Abstract
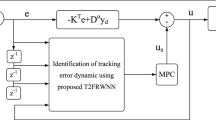
The major objective of this study is to design an effective control algorithm for dealing with multiple-input–multiple-output uncertain nonlinear systems. Novelty advantages of the proposed method include: (1) The network has the maximum initial rules; it helps to increase the responsiveness of the system; (2) the network has two dynamic thresholds: One dynamic threshold is utilized to consider whether to retain or to delete the existing rules and the other is used for generating a new rule; (3) the fuzzy neural network-based system can automatically construct the network structure and adjust the parameters of the system; (4) the network uses multiple combination techniques, such as sliding mode control, adaptive control, recurrent unit, wavelet function, fuzzy logic, neural network, and technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution multi-criteria decision analysis method. Based on the advantages of the above techniques, a self-organizing recurrent wavelet fuzzy neural network control system is designed comprising a main controller and a robust compensator. The gradient descent method is used to online tune the parameters for the main controller, and a Lyapunov stability theorem is applied to guarantee the system’s stability. Finally, the proposed control system is applied to a nonlinear chaotic system, an inverted double-pendulum system, and an unmanned aerial vehicle motion control to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control scheme. The simulation results show that the proposed control scheme can achieve favorable control performance.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, H., Cui, Y., Wang, Y.: Hybrid fuzzy adaptive fault-tolerant control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with unmeasured states. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(5), 1041–1050 (2017)
Wu, L.-B., Yang, G.-H.: Adaptive output fuzzy fault accommodation for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with multiple time delays. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 1052–1057 (2018)
Gao, Y.-F., Sun, X.-M., Wen, C., Wang, W.: Adaptive tracking control for a class of stochastic uncertain nonlinear systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62, 2498–2504 (2017)
Zouari, F., Boulkroune, A., Ibeas, A., Arefi, M.M.: Observer-based adaptive neural network control for a class of MIMO uncertain nonlinear time-delay non-integer-order systems with asymmetric actuator saturation. Neural Comput. Appl. 28, 993–1010 (2017)
Li, H., Wang, J., Lam, H.-K., Zhou, Q., Du, H.: Adaptive sliding mode control for interval type-2 fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 46(12), 1654–1663 (2016)
Slotine, J.J.E., Li, W.: Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Wang, Y., **e, L., de Souza, C.E.: Robust control of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 19(2), 139–149 (1992)
Utkin, V.I.: Sliding Modes in Control and Optimization. Springer, New York (1992)
Wang, S.-Y., Liu, F.-Y., Chou, J.-H.: Adaptive TSK fuzzy sliding mode control design for switched reluctance motor DTC drive systems with torque sensorless strategy. Appl. Soft Comput. 66, 278–291 (2018)
Wang, Y., Shen, H., Karimi, H.R., Duan, D.: Dissipativity-based fuzzy integral sliding mode control of continuous-time T–S fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2710952
Hung, J.Y., Gao, W., Hung, J.C.: Variable structure control: a survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 40(1), 2–22 (1993)
Tudoroiu, N., Elefterie, L., Tudoroiu, E.-R., Kecs, W., Dobritoiu, M., Ilias, N.: Real-time sliding mode observer estimator integration in hybrid electric vehicles battery management systems. In: Information Systems Architecture and Technology: Proceedings of 37th International Conference on Information Systems Architecture and Technology—ISAT 2016—Part III, pp. 15–28. Springer (2017)
Phoemphon, S., So-In, C., Niyato, D.T.: A hybrid model using fuzzy logic and an extreme learning machine with vector particle swarm optimization for wireless sensor network localization. Appl. Soft Comput. 65, 101–120 (2018)
Matuszek, C., Herbst, E., Zettlemoyer, L., Fox, D.: Learning to parse natural language commands to a robot control system. In: Experimental Robotics, pp. 403–415. Springer (2013)
De Medeiros, T.H., Rocha, H.P., Torres, F.S., Takahashi, R.H.C., Braga, A.P.: Multi-objective decision in machine learning. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 28(2), 217–227 (2017)
Kim, J., Kim, H., Kang, P.: Keystroke dynamics-based user authentication using freely typed text based on user-adaptive feature extraction and novelty detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 62, 1077–1087 (2018)
Hajek, P.: Predicting corporate investment/non-investment grade by using interval-valued fuzzy rule-based systems—a cross-region analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 62, 73–85 (2018)
Lin, D., Wang, X., Nian, F., Zhang, Y.: Dynamic fuzzy neural networks modeling and adaptive backstep** tracking control of uncertain chaotic systems. Neurocomputing 73(16), 2873–2881 (2010)
Wang, Y., Lu, Z., Qu, Y., Li, L., Wang, N.: Improving prediction performance of GPS satellite clock bias based on wavelet neural network. GPS Solut. 21(2), 523–534 (2017)
Capizzi, G., Sciuto, G.L., Napoli, C., Tramontana, E.: An advanced neural network based solution to enforce dispatch continuity in smart grids. Appl. Soft Comput. 62, 768–775 (2018)
Wei, Y., Park, J.H., Qiu, J., Wu, L., Jung, H.Y.: Sliding mode control for semi-Markovian jump systems via output feedback. Automatica 81, 133–141 (2017)
Ganesan, S., Ramesh, V., Umashankar, S., Sanjeevikumar, P.: Fuzzy-based microgrid energy management system using interleaved boost converter and three-level NPC inverter with improved grid voltage quality. In: Advances in Smart Grid and Renewable Energy. pp. 325–337. Springer (2018)
Hafaifa, A., Laaouad, F., Laroussi, K.: A numerical structural approach to surge detection and isolation in compression systems using fuzzy logic controller. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 9(1), 69–79 (2011)
Ullah, A.S., Noor-E-Alam, M.: Big data driven graphical information based fuzzy multi criteria decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 63, 23–38 (2018)
Wang, Y., Gao, Y., Karimi, H.R., Shen, H., Fang, Z.: Sliding mode control of fuzzy singularly perturbed systems with application to electric circuit. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2720968
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Shi, P., Chadli, M.: Fixed-order piecewise-affine output feedback controller for fuzzy-affine-model-based nonlinear systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 64(4), 945–958 (2017)
Wang, Y., **a, Y., Shen, H., Zhou, P.: SMC design for robust stabilization of nonlinear Markovian jump singular systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 63(1), 219–224 (2018)
Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L.: PSO-self-organizing interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for antilock braking systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(5), 1362–1374 (2017)
Wei, Y., Qiu, J., Karimi, H.R.: Fuzzy-affine-model-based memory filter design of nonlinear systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 504–517 (2018)
Macnab, C.: Modifying CMAC adaptive control with weight smoothing in order to avoid overlearning and bursting. Neural Comput. Appl. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3182-6
Zhou, Q., Chao, F., Lin, C.-M.: A functional-link-based fuzzy brain emotional learning network for breast tumor classification and chaotic system synchronization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(2), 349–365 (2018)
Liu, T., Deng, Y., Chan, F.: Evidential supplier selection based on DEMATEL and game theory. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(4), 1321–1333 (2018)
Hwang, C.L., Yoon, K.: Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications: A State-of-The-Art Survey. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Estay-Ossandon, C., Mena-Nieto, A., Harsch, N.: Using a fuzzy TOPSIS-based scenario analysis to improve municipal solid waste planning and forecasting: a case study of Canary archipelago (1999–2030). J. Clean. Prod. 176, 1198–1212 (2018)
Liu, L., Liu, X., Pei, J., Fan, W., Pardalos, P.M.: A study on decision making of cutting stock with frustum of cone bars. Oper. Res. Int. J. 17(1), 187–204 (2017)
Afsordegan, A., Sánchez, M., Agell, N., Zahedi, S., Cremades, L.V.: Decision making under uncertainty using a qualitative TOPSIS method for selecting sustainable energy alternatives. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13(6), 1419–1432 (2016)
İç, Y.T.: A TOPSIS based design of experiment approach to assess company ranking. Appl. Math. Comput. 227(Supplement C), 630–647 (2014)
Margain, L., Ochoa, A., Castillo, O., González, S., Gutiérrez, G.: Fuzzy TOPSIS method associated with improved selection of machines of high productivity. In: Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 13th International Conference, pp. 3–12. Springer (2016)
Liu, J., Wei, Q.: Risk evaluation of electric vehicle charging infrastructure public-private partnership projects in China using fuzzy TOPSIS. J. Clean. Prod. 189, 211–222 (2018)
Lin, C.-M., Huynh, T.-T.: Function-link fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller design for nonlinear chaotic systems using TOPSIS multiple attribute decision-making method. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0482-7
Rao, R.V.: Decision Making in The Manufacturing Environment: Using Graph Theory and Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making Methods. Springer, London (2007)
Lee, L.-W., Li, I.-H.: Design and implementation of a robust FNN-based adaptive sliding-mode controller for pneumatic actuator systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 30(1), 381–396 (2016)
Huang, X., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y.: Neural network-based adaptive second order sliding mode control of Lorentz-augmented spacecraft formation. Neurocomputing 222, 191–203 (2017)
Ma, X., Sun, F., Li, H., He, B.: Neural-network-based sliding-mode control for multiple rigid-body attitude tracking with inertial information completely unknown. Inf. Sci. 400–401, 91–104 (2017)
Lin, F.-J., Chen, S.-G., Sun, I.-F.: Intelligent sliding-mode position control using recurrent wavelet fuzzy neural network for electrical power steering system. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(5), 1344–1361 (2017)
Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Huynh, T.-T.: Self-evolving function-link interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for nonlinear system identification and control. Neurocomputing 275, 2239–2250 (2018)
Wang, X., Jiang, R., Li, L., Lin, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, F.Y.: Capturing car-following behaviors by deep learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 99, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2706963
El-Sousy, F.F., Abuhasel, K.A.: Self-organizing recurrent fuzzy wavelet neural network-based mixed H 2/H ∞ adaptive tracking control for uncertain two-axis motion control system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(6), 5139–5155 (2016)
Wei, Y., Park, J.H., Karimi, H.R., Tian, Y.-C., Jung, H.: Improved stability and stabilization results for stochastic synchronization of continuous-time semi-Markovian jump neural networks with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(6), 2488–2501 (2018)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 5(1), 3–55 (2001)
Zeleny, M.: Multiple Criteria Decision Making. McGraw-Hill, New York (1982)
Yu, Y., Zhang, S.: Adaptive backstep** synchronization of uncertain chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 21(3), 643–649 (2004)
Lin, C.-M., Li, H.-Y.: Self-organizing adaptive wavelet CMAC backstep** control system design for nonlinear chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14(1), 206–223 (2013)
Kurfess, T.R.: Robotics and Automation Handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2004)
Zhou, S., Feng, G., Feng, C.-B.: Robust control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems: adaptive fuzzy approach based on backstep**. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 151(1), 1–20 (2005)
Lin, C.-M., Lin, H.Y.: TSK fuzzy CMAC-based robust adaptive backstep** control for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(6), 1147–1154 (2012)
Lin, C.-M., Tai, C.-F., Chung, C.-C.: Intelligent control system design for UAV using a recurrent wavelet neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 24(2), 487–496 (2014)
McLean, D.: Automatic Flight Control Systems. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, TT., Le, TL. & Lin, CM. Self-Organizing Recurrent Wavelet Fuzzy Neural Network-Based Control System Design for MIMO Uncertain Nonlinear Systems Using TOPSIS Method. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 468–487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0550-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0550-z