Abstract
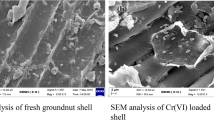
For the conservation of our environment, removing water pollutants from the different wastewater sources is getting critical. This study used a low-cost, green, agricultural waste, Arachis hypogaea’s shell (local name—groundnut shell) to remove Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. SEM analyzed surface morphology. FTIR determined functional groups present in the groundnut shell. The effects of different operating parameters on metal removal are investigated. The percentage removal is maximum at pH 5. Langmuir’s adsorption capacity is 3.53 mg/g and is not very high, but the adsorbent is abundantly available in India's rural areas. The adsorption process follows the Pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models. As the values of sorption energy lie between 8 and 16 kJ/mol, the adsorption process is chemical. The positive value of entropy (0.193 kJ/mol.K) and enthalpy (53.63 kJ/mol) proves that the process is spontaneous and endothermic. The blood cell count of Gallus gallus domesticus has revealed Pb(II)’s toxic effects with the treated solution. The applicability of MLR and the Genetic Algorithm has also been successfully applied and presented in this study. The scale-up design has been reported. This study aims to develop the utilization of low-cost natural adsorbent, groundnut shell, a natural waste material, widely available throughout India. This adsorbent is expected to provide an excellent and highly porous surface structure with different functional groups that assist the binding of metal ions.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A H :
-
Harkins Jura isotherm constant
- A T :
-
Equilibrium binding constant of Temkin isotherm (L/g)
- a :
-
Fractional power model constant (g/(mg.min))
- a e :
-
Adsorption rate (initial) (mg/(g.min))
- B :
-
Heat of adsorption (J/mol)
- B H :
-
Harkins Jura isotherm constant
- b :
-
Fractional power model constant (mg/g)
- b e :
-
Chemisorption activation energy (g/mg)
- b T :
-
Constant of Temkin isotherm
- C :
-
External convective mass transfer (mg/g)
- C a :
-
Pb(II) ion concentration at the adsorbent at equilibrium (mg/L)
- C 0 :
-
Initial Pb(II) ion concentration (initial) (mg/L)
- C e :
-
Pb(II) ion concentration at equilibrium (mg/L)
- C t :
-
Ion concentration of Pb(II) at time t (mg/L)
- D e :
-
Absorbate’s effective diffusion coefficient in the absorbent phase (m2/s)
- E :
-
Adsorption free energy (kJ/mol)
- ∆G 0 :
-
Gibbs free energy change (kJ/mol)
- ∆H :
-
Enthalpy change (kJ/mol)
- k 1 :
-
Rate constant of Lagergren’s model (min−1)
- k 2 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-second-order model (g/mg.min)
- K ad :
-
Rate constant of Natarajan and Khalaf model (min−1)
- K f :
-
Constant of Freundlich model (mg/g)/(mg/L)1/n
- k i :
-
Rate constant of intra-particle diffusion model (mg/(g.min0.5))
- \({K}_{L}\) :
-
Constant of Langmuir model (L/mg)
- \({K}_{C}^{0}\) :
-
Thermodynamic equilibrium constant
- \({K}_{C}^{^{\prime}}\) :
-
Apparent equilibrium constant
- n :
-
Factor of heterogeneity
- q e :
-
Sorption capacity at equilibrium (mg/g)
- q m :
-
Adsorption capacity of Langmuir isotherm (mg/g)
- q s :
-
Theoretical isotherm saturation capacity (mg/g)
- q t :
-
Sorption capacity at time t (mg/g)
- R :
-
Ideal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- R a :
-
Adsorbent particle radius (m)
- R L :
-
Dimensionless factor
- ∆S :
-
Change of entropy (kJ/mol.K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- t :
-
Time (min)
- V :
-
Solution volume (L)
- W :
-
Adsorbent mass (g
- λ :
-
Constant of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm (mol2/KJ 2)
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Polanyi potential
References
Apaydın-Varol E, Pütün AE (2012) Preparation and characterization of pyrolutic chars from different biomass samples. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 98:29–36
Banerjee M, Bar N, BasuDas RKSK (2017) Comparative study of adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ion from aqueous solution in fixed bed column by peanut shell and almond shell using empirical models and ANN. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10604–10620
Banerjee M, Bar N, Basu RK, Das SK (2018) Removal of Cr(VI) from its aqueous solution using green adsorbent pistachio shell: a fixed bed column study and GA-ANN modeling. Water Conserv Sci Eng 3(1):19–31
Banerjee M, Basu RK, Das SK (2019) Cu(II) removal using green adsorbents: kinetic modeling and plant scale-up design. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):11542–11557
Bhattacharya AK, Naiya TK, Mandal SN, Das SK (2008) Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using different low-cost adsorbents. Chem Eng J 137(3):529–541
Blazquez G, Calero M, Hernainz F, Tenorio G, Martin-Lara MA (2010) Equilibrium biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by solid waste from olive-oil production. Chem Eng J 160(2):615–622
Boeykens SP, Redondo N, Alvarado R, Caracciolo N, Vázquez C (2019) Chromium and Lead adsorption by avocado seed biomass study through the use of Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence analysis. App Rad Isotopes 153:108809
Cimino G, Passerini A, Toscano G (2000) Removal of toxic cations and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by hazelnut shell. Water Res 34:2955–2962
Dahiya S, Tripathi RM, Hegde AG (2008) Biosorption of lead and copper from aqueous solutions by pre-treated crab and arca shell biomass. Bioresour Technol 99:179–187
Das A, Banerjee M, Bar, Das SK (2019) Adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamics, toxicity, scale-up design, and GA modeling. SN Appl Sci 1:776
Das A, Bar N, Das SK (2020) Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by nutshells, green adsorbent: adsorption studies, regeneration studies, scale-up design, its effect on biological indicator and MLR modeling. J Coll Interface Sci 580:245–255
Dubinin MM (1960) The potential theory of adsorption of gases and vapors for adsorbents with energetically non-uniform surface. Chem Rev 60:235–266
Dubinin MM, Zaverina ED, Radushkevich LV (1947) Sorption and structure of active carbons I. Adsorption of organic vapors. ZhurnalFizicheskoiKhimii 21:1351–1362
Freundlich HMF (1906) Über die adsorption in losungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470
Ghosh K, Bar N, Biswas AB, Das SK (2019) Removal of methylene blue (aq) using untreated and acid treated eucalyptus leaves and GA-ANN modelling. Can J Chem Eng 97(11):2883–2898
Groundnut outlook report, (2021) Angrau.ac.in/downloads/AMIC/GROUNDNUT%20OUTLOOK%20REPORT%20-%20January%20to%20May%202021.pdf, assessed on 29th Sept. 2021.
Han R, Zhang J, Zou W, Shi J, Lui H (2005) Equilibrium biosorption isotherm for lead ion on chaff. J Hazard Mater 125:266–271
Harkins WD, Jura G (1943) An absolute method for the determination of the area of a fine crystalline powder. J Chem Phys 11:430
Huang L, Kong J, Wang W, Zhang C, Niu S, Gao B (2012) Study on Fe(III) and Mn(II) modified activated carbons derived from Zizanialatifolia to remove basic fuchsin. Desalination 286:268–276
Huang Y, Li S, Chen J, Zhang X, Chen Y (2014) Adsorption of Pb (II) on mesoporous activated carbonsfabricated from water hyacinth using H3PO4 activation: Adsorption capacity, kinetic and isotherm studies. Appl Surf Sci 293:160–168
IS 10500: (1992) Drinking water specification (reaffirmed 1993). http://www.hppcb.nic.in/EIAsorang/Spec.pdf. Accessed 09 Aug 2007
Kharif, (2018) Survey of Groundnut Crop, Agricultural & Processed Food Products Export Development Authority, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India. 2018
Kyzas G, Kostoglou ZM (2014) Green adsorbents for wastewaters: a critical review. Materials 7:333–364
Lagergren S (1898) Zurtheorie der sogenannten adsorption gelӧsterstoffle. Kungliga Sevenska Vetenskapasakdemiens Handilinger 24(4):1–39
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Li S, Xu S, Liu S, Yang C, Lu Q (2004) Fast pyrolysis of biomass in free-fall reactor for hydrogen-rich gas. Fuel Proc Technol 85:1201–1211
Li Q, Zhai J, Zhang W, Wang M, Zhou J (2007) Kinetic studies of adsorption of Pb(II), Cr(III) and Cu(II) from aqueous solutions by saw dust and modified peanut husk. J Hazard Mater 141:163–167
Li Y, Du Q, Wang X, Zhang P, Wang D, Wang Z, **a Y (2010) Removal of lead from aqueous solution byactivated carbon prepared from Enteromorphaprolifera by zinc chloride activation. J Hazard Mater 183:583–589
Mitra T, Singha B, Bar N, Das SK (2014) Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution using water hyacinth root by fixed-bed column & ANN modeling. J Hazard Mater 273:94–103
Nag S, Mondal A, Roy AN, Bar N, Das SK (2018) Sustainable bioremediation of Cd(II) from aqueous solution using natural waste materials: Kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, toxicity studies and GA-ANN hybrid modeling. Environ Tech & Innovation 11:83–104
Nag S, Bar N, Das SK (2019) Sustainable bioremadiation ofCd(II) in fixed bed column using green adsorbents: Application of Kinetic models and GA-ANN technique. Environ Technol Innov 13:130–145
Nag S, Bar N, Das SK (2020) Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution using green adsorbents in continuous bed column - Statistical and GA-ANN hybrid modeling. Chem Eng Sci 226:115904
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Das SK (2008) Adsorption of Pb(II) by sawdust and neem bark from aqueous solutions. Environ Prog 27(3):313–328
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Mandal S, Das SK (2009) The sorption of lead (II) ions on rice husk ash. J Hazard Mater 163:1254–1264
Pang X, Sellaoui L, Franco D, Dotto GL, Georgin J, Bajahzar A, Belmabrouk H, LamineA B, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, LiZ (2018) Adsorption of crystal violet on biomasses from pecan nutshell, para chestnut husk, araucaria bark and palm cactus: experimental study and theoretical modeling via monolayer and double layer statistical physics models. Chem Eng J 378:122101
Pehlivan E, Altun T, Parlayici S (2009) Utilization of barley straws as biosorbents for Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions. J Hazard Mater 164:982–986
Polanyi M (1932) Section III—theories of the adsorption of gases. A general survey and some additional remarks. Trans Faraday Soc 28:316–333
Rudzinski W, Panczyk T (2002) The Langmuirian adsorption kinetics revised: a farewell to the XXth century theories? Adsorption 8:23–34
Sellaoui L, Franco D, Ghalla H, Georgin J, Netto MS, Dotto GL, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Belmabrouk H, Bajahzar A (2020) Insights of the adsorption mechanism of methylene blue on brazilian berries seeds: experiments, phenomenological modelling and DFT calculations. Chem Engg J 394:125011
Shahul HK, Sivakumar S, Satheesh KR (2016) Isotherm and kinetic studies on the adsorption of Commassie Brilliant Blue on commercial activated carbon and kaolin. Global J Adv Res 3:723–731
Siddiqui SI, Chaudhry SA (2018) A review on graphene oxide and its composites preparation and their use for the removal of As3+and As5+ from water under the effect of various parameters: Application of isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics. Process Saf Environ Protect 119:138–163
Siddiqui SI, Chaudhry SA (2019) Nanohybrid composite Fe2O3-ZrO2/BC for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and adsorptive removal of arsenic and dyes from water. J Clean Prod 223:849–868
Singha B, Das SK (2012) Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural biosorbents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(6):2212–2226
Singha B, Bar N, Das SK (2015) The use of artificial neural network (ANN) for modeling of Pb(II) adsorption in batch process. J Mol Liquids 211:228–232
Tempkin MI, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst, Acta Phys Chim USSR12, pp. 327–356
Venckatesh R, Amudha T, Sivaraj R, Chandramohan M, Jambulingam M (2010) Kinetics and equilibrium studies of adsorption of direct Red-28 onto Punicagranatum Carbon. Int J Engg Sci Technol 2(6):2040–2050
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanitary Eng Div 89:31–60
Yang X, Wan Y, Zheng Y, He F, Yu Z, Huang J, Wang H, Ok YS, Jiang Y, Gao B (2019) Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Chem Eng J 366:608–621
Zainuddin MF, Shamsudin R, Mokhtar MN, Ismail D (2014) Physicochemical properties of pineapple plant waste fibres from the leaves and stems of different varieties. Bio Resour 9:5311–5324
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD is a research scholar, planned and executed experiments and data analysis, prepared the draft manuscript. NB performed software applications. SKD was involved in conceiving the idea, planning the experiments, overall supervision and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Gaurav Sharma.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, A., Bar, N. & Das, S.K. Adsorptive removal of Pb(II) ion on Arachis hypogaea’s shell: Batch Experiments, statistical, and GA modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 537–550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03842-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03842-w