on lung volume, may benefit from a decrease in intrathoracic pressure during APRV/BiPAP. Ventilatory support of each individual inspiration with PSV at identical airway pressures produces no or a small increase in cardiac index [11]. The increase in cardiac index observed during PSV as compared with CMV was primarily a function of the pressure support level. This indicates that during assisted inspiration with PSV spontaneous respiratory activity may not decrease intrathoracic pressures sufficiently to counteract the cardiovascular depression of positive airway pressure. Räsänen and coworkers [28] observed no decrease in cardiac output and tissue DO2 by switching from CPAP to spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP. In contrast, similar ventilatory support with CMV reduced the stroke volume and DO2.
Theoretically, augmentation of the venous return to the heart and increased left ventricular afterload as a result of an intermittent decrease in intrathoracic pressure during APRV/BiPAP should have a negative impact on cardiovascular function in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Provided that spontaneous breathing receives adequate support and sufficient CPAP levels are applied, maintenance of spontaneous breathing during APRV/BiPAP should not prove disadvantageous and is not per se contraindicated in patients with ventricular dysfunction [29–31].
Oxygen supply and demand balance
The concomitant increase in cardiac index and arterial oxygen tension during APRV/BiPAP improved the relationship between tissue oxygen supply and demand because oxygen consumption remained unchanged despite the work of spontaneous breathing (Fig. 4). In accordance with previous experimental [32] and clinical findings [11, 33], total oxygen consumption is not measurably altered by adequately supported spontaneous breathing in patients with low lung compliance during APRV/BiPAP.
Oxygen consumption plotted against oxygen delivery during airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)/biphasic positive airway pressure (BiPAP) with and without spontaneous breathing and during inspiratory assistance with pressure support ventilation (PSV). Oxygen consumption was determined by indirect calorimetry. Bars indicate standard deviation.
Organ perfusion
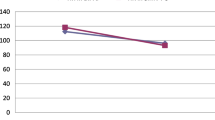
By reducing cardiac index and venous return to the heart, mechanical ventilation can have a negative effect on the perfusion and functioning of extrathoracic organ systems. Increase in venous return and cardiac index, caused by the periodic fall in intrathoracic pressure during spontaneous inspiration, should significantly improve organ perfusion and function during partial ventilatory support. In patients with ARDS, spontaneous breathing with IMV leads to an increase in glomerular filtration rate and sodium excretion [34]. This has also been documented during spontaneous breathing with APRV/BiPAP [35] (Fig. 5). Thus, maintained spontaneous breathing may be favourable with respect to the perfusion and function of the kidney in patients requiring ventilatory support because of severe pulmonary dysfunction.
Urine volume (Uvol), effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) during airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) with and without spontaneous breathing (SB). During APRV without SB, airway pressure was adjusted to produce equal minute ventilation (VE; normocapnia) while APRV without spontaneous breathing was administered with equal airway pressure limits (Paw; permissive hypercapnia). Vertical bars indicate standard deviation.
Preliminary data in patients requiring ventilatory support for acute lung injury suggest that maintained spontaneous breathing may be beneficial for liver function. These clinical data are supported by experiments in which coloured microspheres were used in pigs with oleic acid induced lung injury [36]; improved perfusion of the splanchnic area was demonstrated.
Conclusion
Development in mechanical ventilatory support has produced techniques that allow unrestricted breathing throughout mechanical ventilation. Investigations demonstrate that uncoupling of even minimal spontaneous and mechanical breaths during BiPAP/APRV contributes to improved pulmonary gas exchange, systemic blood flow and oxygen supply to the tissue. This is reflected by clinical improvement in the patient's condition, which is associated with significantly fewer days on ventilatory support, earlier extubation and a shorter stay in the intensive care unit [16].
Abbreviations
- APRV:
-
airway pressure release ventilation
- ARDS:
-
acute respiratory distress syndrome
- ATC:
-
automatic tube compensation
- BiPAP:
-
biphasic positive airway pressure
- CMV:
-
controlled mechanical ventilation
- CPAP:
-
continuous positive airway pressure
- CT:
-
computed tomography
- DO2:
-
oxygen delivery
- IMV:
-
intermittent mandatory ventilation
- PSV:
-
pressure support ventilation
- VA/Q:
-
ventilation/perfusion
- VT:
-
tidal volume.
References
Hansen J, Wendt M, Lawin P: A new weaning procedure (inspiratory flow assistance). Anaesthesist 1984, 33: 428-432.
Younes M: Proportional assist ventilation, a new approach to ventilatory support. Theory. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992, 145: 114-120.
Downs JB, Klein EF Jr, Desautels D, Modell JH, Kirby RR: Intermittent mandatory ventilation: a new approach to weaning patients from mechanical ventilators. Chest 1973, 64: 331-335.
Baum M, Benzer H, Putensen C, Koller W: Biphasic positive airway pressure (BIPAP): a new form of augmented ventilation. Anaesthesist 1989, 38: 452-458.
Stock MC, Downs JB: Airway pressure release ventilation. Crit Care Med 1987, 15: 462-466.
Putensen C, Leon MA, Putensen-Himmer G: Timing of pressure release affects power of breathing and minute ventilation during airway pressure release ventilation. Crit Care Med 1994, 22: 872-878.
Wrigge H, Zinserling J, Hering R, Schwalfenberg N, Stuber F, von Spiegel T, Schroeder S, Hedenstierna G, Putensen C: Cardiorespiratory effects of automatic tube compensation during airway pressure release ventilation in patients with acute lung injury. Anesthesiology 2001, 95: 382-389. 10.1097/00000542-200108000-00020
Räsänen J: IMPRV: synchronized APRV, or more? Intensive Care Med 1992, 18: 65-66.
Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D, Munoz C, Oliveira R, et al.: Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 1998, 338: 347-354. 10.1056/NEJM199802053380602
ARDS network: Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med 2000, 342: 1301-1308. 10.1056/NEJM200005043421801
Putensen C, Mutz NJ, Putensen-Himmer G, Zinserling J: Spontaneous breathing during ventilatory support improves ventilation-perfusion distributions in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999, 159: 1241-1248.
Katz JA, Marks JD: Inspiratory work with and without continuous positive airway pressure in patients with acute respiratory failure. Anesthesiology 1985, 63: 598-607.
Wheeler AP: Sedation, analgesia, and paralysis in the intensive care unit. Chest 1993, 104: 566-577.
Burchardi H, Rathgeber J, Sydow M: The concept of analgosedation depends on the concept of mechanical ventilation. In Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine (Edited by: Vincent JL). Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag 1995, 155-164.
Rathgeber J, Schorn B, Falk V, Kazmaier S, Spiegel T: The influence of controlled mandatory ventilation (CMV), intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV) and biphasic intermittent positive airway pressure (BIPAP) on duration of intubation and consumption of analgesics and sedatives. A prospective analysis in 596 patients following adult cardiac surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1997, 14: 576-582. 10.1046/j.1365-2346.1997.00108.x
Putensen C, Zech S, Wrigge H, Zinserling J, Stüber F, von Spiegel T, Mutz N: Long-term effects of spontaneous breathing during ventilatory support in patients with acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001, 164: 43-49.
Gattinoni L, Presenti A, Torresin A, Baglioni S, Rivolta M, Rossi F, Scarani F, Marcolin R, Cappelletti G: Adult respiratory distress syndrome profiles by.computed tomography. J Thorac Imaging 1986, 1: 25-30.
Puybasset L, Cluzel P, Chao N, Slutsky AS, Coriat P, Rouby JJ: A computed tomography scan assessment of regional lung volume in acute lung injury. The CT Scan ARDS Study Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998, 158: 1644-1655.
Froese AB, Bryan AC: Effects of anesthesia and paralysis on diaphragmatic mechanics in man. Anesthesiology 1974, 41: 242-255.
Hedenstierna G, Tokics L, Lundquist H, Andersson T, Strandberg A: Phrenic nerve stimulation during halothane anesthesia. Effects of atelectasis. Anesthesiology 1994, 80: 751-760.
Wrigge H, Zinserling J, Neumann P, Defosse J, Magnusson A, Putensen C, Hedenstierna G: Spontaneous breathing improves lung aeration in oleic acid-induced lung injury. Anesthesiology 2003, 99: 376-384. 10.1097/00000542-200308000-00019
Henzler D, Dembinski R, Bensberg R, Hochhausen N, Rossaint R, Kuhlen R: Ventilation with biphasic positive airway pressure in experimental lung injury: influence of transpulmonary pressure on gas exchange and haemodynamics. Intensive Care Med 2004, 30: 935-943. 10.1007/s00134-003-2146-8
Sydow M, Burchardi H, Ephraim E, Zielmann S: Long-term effects of two different ventilatory modes on oxygenation in acute lung injury. Comparison of airway pressure release ventilation and volume-controlled inverse ratio ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994, 149: 1550-1556.
Cereda M, Foti G, Marcora B, Gili M, Giacomini M, Sparacino ME, Pesenti A: Pressure support ventilation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 2000, 28: 1269-1275. 10.1097/00003246-200005000-00002
Pinsky MR: Determinants of pulmonary arterial flow variation during respiration. J Appl Physiol 1984, 56: 1237-1245. 10.1063/1.334058
Kirby RR, Perry JC, Calderwood HW, Ruiz BC: Cardiorespiratory effects of high positive.end-expiratory pressure. Anesthesiology 1975, 43: 533-539.
Samniah N, Voelckel WG, Zielinski TM, McKnite S, Patterson R, Benditt DG, Lurie KG: Feasibility and effects of transcutaneous phrenic nerve stimulation combined with an inspiratory impedance threshold in a pig model of hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med 2003, 31: 1197-1202. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000059727.50443.97
Räsänen J, Downs JB: Cardiovascular effects of conventional positive.pressure ventilation and airway pressure release ventilation. Chest 1988, 93: 911-915.
Räsänen J, Heikkila J, Downs J, Nikki P, Vaisanen I, Viitanen A: Continuous positive airway pressure by face mask in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Am J Cardiol 1985, 55: 296-300. 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90364-9
Nikki P, Tahvanainen J, Räsänen J, Makelainen A: Ventilatory pattern in respiratory failure arising from acute myocardial infarction. II. PtcO2 and PtcCO2 compared to Pao2 and PaCO2 during IMV4 vs IPPV12 and PEEP0 vs PEEP10. Crit Care Med 1982, 10: 79-81.
Räsänen J, Nikki P: Respiratory failure arising from acute myocardial infarction. Ann Chir Gynaecol Suppl 1982, 196: 43-47.
Putensen C, Räsänen J, Lopez FA: Effect of interfacing between spontaneous breathing and mechanical cycles on the ventilation-perfusion distribution in canine lung injury. Anesthesiology 1994, 81: 921-930.
Staudinger T, Kordova H, Roggla M, Tesinsky P, Locker GJ, Laczika K, Knapp S, Frass M: Comparison of oxygen cost of breathing with pressure-support ventilation and biphasic intermittent positive airway pressure ventilation. Crit Care Med 1998, 26: 1518-1522. 10.1097/00003246-199809000-00018
Steinhoff H, Falke K, Schwarzhoff W: Enhanced renal function associated with intermittent mandatory ventilation in acute respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med 1982, 8: 69-74.
Hering R, Peters D, Zinserling J, Wrigge H, von Spiegel T, Putensen C: Effects of spontaneous breathing during airway pressure release ventilation on renal perfusion and function in patients with acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med 2002, 28: 1426-1433. 10.1007/s00134-002-1442-z
Hering R, Viehofer A, Zinserling J, Wrigge H, Kreyer S, Berg A, Minor T, Putensen C: Effects of spontaneous breathing during airway pressure release ventilation on intestinal blood flow in experimental lung injury. Anesthesiology 2003, 99: 1137-1144. 10.1097/00000542-200311000-00021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None declared.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Putensen, C., Wrigge, H. Clinical review: Biphasic positive airway pressure and airway pressure release ventilation. Crit Care 8, 492 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2919
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2919