Abstract
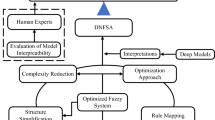
Although fuzzy system (FS) is highly interpretable, it is difficult to address high-dimensional big data due to the curse of dimensionality. On the contrary, deep neural network (DNN), a fashion deep learning algorithm, can deal with high-dimensional big data with shortcomings of complex model, huge calculation, and poor interpretability. We present a model of random locally optimized deep fuzzy system (RLODFS) and four specific heuristic implementation algorithms, which combines the advantages of high interpretability of FS and great ability of processing high-dimensional big data of DNN. This method takes Wang-Mendel (WM) algorithm as the basic module, to construct a RLODFS by bottom-up parallel structure. Through hierarchical, random group and combination-based learning, and input sharing, it can retain the interpretability and dramatically improve the computational efficiency. The input variables of the low-dimensional FS are randomly grouped by isometric sampling. Four implementation algorithms of RLODFS based on random local search for optimal combination, group learning, and deep structure with 0, 1, 2, and 3 input sharing, respectively, named as RLODFS-S0, RLODFS-S1, RLODFS-S2, and RLODFS-S3, are developed for regression-oriented problems. Using local loops to find the best combination of parameters, our final algorithms, RLODFS, can achieve fast convergence in training phase, and also superior generalization performance in testing. Compared with six classic algorithms in 12 datasets, the proposed RLODFS algorithms are not only highly interpretable with just some fuzzy rules but also can achieve higher precision, less complexity, and better generalization. Furthermore, it can be used for training fuzzy systems on datasets of any size, particularly for big datasets. Relatively, RLODFS-S3 and RLODFS-S2 achieve the best in comprehensive performance. More importantly, the proposed RLODFS is a new promising method of deep learning with good interpretability and high accuracy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Roux, N., Bengio, Y.: Representational power of restricted Boltzmann machines and deep belief networks. Neural Comput. 20(6), 1631–1649 (2008)
Salakhutdinov, R., Hinton, G.E.: Deep Boltzmann machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 5(2), 448–455 (2009)
Lerch, F., Ultsch, A., Lötsch, J.: Distribution optimization: an evolutionary algorithm to separate Gaussian mixtures. Sci. Rep. 10, 648 (2020)
Wang, P., Li, N.: Stable Controller Design for T-S Fuzzy Control Systems with Piecewise Multi-linearInterpolations into Membership Functions. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 21, 1585 (2019)
Palacios, A.M., Palacios, J.L., Sánchez, L., et al.: Genetic learning of the membership functions for mining fuzzy association rules from low quality data. Inform. Sci. 295, 358–378 (2015)
Li, L.Q., Wang, X.L., Liu, Z.X., et al.: A novel intuitionistic fuzzy clustering algorithm based on feature selection for multiple object tracking. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 21, 1613 (2019)
Hata, R., Islam, M.M., Murase, K.: Quaternion neuro-fuzzy learning algorithm for generation of fuzzy rules. Neurocomputing 216, 638–648 (2016)
Wang, L.X., Mendel, J.M.: Fuzzy basis functions, universal approximation, and orthogonal least-squares learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 3(5), 807–814 (1992a)
Wu, D., Lin, C., Huang, J., et al.: On the Functional Equivalence of TSK Fuzzy Systems to Neural Networks, Mixture of Experts, CART, and Stacking Ensemble Regression. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(10), 2570–2580 (2020)
Wu, D., Yuan, Y., Huang, J., et al.: Optimize TSK fuzzy systems for big data regression problems: mini-batch gradient descent with regularization, DropRule and AdaBound (MBGD-RDA). IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(5), 1003–1015 (2020)
Kalia, H., Dehuri, S., Ghosh, A., et al.: Surrogate-assisted multi-objective genetic algorithms for fuzzy rule-based classification. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 20, 1938 (2018)
Lee, C.W., Shin, Y.C.: Construction of fuzzy systems using least-squares method and genetic algorithm. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 137(3), 297–323 (2003)
Kosko, B.: Fuzzy systems as universal approximators. IEEE Trans. Comput. 43(11), 1329–1333 (1994)
Wang, L.X., Mendel, J.M.: Generating fuzzy rules by learning from examples. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 22(6), 1414–1427 (1992b)
Cui Y, Wu D.: Optimize TSK Fuzzy Systems for Big Data Classification Problems: Bag of Tricks. ar**v: Learning (2019)
Leski, J.M.: Fuzzy c-ordered-means clustering. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 286, 114–133 (2016)
Fan, Z., Chiong, R., Hu, Z., et al.: A two-layer Wang-Mendel fuzzy approach for predicting the residuary resistance of sailing yachts. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 36(6), 6219–6229 (2019)
**, Y.: Decentralized adaptive fuzzy control of robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern 28(1), 47–57 (1998)
**, Y., Von-Seelen, W., Sendhoff, B.: On generating flexible, complete, consistent and compact fuzzy rule systems from data using evolution strategies. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 29, 829–845 (1999)
Wang, L.X.: Fast training algorithms for deep convolutional fuzzy systems with application to stock index prediction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(7), 1301–1314 (2020)
Raju, G.V.S., Zhou, J., Kisner, R.A.: Hierarchical fuzzy control. Int. J. Contr. 54(5), 1201–1216 (1999)
Wang, L.X.: Analysis and design of hierarchical fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 7(5), 617–624 (1999)
Hinton, A., Geoffrey, E., Osindero, S., et al.: A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 18(7), 1527–1554 (2006)
Lee, M.L., Chung, H.Y., Yu, F.M.: Modeling of hierarchical fuzzy systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 138(2), 343–361 (2003)
Hagras, H.A.: A Hierarchical Type-2 fuzzy logic control architecture for autonomous mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(4), 524–539 (2004)
Peres, C.R., Guerra, R.E., et al.: Fuzzy model and hierarchical fuzzy control integration: an approach for milling process optimization. Comput. Indus 39(3), 199–207 (1999)
Luo, R.C., Chen, T.M., Su, K.L.: Target tracking using a hierarchical grey-fuzzy motion decision-making method. Syst. Man Cybern. 31(3), 179–186 (2001)
Salgado, P., Cunha, J.B.: Greenhouse Climate Hierarchical Fuzzy Modelling. Control Eng. Practice 13(5), 613–628 (2005)
Fayaz, M., Ullah, I., Park, D.-H., et al.: An integrated risk index model based on hierarchical fuzzy logic for underground risk assessment. Appl. Sci. 7(10), 1037 (2017)
Zimmerman, L., Zelichov, O., Aizenmann, A., et al.: A novel system for functional determination of variants of uncertain significance using deep convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 10, 4192 (2020)
Esteva, A., Kuprel, B., Novoa, R.A., et al.: Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542, 115–118 (2017)
Xu, Q., Yang, Y., Zhang, C., et al.: Deep convolutional neural network-based autonomous marine vehicle maneuver. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 20(2), 687–699 (2018)
Nguyen, T.L., Kavuri, S., Lee, M.: A fuzzy convolutional neural network for text sentiment analysis. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 35(6), 6025–6034 (2018)
Arrieta, A.B., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot, A., Tabik, S., et al.: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inform. Fusion 58, 82–115 (2020)
Islam, M.A., Anderson, D.T., Pinar, A.J., Havens, T.C., Scott, G., Keller, J.M.: Enabling explainable fusion in deep learning with fuzzy integral neural networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(7), 1291–1300 (2020)
Adadi, A., Mohammed, B.: Peeking inside the black-box: a survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 6, 52138–52160 (2018)
Wachter, S., Mittelstadt, B., Floridi, L.: Transparent, Explainable, and Accountable AI for Robotics. Sci. Robot. 2, 6 (2017)
Chen, D., Zhang, J., Jiang, S.: Forecasting the short-term metro ridership with seasonal and trend decomposition using loess and LSTM neural networks. IEEE Access 8, 91181–91187 (2020)
Huang, W., Song, G., Hong, H., **e, K., et al.: Deep architecture for traffic flow prediction: deep belief networks with multitask learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(5), 2191–2201 (2014)
Wang, L.X.: The WM method completed: a flexible fuzzy system approach to data mining. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 11(6), 768–782 (2003)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E., et al.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Carlyle, W.M., Royset, J.O., Wood, R.K., et al.: Lagrangian relaxation and enumeration for solving constrained shortest-path problems. Networks 52(4), 256–270 (2008)
Casillas, J., Cordon, O., del Jesus, M., et al.: Genetic tuning of fuzzy rule deep structures preserving interpretability and its interaction with fuzzy rule set reduction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 13(1), 13–29 (2005)
Li T, Suyu, Mei, and Zhu Hao.: Model Performance Estimation by 10-Fold Cross Validation. PLOS ONE, (2014)
Li, J., Liu, Z.L., Li, P., Jia, C.F.: Differentially private Naïve Bayes learning over multiple data sources. Inform. Sci. 444, 89–104 (2018)
García, S., Fernández, A., Luengo, J., Herrera, F.: Advanced nonparametric tests for multiple comparisons in the design of experiments in computational intelligence and data mining: Experimental analysis of power. Inform. Sci. 180, 2044–2064 (2010)
Zar, J.H.: Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1984)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for their invaluable insights, and this work was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61976055 and Foundation of Key Laboratory of Intelligent Metro of Universities in Fujian Province under Grant 53001703, and 50013203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Chen, D., Zhao, W. et al. Deep Fuzzy System Algorithms Based on Deep Learning and Input Sharing for Regression Application. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 727–742 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00998-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00998-4