Abstract
Background
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) is an important pathogen in swine and is responsible for substantial economic losses. Previous studies suggest that the PEDV E protein plays an important role in the viral assembly process. However, the subcellular localization and other functions of PEDV E protein still require more research.
Methods
The subcellular localization and function of PEDV E protein were investigated by examining its effects on cell growth, cell cycle progression, interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression and cell survival.
Results
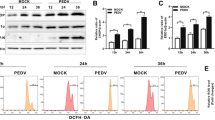
The results show that plenty of PEDV E protein is localized in the ER, with small quantities localized in the nucleus. The PEDV E protein has no effect on the intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) growth, cell cycle and cyclin A expression. The cells expressing PEDV E protein express higher levels of IL-8 than control cells. Further studies show that PEDV E protein induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activated NF-κB which is responsible for the up-regulation of IL-8 and Bcl-2 expression.
Conclusions
This study shows that the PEDV E protein is localized in the ER and the nucleus and it can cause ER stress. The PEDV E protein had no effect on the IEC growth and cell cycle. In addition, the PEDV E protein is able to up-regulate IL-8 and Bcl-2 expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) is an acute and highly contagious enteric disease of swine characterized by severe enteritis, vomiting, and watery diarrhea and results in high mortality in piglets [1]. The causative agent belonging to the family Coronaviridae is porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), which is first reported by Pensaert and DeBouck in Belgium and the United Kingdom [2, 3]. PED is currently a source of concern in Asia countries, where outbreaks are often more acute and severe than those observed in Europe [4]. PED is one of the most important diseases incurring economic loss in many swine-raising countries, mainly due to its high prevalence, compared to the rare incidence of transmissible gastroenteritis (TGE) and the asymptomatic characteristics of the Rotavirus (RV) infections [3, 5]. PEDV is an enveloped virus possessing an approximately 28 kb, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome with a 5’ cap and a 3’ polyadenylated tail [4, 36].
Detection of NF-κB activity
To determine the alteration of NF-κB activity by GFP and GFP-E proteins in the established cell lines, the level of NF-κB activity was measured using western blot assay and the NF-κB p65 TransAM kit (Active Motif) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells nuclear extraction was prepared by using the Nuclear Extract Kit (KeyGEN, Nan**g, China) and protein concentrations were measured using the BCA Protein Assay Reagent (Pierce, Rockford, IL, US). Lysates (50 μg total proteins) were incubated in ELISA wells coated with the oligo-nucleotide motif recognized by active p65, then detected using a specific antibody against p65, followed by a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody. The colorimetric reaction was measured at 450 nm. This experiment was repeated three times.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The stable PEDV E gene expressing cells and the control cells were seeded in 24-well plates at a density of 1 × 105 cells/ml in DMEM with 10% new born calf serum (NCS) and cultured for 48 h. In some experiments, MG132 previously found to block IL-8 expression was added after 24 h [37]. The culture medium was then collected and centrifuged in a microcentrifuge at 1, 000 × g for 5 min to remove debris, the supernatants were then frozen at −80°C until analysed. The concentrations of IL-8 were measured using a swine IL-8 ELISA kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen, USA).
Statistical analysis
Data are shown as the means ± SD of three independent experiments done in triplicate. For each assay, student’s t-test was used for statistical comparison. A value of P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Authors’ information
Dr. De-Wen Tong, professor of College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University, Vice Dean of College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University. Dr. Hung-Jen Liu, professor of Institute of Molecular Biology, National Chung Hsing University. Dr. **n-Gang Xu and Dr. Yong Huang are associate professors of College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University. Honglei Zhang, graduate students of College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University.
References
Ducatelle R, Coussement W, Pensaert MB, Debouck P, Hoorens J: In vivo morphogenesis of a new porcine enteric coronavirus, CV 777. Arch Virol 1981, 68: 35-44. 10.1007/BF01315165
Pensaert MB, de Bouck P: A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch Virol 1978, 58: 243-247. 10.1007/BF01317606
Hou X-L, Yu L-Y, Liu J: Development and evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant nucleocapsid protein for detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea (PEDV) antibodies. Vet Microbiol 2007, 123: 86-92. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.02.014
Song D, Park B: Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: a comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines. Virus Genes 2012, 44: 167-175. 10.1007/s11262-012-0713-1
Carvajal A, Lanza I, Diego R, Rubio P, Camenes P: Evaluation of a blocking ELISA using monoclonal antibodies for the detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and its antibodies. J Vet Diagn Invest 1995, 7: 60-64. 10.1177/104063879500700109
Wang K, Lu W, Chen J, **e S, Shi H, Hsu H, Yu W, Xu K, Bian C, Fischer WB, et al.: PEDV ORF3 encodes an ion channel protein and regulates virus production. FEBS Lett 2012, 586: 384-391. 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.005
Egberink HF, Ederveen J, Callebaut P, Horzinek MC: Characterization of the structural proteins of porcine epizootic diarrhea virus, strain CV777. Am J Vet Res 1988, 49: 1320-1324.
Bridgen A, Kocherhans R, Tobler K, Carvajal A, Ackermann M: Further analysis of the genome of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus. Adv Exp Med Biol 1998, 440: 781-786.
Kocherhans R, Bridgen A, Ackermann M, Tobler K: Completion of the porcine epidemic diarrhoea coronavirus (PEDV) genome sequence. Virus Genes 2001, 23: 137-144. 10.1023/A:1011831902219
Locker JK, Rose JK, Horzinek MC, Rottier PJ: Membrane assembly of the triple-spanning coronavirus M protein. Individual transmembrane domains show preferred orientation. J Biol Chem 1992, 267: 21911-21918.
Yeo SG, Hernandez M, Krell PJ, Nagy EE: Cloning and sequence analysis of the spike gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus Chinju99. Virus Genes 2003, 26: 239-246. 10.1023/A:1024443112717
Ortego J, Ceriani JE, Patiño C, Plana J, Enjuanes L: Absence of E protein arrests transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus maturation in the secretory pathway. Virology 2007, 368: 296-308. 10.1016/j.virol.2007.05.032
Schierack P, Nordhoff M, Pollmann M, Weyrauch KD, Amasheh S, Lodemann U, Jores J, Tachu B, Kleta S, Blikslager A, et al.: Characterization of a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line for in vitro studies of microbial pathogenesis in swine. Histochem Cell Biol 2005, 125: 293-305.
Todd DJ, Lee A-H, Glimcher LH: The endoplasmic reticulum stress response in immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2008, 8: 663-674. 10.1038/nri2359
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ: From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 2008, 454: 455-462. 10.1038/nature07203
Luppi F, Longo AM, de Boer WI, Rabe KF, Hiemstra PS: Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Lung Cancer 2007, 56: 25-33. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.11.014
Waugh DJ, Wilson C: The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14: 6735-6741. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4843
Hong M: Transcriptional regulation of the Grp78 promoter by endoplasmic reticulum stress: role of TFII-I and its tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2005, 280: 16821-16828. 10.1074/jbc.M413753200
Li J, Ni M, Lee B, Barron E, Hinton DR, Lee AS: The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP is required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ 2008, 15: 1460-1471. 10.1038/cdd.2008.81
Quinones QJ, de Ridder GG, Pizzo SV: GRP78: a chaperone with diverse roles beyond the endoplasmic reticulum. Histol Histopathol 2008, 23: 1409-1416.
Hoffmann E, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Holtmann H, Kracht M: Multiple control of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Leukoc Biol 2002, 72: 847-855.
Waris G, Tardif KD, Siddiqui A: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress: hepatitis C virus induces an ER-nucleus signal transduction pathway and activates NF-kappaB and STAT-3. Biochem Pharmacol 2002, 64: 1425-1430. 10.1016/S0006-2952(02)01300-X
Fahy BN, Schlieman MG, Mortenson MM, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ: Targeting BCL-2 overexpression in various human malignancies through NF-κB inhibition by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2005, 56: 46-54. 10.1007/s00280-004-0944-5
Ricca A, Biroccio A, Del Bufalo D, Mackay AR, Santoni A, Cippitelli M: Bcl-2 over-expression enhances NF-kappaB activity and induces mmp-9 transcription in human MCF7(ADR) breast-cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2000, 86: 188-196. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000415)86:2<188::AID-IJC7>3.0.CO;2-W
Batsi C, Markopoulou S, Kontargiris E, Charalambous C, Thomas C, Christoforidis S, Kanavaros P, Constantinou AI, Marcu KB, Kolettas E: Bcl-2 blocks 2-methoxyestradiol induced leukemia cell apoptosis by a p27Kip1-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in conjunction with NF-κB activation. Biochem Pharmacol 2009, 78: 33-44. 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.017
Seo M, Nam H-J, Kim S-Y, Juhnn Y-S: Inhibitory heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins inhibit hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of Bcl-2 via NF-κB in H1299 human lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 381: 153-158. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.01.188
Junwei G, Baoxian L, Lijie T, Yi**g L: Cloning and sequence analysis of the N gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus LJB/03. Virus Genes 2006, 33: 215-219. 10.1007/s11262-005-0059-z
Chen J, Wang C, Shi H, Qiu HJ, Liu S, Shi D, Zhang X, Feng L: Complete genome sequence of a chinese virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain. J Virol 2011, 85: 11538-11539. 10.1128/JVI.06024-11
Park SJ, Kim HK, Song DS, An DJ, Park BK: Complete genome sequences of a korean virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and its attenuated counterpart. J Virol 2012, 86: 5964. 10.1128/JVI.00557-12
Anelli T, Sitia R: Protein quality control in the early secretory pathway. EMBO J 2008, 27: 315-327. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601974
Li Q, Verma IM: NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2002, 2: 725-734. 10.1038/nri910
Wietek C, O’Neill LAJ: Diversity and regulation in the NF-κB system. Trends Biochem Sci 2007, 32: 311-319. 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.05.003
Geng H, Wittwer T, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M, Schmitz ML: Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at Ser468 controls its COMMD1-dependent ubiquitination and target gene-specific proteasomal elimination. EMBO Rep 2009, 10: 381-386. 10.1038/embor.2009.10
Honglei Z, Jie D, Yabing L, **ngang X, Dewen T: RT-PCR identification of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and sequence analysis of its M, N and E gene. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica 2012, 21: 24-28.
**g W, Yanming Z, Gang T, Fangning L, Hongchao Z, Lei H, **aoyun Y, Yanzhao X, Haixia H: The isolation and identification of neonatal swine intestinal epithelial cells. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica 2010, 41: 92-98.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 − ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25: 402-408. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Matsuo Y, Sawai H, Ochi N, Yasuda A, Sakamoto M, Takahashi H, Funahashi H, Takeyama H, Guha S: Proteasome inhibitor MG132 inhibits angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer by blocking NF-κB activity. Dig Dis Sci 2009, 55: 1167-1176.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the basic research and operating expenses of Northwest A&F University (Grant No. QN2012017 and No. Z109021119) and the international science and technology cooperation fund of Northwest A&F University (Grant No. A213021202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ contributions
XX and HZ performed the majority of experiments and involved in manuscript preparation, QZ, JD, YL and YH participated part of the experiments. DT and HJL conceived of the study, participate in its design and coordination, and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
**ngang Xu, Honglei Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, Q. et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus E protein causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and up-regulates interleukin-8 expression. Virol J 10, 26 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-26
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-26