Abstract
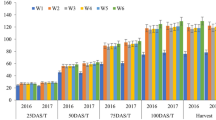
The rice planthoppers (RPHs) are considered as important rice pests in Asia including Pakistan. As phloem-feeders, they can cause severe losses to rice. Besides climate their population abundance is also affected by plant spacing. The optimum plant spacing is among the key agronomic parameters that influence crop growth, performance and yield. The present study to examine the effect of rice plant spacing on incidence of RPHs was conducted during Kharif season of 2018 and 2019 at farmer’s field in the Kallar tract. The study composed of four treatments of rice plant spacing viz. 18 × 18 cm, 23 × 23 cm, 28 × 28 cm and 33 × 33 cm. The experiment was set in a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three repeats. The nursery of rice cultivar Super Basmati was transplanted with uniform age of 35 days in all treatments. The data regarding RPHs was recorded 60 DAT till harvesting of crop. Results revealed that plant spacing had significant effect on number of tillers per plant, panicle length, sterility %age, plant height, straw and grain yield. The highest grain yield 6.75 tonns per ha was obtained from 23 × 23 cm plant spacing followed by 6.59, 5.83 and 5.46 tonns per ha from 28 × 28 cm, 33 × 33 cm and 18 × 18 cm plant spacing, respectively. Whereas, on an average RPHs population per plant was maximum (48.81) at minimum plant spacing (18 × 18 cm) and was minimum (3.57) at maximum (33 × 33 cm) plant spacing. The incidence of RPHs started 70 DAT and was very low in the beginning of the crop** season. It increased with the age of the crop and reached to a maximum level of 60 per plant at 110 DAT. On the basis of results 28 × 28 cm rice plant spacing could be recommended in RPHs vulnerable areas having good yield, low resource intensive and compatible with green plant protection measures. In turn this little yield reduction will highly pay in lieu of sustainable rice production and environment protection by reducing excessive and irrational use of pesticides and their cost of application and thus enhancing the biodiversity conservation potential of rice crop agroecosystem.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham CC, Nair MRGK (1975) The brown planthopper outbreaks in Kerala. India Rice Entomol Newsl 2:36
Anonymous (2020a) Gujranwala, Punjab, Pakistan Lat Long Coordinates Info. https://www.latlong.net/place/gujranwala-punjab-pakistan-8699.html. Accessed 01 June 2020
Anonymous (2020b) Control of rice insect pests. http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/ ericeproduction/PDF_&_Docs/Control_of_rice_insect_pests.pdf. Accessed 07 June 2020
Asghar M, Suhail A, Afzal M, Khan MA (2009) Determination of economics threshold levels for the stem borers (Scirpophaga sp.) and Leaffolder (Cnaphalocrosis medinalis) of Rice (Oryza sativa) in the Kallar tract of Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol 11:717–720
Asghar (2010) Biodiversity of insects associated with rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop agroecosystem in the Punjab, Pakistan. Ph.D. Thesis. Department of Entomology, University of Agriculture Faisalabad. Pakistan
Asghar M, Arshad M, Fiaz M, Suhail A, Sabir AM (2013) A survey of rice farmers’ farming practices posing threats to insect biodiversity of rice crop in the Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Biodivers Conserv 5(10):647–654
Bae SH, Pathak MD (1966) A mirid bug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter, predator of the eggs and nymphs of the brown planthopper. Int Rice Comm Newsl 15(3):33–36
Bezbaruha R, Sharma RC Banik P (2011) Effect of nutrient management and planting geometry on productivity of hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars. Americ J Pl Sci 2:297–302. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2011.23033
Bozorgi HR, Faraji A, Danesh RK, Keshavarz A, Azarpour E, Tarighi F (2011) Effect of plant density on yield and yield components of Rice. World Appl Sci J 12(11):2053–2057
Chatterjee BN, Mandal LN (1978) Rice culture in typical Aman land. Proceeding of the national symposium on increasing rice yield in Kharif. CRRI, Cuttack. In Satpathi CR, Chakraborty K, Acharjee P (2012). Impact of seedling spacing and fertilizer on brown plant hopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal. Incidence in rice field. J Biol Chem Res 29(1):26–36
Chiu, S (1979) Biological control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/5167.pdf. Accessed 06 June 2020
Clark LR, Geir PW, Hughes RD, Morries RF (1970) The ecology of insect populations in theory and practice. A Halsted Press Book, John Wiley & Sons, N.Y. pp 232
Conway GR, Pretty JN (1991) Unwelcome Harvest: Agriculture and Pollution. London: Earthscan Publications Ltd. In: Hong, X. X, Ya-jun Y, Yan-hui L, Xu-song Z, Jun-ce T, Feng-xiang L, Qiang F, Zhong-xian L (2017) Sustainable management of rice insect pests by non-chemical-insecticide technologies in China. Rice Sci 24(2): 61–72
Dyck VA (1973) The role of ecology in insect pest control. Paper presented at a Saturday seminar, 26 May 1973. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines. pp 11. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Fernando HE (1975) The brown planthopper problem in Sri Lanka. Rice Entomol Newsl 2:34–36. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Garbe AA, Mahmoud BA, Adamu Y, Ibrahim U (2013) Effect of variety, seed rate and row spacing on the growth and yield of rice in Bauchi, Nigeria. African J Food Agric Nut Dev 13(4):8155–8166
Garcia AU, Sanchez FF (1994) Influence of variety and plant spacing on the incidence of major insect pests and predators of lowland rice. Phil Entomol 9(4):399–405
Ghosh BC, Reddy MA, Reddy BB (1988) Effect of seedling density on growth and yield of transplanted rice. Central Rice Res Inst Cuttack Orssa India 21(1):13–21
Haque MA, Razzaque AHM, Haque ANA, Ullah MA (2015) Effect of plant spacing and nitrogen on yield of transplant Aman rice var. BRRI Dhan52. J. Biosci Agric Res 04(02):52–59
Hong XU, Ya-jun Y, Yan-hui LU, Xu-song Z, Jun-ce T, Feng-xiang L, Qiang FU, Zhong-xian LU (2017) Sustainable management of rice insect pests by non-chemical-insecticide technologies in China. Rice Sci 24(2):61–72
IRRI (International Rice Research Institute). 1972. Annual report for 1971. Los Banos, Philippines Pp.238. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Islam MS, Sarkar MAR, Rahman MS, Musa AM, Dham SC (1994) Effect of cultivar and NPK combination on the yield contributing characters of rice. Bangla J Agril Sci 15(1):105–110
**g Q, Bouman B, Keulen H, HV HH, Cao W, Dai T (2008) Disentangling the effect of environmental factors on yield and nitrogen uptake of irrigated rice in Asia. Agric Syst 98(3):177–188
Jones JM Sheats DB (2016) Consumer Trends in Grain Consumption. St. Catherine University., St Paul, MN, USA. Elsevier Ltd. In: Mahato M, Adhikari BB (2017) Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 5(4): 423–429
Kalode MB (1976) Brown planthopper in rice and its control. Indian Farming 27(5):3–5
Kisimoto R (1976) Bionomics, forecasting of outbreaks and injury caused by the rice brown planthopper. Paper presented at a seminar on the rice brown planthopper, food and fertilizer technology center for the Asian and Pacific Region, October 4–10. Tokyo. pp 15. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Kulshreshtha JP, Anjaneyulu A, Padmanabhan SY (1974) The disastrous brown planthopper attack in Kerala. Reprinted from December 1974 issue of Indian Farming. Pp.3. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Liou TM (1987) Effect of spacing and fertilizer levels on changes of ear type in rice. J.Agric. Assoc. China. 140: 1-10. In: Sohel MAT, Siddique MAB, Asaduzzaman M, lam MNA, Karim MM (2009) varietal performance of transplanted Aman rice under different hill densities. Bang J Agril Res 34(1):33–39
Lu ZX, Yang YJ, Yang PY, Zhao ZH (2012) China’s ‘Green Plant Protection’ initiative: Coordinated promotion of biodiversity-related technologies. In: Gurr GM, Wratten SD, Suyder WE, Read DMY (2012) Biodiversity and insect pests: Key Issues for Sustainable Management. John Wiley & Sons, pp 230–240. In: Hong XX, Ya-jun Y, Yan-hui L, Xu-song Z, Jun-ce T, Feng-xiang L, Qiang F, Zhong-xian L (2017) Sustainable management of rice insect pests by non-chemical-insecticide technologies in China. Rice Sci 24(2): 61–72
Macquillan MJ (1974) Influence of crop husbandry on rice planthoppers (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in the Solomon Islands. Agro-Ecosys 1(4):339–358
Mahato M, Adhikari BB (2017) Effect of planting geometry on growth of rice varieties. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 5(4):423–429
Manna GB, Rao KS (1982) Studies on skip row planting and related economization of inputs. CRRI Annual Report, pp 17–18
Matsukawa M, Kasum ITO, Kawakita K, Tanaka T (2015) Farmer perceptions and management of rice planthoppers in Cambodia. JARQ 49(2):103–109
Miah MHN, Karim MA, Rahman MS, Islam MS (1990) Performance of Nizersail mutant under different row spacing. Bangl J Train Dev 3(2):31–34
Mohaddesi A, Abbasian A, Bakhshipour S, Aminpanah H (2011) Effect of different levels of nitrogen and plant spacing on yield, yield components and physiological indices in high yield rice. Amer-Eur J Agric Environ 10:893–900
Shahbaz M, Ahmad F, Muhammad S, Javed A, Waqar MQ, Ali MA (2016) Efficacy of different chemicals for the management of bacterial leaf blight of rice (Oryza sativa L.) at various locations of adaptive research zone Sheikhupura. Pak J Phytopathol 28(2):223–230
NAS (NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES). 1971. Insect-pest management and control. Vol. 3.Washington, D. C. 508 p. In: Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper. pp 358 http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June2020
Nasir J (2020) Pakistan’s Rice exports increased 38.58% in first five months of FY 2019-20. https://propakistani.pk/2020/01/01/pakistans-rice-exports-increased-38-58-in-first-five-months-of-fy-2019-20/. Accessed 31May 2020
Nishida T (1975) Causes of brown planthopper outbreaks. Rice Entomol Newsl 2:38
Oka IN (1977) Cultural control of the brown planthopper pp 358 http://delphacid.s3.amazonaws.com/9169.pdf. Accessed 09 June 2020
Om H, Singh OP, Joon RK (1993) Effect of time of transplanting and spacing on basmati rice. Haryana J Agron 9(1):87
Pathak MD, Khan ZR (1994) Insect pests of rice. International rice research institute (IRRI). International Centre of insect physiology and ecology (ICIPE). Pp 23
Prasad RB, Pasalu IC, Thammi NB, Verma RG (2003) Influence of nitrogen and rice varieties on population buildup of brown plant hopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stal). J En Res 27(2):167–170
Rao KS, Moorhy BTS, Manna GB (1990) Plant population for higher productivity in basmati type scented rice. Int Rice Res Notes (IRRN) 15(1):25
Rasool F, Habib R, Bhat MI (2013) Agronomic evaluation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) for plant spacing and seedlings per hill under temperate condition. Afric J Agric Res 8(37):4650–4653. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR10.411
Rehman A, **gdong L, Chandio AA, Shabbir M, Hussain I (2017) Economic outlook of rice crops in Pakistan: a time series analysis (1970–2015). Financ Innov 3:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-017-0063-z
Saddler HD (2019) Pakistan rice exports reach record. Available at: https://www.world-grain.com/articles/13092-pakistan-rice-exports-reach-record. Accessed 31 May 2020
Satpathi CR, Chakraborty K, Acharjee P (2012) Impact of seedling spacing and fertilizer on brown plant hopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal. Incidence in rice field J Biol Chem Research 29(1):26–36
Shah MH, Khusu MK, Khandays BA, Bali AS (1991) Effect of spacing and seedlings per hill on transplanted rice under late sown condition. Indian J Agron 36(2):274–275
Sheikh AD, Mahmood MA, Bashir A, Kashif M (2006) Adoption of rice technological package by the farmers of irrigated Punjab. J Agric Res 44(4):341–352
Shohab A (2006) Agri overview: Introduction to rice. http://www.pakissan.com/english/agri.overview/introduction.to.rice.shtmlwww. Accessed 23 June 2009
Silvertooth JC, Edmisten KL, McCarty WH (1999) Production practices. In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton: Origin, history, tech., and prod. John Wiley & Sons, NY. pp 451–488 In: Anegbeh PO, Ighere DA, Abaku NS, Oham RO, Adunoye FO, Okere DO, Nwabueze NE, Omozusi EJ, Igbinosa M (2019) Effect of plant spacing and rice variety on vegetative growth and rice performance at acidic conditions of Iyanomo, south-South Nigeria. Direct Res J Agric Food Sci 7 (11):319–328
Sivasubramaniam N, Saleem M, Imthiyas M (2018) Evaluation of the major factors associated in controlling of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in paddy cultivation during its outbreak in selected divisional secretariats of the Ampara district of Sri Lanka. Sch J Agric Vet Sci 5(11):595–600
Sogawa K, Cheng CH (1979) Economic thresholds, nature of damage, and losses caused by the brown planthopper. Brown planthopper: threat to rice production in Asia. Int Rice Res Ins Los Banos, Laguna Philippines, pp125–142
Sohel MAT, Siddique MAB, Asaduzzaman M, Lam MNA, Karim MM (2009) Varietal performance of transplanted Aman rice under different hill densities. Bang J Agril Res 34(1):33–39
Srivastava SK, Biswas R, Garg DK, Gyawali BK, Haque NMM, Ijaj P, Jaipal S, Kamal NQ, Kumar P, Pathak M, Pathak PK, Prasad CS, Ramzan M, Rehman A, Rurmzan M, Salim M, Singh A, Singh US Tiwari SN (2004) Management of stem borers of rice and wheat in rice-wheat system of Pakistan, Nepal, India and Bangladesh, pp 1-204. Rice-wheat consortium paper series 17. Rice-wheat consortium for the indo-Gangetic Plains, New Delhi, India
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill Book Co. Inc, New York, pp 400–428
Suenaga H (1963) Analytical studies on the ecology of the two species of planthoppers the white back planthoppers (Sogatella furcifera Horvath) and the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) with special reference to their outbreaks. Bull Kyushu Agr Expt Sta 8:1–152
Suhail A, Ahmad J, Asghar M, Tayyib M, Majeed MM (2008) Determination of economic threshold level for the chemical control of rice stem borers (Scirpophaga incertulas wlk. And Scirpophaga innotata wlk.). Pak Entomol 30(2):175–178
Suhail A, Asghar M, Arshad M (2007) Insect faunal biodiversity associated with rice in Pakistan, with particular reference to rice black bug. In: Joshi RC, Barrion AT, Sebastian LS (2007) (eds) Rice black bugs: taxonomy, ecology, and management of invasive species. Science City of Munoz, Nueva Ecija, Philippine Rice Res Inst pp 643–652
Tilahun ZM (2019) Effect of row spacing and nitrogen fertilizer levels on yield and yield components of rice varieties. World Sci News 116:180–193
Usman M, Kazmi I, Khaliq T, Ahmad A, Saleem MF, Shabbir A (2012) Variability in water use, crop water productivity and profitability of rice and wheat in Rechna doab, Punjab, Pakistan. J Ani Pl Sci 22(4):998–1003
WARDA (West African Rice Development Association) (2008) NERICA: the new rice for Africa-a compendium. Africa rice center (WARDA); Rome, Italy: FAO; Tokyo, Japan: Sasakawa Africa Association. pp 210. In. Tilahun ZM (2009) Effect of row spacing and nitrogen fertilizer levels on yield and yield components of rice varieties. World Sci News 116:180–193
Wilson C, Tisdell C (2001) Analysis, why farmers continue to use pesticides despite environmental, health and sustainability costs. Ecol Econ 39:449–462
Win SS, Muhamad R, Ahmad ZAM, Adam NA (2011) Population fluctuation of brown plant hopper Nilaparvat lugens Stal. And white backed plant hopper Sogatella furcifera Horvath on rice. J Ent 8(2):183–190
Xu S, Wang H, Wang E, Zhao G (2013) Reproductive rate of rice brown planthopper population of super rice. Adv J Food Sci Tech 5(5):539–542
Ye ZQ (2013) Accelerate the construction of modern plant protection with vigorously implements of green control. China Plant Prot 33(2): 5–9, 23. In: Hong XX, Ya-jun Y, Yan-hui L, Xu-song Z, Jun-ce T, Feng-xiang L, Qiang F, Zhong-xian L (2017) Sustainable management of rice insect pests by non-chemical-insecticide technologies in China. Rice Sci 24(2): 61–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors I, Muhammad Asghar, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asghar, M., Hassan, Tu., Arshad, M. et al. Effect of plant spacing on incidence of rice planthoppers in transplanted rice crop. Int J Trop Insect Sci 41, 575–585 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00242-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00242-4