Abstract
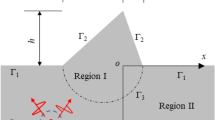
Seismic waves might be unavoidably triggered during underground energy and resource exploitation. Surface irregularities and subsurface cavities have significant effects on seismic wave propagation and cause amplification or reduction of ground motion. Hence, it is significant to address the scattering problem of SH waves induced by topography features and subsurface cavities in earthquake engineering. In this paper, based on the wave function expansion method coupling with the conjunction concept and the Graf’s addition formula, a series solution to this scattering problem of SH waves induced by a semi-cylindrical hill and a nearby cylindrical cavity in a homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic half-space is derived. The displacement amplitudes on the hill surface and its environs are calculated, and compared with the results in the existing works to verify the validity of the deriving process. Then, parametric studies are performed to analyze the effects of the cavity (its location and size), and the characteristics of incident waves (the frequency and incident angle) on the seismic response of the semi-cylindrical hill. Finally, the seismic behavior of the cylindrical cavity near or away from the hill for different frequencies and incident angles is examined.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a_{1}\) :
-
Semi-cylindrical hill radius
- \(d\) :
-
Burial depth of the cavity
- \(\theta\), \(\theta_{ 1}\), \(\theta_{ 2}\) :
-
Polar angles measured from the vertical y-, y1-, y2-axes, respectively
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Incident angle
- u f :
-
Steady-state out-of-plane motion corresponding to free field
- i :
-
\(\sqrt { - 1}\)
- c :
-
Shear wave velocity
- k :
-
Shear wavenumber
- \(J_{n} \left( \cdot \right)\) :
-
nth order Bessel function of the first kind
- \(\varepsilon_{n}\) :
-
Neumann factor
- \(\left| u \right|\) :
-
Displacement amplitude
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Wavelength of incident SH wave
- Im():
-
Imaginary part of a complex expression
- \(a_{2}\) :
-
Subterranean cylindrical cavity radius
- \(l\) :
-
Horizontal distance between the centers of the hill and the cavity
- \(\omega\) :
-
Circular frequency of incident SH wave
- \(u^{\left( j \right)}\) :
-
Steady-state out-of-plane motion in the region j
- u s :
-
Steady-state out-of-plane motion corresponding to scattered field
- t :
-
Time
- \(\mu\) :
-
Shear modulus
- \(\tau\) :
-
Shear stress
- \(H_{n}^{\left( 1 \right)} \left( \cdot \right)\) :
-
nth order Hankel function of the first kind
- \(x\) :
-
Abscissa corresponding to the rectangular coordinate system x–o–y
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless frequency
- Re():
-
Real part of a complex expression
- n, q, s, m :
-
Summation indexes
- N, QQ, SS, M :
-
Values corresponding to n, q, s, m, respectively, when the infinite series is truncated to a finite number
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1972) Handbook of mathematical functions, with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. Dover, New York
Alielahi H, Adampira M (2016) Effect of twin-parallel tunnels on seismic ground response due to vertically in-plane waves. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 85:67–83
Alielahi H, Kamalian M, Adampira M (2015) Seismic ground amplification by unlined tunnels subjected to vertically propagating SV and P waves using BEM. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 71:63–79
Alielahi H, Kamalian M, Adampira M (2016) A BEM investigation on the influence of underground cavities on the seismic response of canyons. Acta Geotech 11(2):391–413
Assimaki D, Kausel E, Gazetas G (2005) Wave propagation and soil–structure interaction on a cliff crest during the 1999 Athens Earthquake. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 25(7–10):513–527
Buech F, Davies TR, Pettinga JR (2010) The little red hill seismic experimental study: topographic effects on ground motion at a bedrock-dominated mountain edifice. Bull Seismol Soc Am 100(5A):2219–2229
Cen WJ, Du XH, Li DJ, Yuan LN (2018) Oblique incidence of seismic wave reflecting two components of design ground motion. Shock Vib 4127031-16
Chang KH, Tsaur DH, Wang JH (2016) Ground motions around a semicircular canyon with a dip** edge under SH plane wave incidence. J Seismol 20:117–136
Clarke H, Eisner L, Styles P, Turner P (2014) Felt seismicity associated with shale gas hydraulic fracturing: the first documented example in Europe. Geophys Res Lett 41:8308–8314
Ducellier A, Aochi H (2012) Interactions between topographic irregularities and seismic ground motion investigated using a hybrid FD–FE method. Bull Earthq Eng 10:773–792
Gao YF, Dai DH, Zhang N, Wu YX, Mahfouz AH (2017) Scattering of plane and cylindrical SH waves by a horseshoe shaped cavity. J Earthq Tsunami 11(2):1650011–1650023
Gao YF, Chen X, Zhang N, Dai DH, Yu X (2018) Scattering of plane SH waves induced by a semicylindrical canyon with a subsurface circular lined tunnel. Int J Geomech 06018012-10
Gizzi FT, Masini N (2006) Historical damage pattern and differential seismic effects in a town with ground cavities: a case study from Southern Italy. Eng Geol 88:41–58
Glinsky N, Bertrand E, Régnier J (2019) Numerical simulation of topographical and geological site effects. Applications to canonical topographies and Rognes hill, South East France. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 116:620–636
Graizer V (2009) Low-velocity zone and topography as a source of site amplification effect on Tarzana hill, California. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 29(2):324–332
Hough SE, Altidor JR, Anglade D, Given D, Janvier MG, Maharrey JZ, Meremonte M, Mildor BSL, Prepetit C, Yong A (2010) Localized damage caused by topographic amplification during the 2010M 7.0 Haiti earthquake. Nat Geosci 3(11):778–782
Jafarzadeh F, Shahrabi MM, Jahromi HF (2015) On the role of topographic amplification in seismic slope instabilities. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7(2):163–170
Jayalakshmi S, Raghukanth STG (2016) Regional ground motion simulation around Delhi due to future large earthquake. Nat Hazards 82:1479–1513
Kamalian M, Jafari MK, Sohrabi-bidar A, Razmkhah A, Gatmiri B (2006) Time-domain two-dimensional site response analysis of non-homogeneous topographic structures by a hybrid BE/FE method. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 26:753–765
Kang JQ, Zhu JB, Zhao J (2019) A review of mechanisms of induced earthquakes: from a view of rock mechanics. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 5:171–196
Karkooti E, Shomali ZH, Pakzad M (2016) Investigating the role of source mechanism, surface topography, and attenuation on the observed PGA pattern in May 28, 2004, Mw 6.2 Baladeh earthquake (Iran). J Seismol 20:495–510
Lee VW, Trifunac MD (1979) Response of tunnels to incident SH-waves. J Eng Mech 105:643–659
Lee VW, Chen S, Hsu IR (1999) Antiplane diffraction from canyon above subsurface unlined tunnel. J Eng Mech 125(6):668–675
Lee VW, Luo H, Liang JW (2006) Antiplane (SH) waves diffraction by a semicircular cylindrical hill revisited: an improved analytic wave series solution. J Eng Mech 132(10):1106–1114
Lenti L, Martino S (2012) The interaction of seismic waves with step-like slopes and its influence on landslide movements. Eng Geol 2012:19–36
Lenti L, Martino S (2013) A parametric numerical study of the interaction between seismic waves and landslides for the evaluation of the susceptibility to seismically induced displacements. Bull Seismol Soc Am 103(1):33–56
Li JC, Li HB, Ma GW, Zhou YX (2013) Assessment of underground tunnel stability to adjacent tunnel explosion. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 35:227–234
Lin ML, Wang KL (2006) Seismic slope behavior in a large-scale shaking table model test. Eng Geol 86:118–133
Lin CH, Lee VM, Todorovska MI, Trifunac MD (2010) Zero-stress, cylindrical wave functions around a circular underground tunnel in a flat, elastic half-space: incident P-waves. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:879–894
Liu HX, Xu Q, Li YR, Fan XM (2013a) Response of high-strength rock slope to seismic waves in a shaking table test. Bull Seismol Soc Am 103(6):3012–3025
Liu QJ, Zhao MJ, Wang LH (2013b) Scattering of plane P, SV or Rayleigh waves by a shallow lined tunnel in an elastic half space. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 49:52–63
Liu QJ, Zhang C, Todorovska MI (2016) Scattering of SH waves by a shallow rectangular cavity in an elastic half space. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 90:147–157
Liu XB, Chen JY, Zhao ZC, Lan HQ, Liu FP (2018) Simulating seismic wave propagation in viscoelastic media with an irregular free surface. Pure Appl Geophys 175:3419–3439
Lovati S, Bakavoli MKH, Massa M, Ferretti G, Pacor F, Paolucci R, Haghshenas E, Kamalian M (2011) Estimation of topographical effects at Narni ridge (Central Italy): comparisons between experimental results and numerical modelling. Bull Earthq Eng 9:1987–2005
Luo YH, Gaudio VD, Huanga R, WangY S, Wasowski J (2014) Evidence of hillslope directional amplification from accelerometer recordings at Qiaozhuang (Sichuan, China). Eng Geol 183:193–207
Massa M, Lovati S, Alema ED, Ferretti G, Bakavoli M (2010) An experimental approach for estimating seismic amplification effects at the top of a ridge, and the implication for ground-motion predictions: the case of Narni, Central Italy. Bull Seismol Soc Am 100(6):3020–3034
Moghadam MR, Baziar MH (2016) Seismic ground motion amplification pattern induced by a subway tunnel: shaking table testing and numerical simulation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 83:81–97
Nagashima F, Matsushima S, Kawase H, Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Hayakawa T, Satoh T, Oshima M (2014) Application of horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios of earthquake ground motions to identify subsurface structures at and around the K-NET site in Tohoku, Japan. Bull Seismol Soc Am 104(5):2288–2302
Nguyen KV, Behrouz G (2007) Evaluation of seismic ground motion induced by topographic irregularity. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 27:183–188
Panji M, Kamalian M, Asgari Marnani J, Jafari MK (2014) Analysing seismic convex topographies by a half-plane time-domain BEM. Geophys J Int 197:591–607
Parvanova SL, Dineva PS, Manolis GD, Wuttke F (2014) Seismic response of lined tunnels in the half-plane with surface topography. Bull Earthq Eng 12(2):981–1005
Patil M, Choudhury D, Ranjith PG, Zhao J (2018) Behavior of shallow tunnel in soft soil under seismic conditions. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 82:30–38
Poursartip B, Fathi A, Kallivokas LF (2017) Seismic wave amplification by topographic features: a parametric study. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 92:503–527
Schultz R, Stern V, Novakovic M, Atkinson G, Gu YJ (2015) Hydraulic fracturing and the Crooked Lake Sequences: insights gleaned from regional seismic networks. Geophys Res Lett 42:2750–2758
Sills LB (1978) Scattering of horizontally-polarized shear waves by surface irregularities. Geophys J R Astron Soc 54:319–348
Srilatha N, Madhavi Latha G, Puttappa CG (2013) Effect of frequency on seismic response of reinforced soil slopes in shaking table tests. Geotext Geomembr 36:27–32
Trifunac MD (1973) Scattering of plane SH waves by a semi-cylindrical canyon. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 1:267–281
Tripe R, Kontoe S, Wongc TKC (2013) Slope topography effects on ground motion in the presence of deep soil layers. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 50:72–84
Tsaur DH (2011) Scattering and focusing of SH waves by a lower semielliptic convex topography. Bull Seismol Soc Am 101(5):2212–2219
Tsaur DH, Chang KH (2009) Scattering and focusing of SH waves by a convex circular-arc topography. Geophys J Int 177:222–234
Wang G, Du CY, Huang D, ** F, Kooc RCH, Kwanc JSH (2018) Parametric models for 3D topographic amplification of ground motions considering subsurface soils. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 115:41–54
Watson GN (1958) A treatise on the theory of Bessel functions, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wu W, Zhao ZH, Duan K (2017) Unloading-induced instability of a simulated granular fault and implications for excavation-induced seismicity. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 63:154–161
Yang GX, Qi SW, Wu FQ, Zhan ZF (2018) Seismic amplification of the anti-dip rock slope and deformation characteristics: a large-scale shaking table test. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 115:907–916
Yu YZ, Deng LJ, Sun X, Lu H (2008) Centrifuge modeling of a dry sandy slope response to earthquake loading. Bull Earthq Eng 6(3):447–461
Yuan XM, Liao ZP (1996) Surface motion of a cylindrical hill of circular-arc cross-section for incident plane SH waves. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 15:189–199
Yuan XM, Men FL (1992) Scattering of plane SH waves by a semi-cylindrical hill. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 21:1091–1098
Zhang N, Gao YF, Cai YQ, Li DY, Wu YX (2012) Scattering of SH waves induced by a non-symmetrical V-shaped canyon. Geophys J Int 191:243–256
Zhang ZL, Wang T, Wu SR, Tang HM, Liang CY (2017) Seismic performance of loess-mudstone slope in Tianshui–Centrifuge model tests and numerical analysis. Eng Geol 222:225–235
Zhang ZZ, Fleurisson JA, Pellet FL (2018a) A case study of topographic site effects on seismic ground motions at **shan Park ridge in Zigong, Sichuan, China. Eng Geol 243:308–319
Zhang ZZ, Fleurisson JA, Pellet FL (2018b) The effects of slope topography on acceleration amplification and interaction between slope topography and seismic input motion. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 113:420–431
Zhao J, Zhou YX, Hefny AM, Cai JG, Chen SG, Li HB, Liu JF, Jain M, Foo ST, Seah CC (1999) Rock dynamics research related to cavern development for ammunition storage. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 14(4):513–526
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (41525009, 41831281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z.L., Li, J.C. & Li, X. Seismic interaction between a semi-cylindrical hill and a nearby underground cavity under plane SH waves. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-energ. Geo-resour. 5, 405–423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-019-00120-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-019-00120-5