Abstract
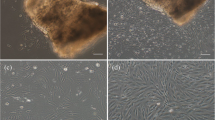
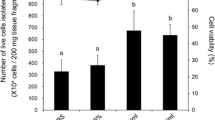
Explantation and trypsinisation methods for tissue dissociation were attempted for the establishment of primary cell cultures from the caerulean damsel, Pomacentrus caeruleus. Among the tissues taken, fin, liver and caudal peduncle showed good attachment with emergence of cells. The cells were best suited to grow in Leibovitz’s L-15 basal medium supplemented with foetal bovine serum (initially 20 % which was later reduced to 5–10 % during subsequent passages) at an ambient temperature of 28 ± 2 °C and pH 7.2 ± 0.2. These cultures persisted at temperatures from 17 to 32 °C, and proliferated at temperatures from 24 to 30 °C. The cells have been cryopreserved successfully with a survival rate of 80 %. Results suggest that fin, caudal peduncle and liver cell cultures have potential for development into cell lines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silas EG, Gopalakrishnan A, Ramachandran A, Anna Mercy TV, Kripan Sarkar, Pushpangadan KR, Anil Kumar P, Ram Mohan MK, Anikuttan KK (2011) Guidelines for green certification of freshwater ornamental fish. The Marine Products Export Development Authority, Kochi, India. xii+106p
FAO (2008) http://www.fao.org/fi/statist/FISOFT/FISHPLUS.asp. Accessed 10 Jul 2015
Gopakumar G, Madhu K, Madhu R, Ignatius B, Krishnan L, Mathew G (2009) Broodstock development, breeding and seed production of selected marine food fishes and ornamental fishes. Mar Fish Info Serv T&E Ser 201:1–9
Lakra WS, Swaminathan TR, Joy KP (2010) Development, characterization, conservation and storage of fish cell lines. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:1–20. doi:10.1007/s10695-010-9411-x
Wolf K, Mann JA (1980) Poikilotherm vertebrate cell lines and viruses: a current listing for fishes. In Vitro 16(2):168–179. doi:10.1007/BF02831507
Hightower LE, Renfro JL (1988) Recent applications of fish cell culture to biomedical research. J Exp Zool 248:290–302
Bols NC, Lee LEJ (1991) Technology and uses of cell cultures from tissues and organs of bony fish. Cytotechnol 6(3):163–187. doi:10.1007/BF00624756
Burkhart JG (2000) Fishing for mutations. Nat Biotechnol 18:21–22. doi:10.1038/71869
Hackett PB, Alvarez MC (2000) The molecular genetics of transgenic fish. In: Fingerman M, Nagabhushanam R (eds) Recent advances in marine biotechnology: vol. 4. Aquaculture: part B fishes. Science Publishers, New York, pp 77–145
Gallardo-Gálvez JB, Méndez T, Béjar J, Alvarez MC (2011) Endogenous transposases affect differently Slee** Beauty and Frog Prince transposons in fish cells. Mar Biotechnol 13:695–705. doi:10.1007/s10126-010-9331-x
Molina A, Carpeaux R, Martial JA, Muller M (2002) A transformed fish cell line expressing a green fluorescent protein-luciferase fusion gene responding to cellular stress. Toxicol In Vitro 16(2):201–207
Kawakami K, Abe G, Asada T, Asakawa K, Fukuda R, Ito A, Lal P, Mouri N, Muto A, Suster ML, Takakubo H, Urasaki A, Wada H, Yoshida M (2010) zTrap: zebrafish gene trap and enhancer trap database. BMC Dev Biol 10:105. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-105
Crespo B, Zanuy S, Gómez A (2013) Development of an in vitro system for functional studies of ovarian follicular cells in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Cytotechnol 65(2):273–286. doi:10.1007/s10616-012-9484-8
Kaltenbach JP, Kaltenbach MH, Lyons WB (1958) Nigrosin as a dye for differentiating live and dead ascites cells. Exp Cell Res 15:112–117
Nicholson BL (1989) Fish cell culture: an update. Adv in Cell Culture 7:1–18
Bols NC, Lee LEJ (1991) Technology and uses of cell cultures from tissues and organs of bony fish. Cytotechnol 6(3):163–187. doi:10.1007/BF00624756
Lakra WS, Goswami M, Yadav K, Gopalakrishnan A, Patiyal RS, Singh M (2011) Development and characterization of two cell lines PDF and PDH from Puntius denisonii (Day 1865). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:89–94. doi:10.1007/s11626-010-9374-3
Lakra WS, Goswami M (2011) Development and characterization of a continuous cell line PSCF from Puntius sophore. J Fish Biol 78:987–1001. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02891.x
Yan W, Nie P, Lu Y (2011) Establishment, characterization and viral susceptibility of a new cell line derived from goldfish, Carassius auratus (L.), tail fin. J Fish Dis 34:757–768. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.2011.01292.x
Swaminathan TR, Lakra WS, Gopalakrishnan A, Basheer VS, Kushwaha B, Sajeela KA (2012) Development and characterization of a fibroblastic-like cell line from caudal fin of the red-line torpedo, Puntius denisonii (Day) (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Aquac Res 43:498–508. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2011.02854.x
Sobhana KS, George KC, Ravi GV, Ittoop G, Paulraj R (2009) Development of a cell culture system from gill explants of the grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus (Bloch and Shneider). Asian Fish Sci 22:1–6
Wei YB, Fan TJ, Jiang GJ, Sun A, Xu XH, Wang J (2009) Establishment of a novel fin cell line from brown-marbled grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (Forsskål), and evaluation of its viral susceptibility. Aquac Res 40:1523–1531. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02253.x
Faisal M, Rutan BJ, Sami-Demmerle S (1995) Development of continuous liver cell cultures from the marine teleost, spot (Leiostomus xanthurus, Pisces: Sciaenidae). Aquaculture 132:59–72. doi:10.1016/0044-8486(94)00382-X
Lai YS, Murali S, Ju HY, Wu MF, Guo IC, Chen SC, Fang K, Chang CY (2000) Two iridovirus-susceptible cell lines established from kidney and liver of grouper, Epinephelus awoara (Temminck and Schlegel), and partial characterization of grouper iridovirus. J Fish Dis 23:379–388. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2761.2000.00247.x
Williams LM, Crane MSJ, Gudkovs N (2003) Development and characterisation of pilchard (Sardinops sagax neopilchardus) cell lines derived from liver and heart tissues. Methods Cell Sci 25:105–113. doi:10.1007/s11022-004-9801-5
Ye HQ, Chen SL, Sha ZX, Xu MY (2006) Development and characterization of cell lines from heart, liver, spleen and head kidney of sea perch, Lateolabrax japonicas. J Fish Biol 69(Supplement A):115–126. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2006.01155.x
Lee LEJ, Clemons JH, Bechtel DG, Caldwell SJ, Han KB, Pasitschniak-Arts M, Mosser DD, Bols NC (1993) Development and characterization of a rainbow trout liver cell line expressing cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase activity. Cell Biol Toxicol 9(3):279–294. doi:10.1007/BF00755606
Karunasagar I, Millar SD, Frerichs GN (1995) A new cell line from Puntius schwanenfeldi sensitive to snakehead fish cell line C-type retrovirus. Asian Fish Sci 8:151–157
Bradford CS, Sun L, Collodi P, Barnes DW (1994) Cell cultures from zebrafish embryos and adult tissues. Methods Cell Sci 16:99–107. doi:10.1007/BF01404818
Imajoh M, Ikawa T, Oshima SI (2007) Characterization of a new fibroblast cell line from a tail fin of red sea bream, Pagrus major, and phylogenetic relationships of a recent RSIV isolate in Japan. Virus Res 126:45–52. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2006.12.020
Sobhana KS, George KC, Ravi GV, Ittoop G, Paulraj R (2008) A cell culture system developed from heart tissue of the greasy grouper, Epinephelus tauvina (Forsskål 1775) by enzymatic dissociation. Indian J Fish 55(3):251–256
Lei XY, Chen ZY, He LB, Pei C, Yuan XP, Zhang QY (2012) Characterization and virus susceptibility of a skin cell line from red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Fish Physiol Biochem 38:1175–1182. doi:10.1007/s10695-012-9603-7
Pärt P, Bergström E (1995) Primary cultures of teleost branchial epithelial cells. In: Wood CM, Shuttleworth TJ (eds) Fish Physiology, volume 14: cellular and molecular approaches to fish ionic regulation. Academic Press, New York, pp 207–227. ISBN 0123504384
Kumar GS, Singh ISB, Rosamma P, Raveendranath M, Shanmugam J (1998) Efficacy of fish and prawn muscle extracts as supplements to development of a primary cell culture system from larval tissue of aquarium fish Poecilia reticulata. Indian J Exp Biol 36:91–94
Kumar GS, Singh ISB, Philip R (2001) Development of a cell culture system from the ovarian tissue of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Aquaculture 194:51–62. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00509-3
Lakra WS, Sivakumar N, Goswami M, Bhonde RR (2006) Development of two cell culture systems from Asian seabass Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Aquac Res 37(1):18–24. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2005.01387
Clem LW, Moewus L, Siegel MM (1961) Studies with cells from marine fish in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 108:762–766
Fryer JL (1964) Methods for the in vitro cultivation of cells from the tissues of salmonid fishes. Doctoral Dissertation, Oregon State University
Fryer JL, Yusha A, Pilcher KS (1965) The in vitro cultivation of tissue and cells of Pacific salmon and steelhead trout. Ann NY Acad Sci 126(1):566–586. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb14303.x
Collodi P, Barnes DW (1990) Mitogenic activity from trout embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(9):3498–3502. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.9.3498
Pärt P, Norrgren L, Bergström E, Sjöberg P (1993) Primary cultures of epithelial cells from rainbow trout gills. J Exp Biol 175:219–232
Avella M, Berhaut J, Payan P (1994) Primary culture of gill epithelial cells from the sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 30:41–49. doi:10.1007/BF02631417
Diago ML, Lòpez-Fierro MP, Razquin B, Villena A (1993) Long-term myelopoietic cultures from the renal hematopoietic tissue of the rainbow trout, Oncorhychus mykiss W. Exp Hematol 21(9):1277–1287
Moritomo T, Watanabe T (1994) Colony growth of carp hematopoietic cells in vitro. In: Stolen JS, Fletcher TC, Rowley AF, Zeliko AF, Kaattari SL, Smith SA (eds) Techniques in fish immunology-3. SOS Publications, Fair Haven, pp 35–44
Prashanth RG, Debala Devi CH, Usha Anandhi D (2012) Growth rate studies of marine ornamental fish Pomacentrus caeruleus in artificial conditions. J Environ Biol 33:929–932
Middlebrooks BL, Ellender RD, Wharton JH (1979) Fish cell culture: a new cell line from Cynoscion nebulosus. In Vitro 15(2):109–111
Grunow B, Noglick S, Kruse C, Gebert M (2011) Isolation of cells from Atlantic sturgeon Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus and optimization of culture conditions. Aquat Biol 14:67–75. doi:10.3354/ab00383
Bain PA, Hutchinson RG, Marks AB, Crane MSJ, Schuller KA (2013) Establishment of a continuous cell line from southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii). Aquaculture 376–379:59–63. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.11.008
Tong SL, Lee H, Miao HZ (1997) The establishment and partial characterization of a continuous fish cell line FG-9307 from the gill of flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 156:327–333. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00070-7
Freshney RI (2010) Culture of animal cells—a manual of basic technique and specialized applications, 6th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, NJ, pp 317–334
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to the Director and staff of the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Kochi for the facilities provided to carry out the study. This work was supported by grants from the Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Ethical approval
Use of animals for research use purpose was done as per norms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, G.A., Sobhana, K.S., Sunny, S.M. et al. Evaluation of Various Tissues of the Caerulean Damsel, Pomacentrus caeruleus for Initiating In Vitro Cell Culture Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 88, 293–303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-016-0751-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-016-0751-x