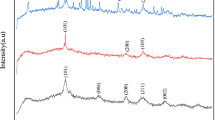
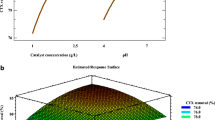
Abstract
Indiscriminate consumption of antibiotics, their discharge into the environment, and the development of resistant genes in a natural ecosystem are ever-increasing global threats. Metronidazole is applied to treat infection diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. In this research, TiO2/Fe+3 was used as a heterogeneous nano-photocatalyst for the degradation of metronidazole with UV-C radiation as the energy source. Parameters tested in the removal process were pH = 3, 7, and 11; antibiotic concentration of 80 mg/L; contact times of 30, 60, 90, and 120 min; and nano-photocatalyst of TiO2/Fe+3 with concentrations of 30, 60, 90, 250, 500, 750, and 1000 mg/L. The photocatalytic degradation kinetics of metronidazole was studied. Optimal conditions were achieved on synthetic solutions; then, all experiments were performed on wastewater from the pharmaceutical industry. Antibiotic concentrations were measured using an HPLC device. All tests were replicated three times according to the standard methods of water and wastewater experiments, the 20th edition. Data were analyzed using SPSS 19 and the statistical test ANOVA. The optimal conditions for removing metronidazole from synthetic solution included, 500 mg/L for nano-photocatalyst concentration, pH = 11 and 120 min contact time. Removal efficiency of antibiotic under optimal conditions was 97% from synthetic solutions and 69.85% from pharmaceutical wastewater. Finally, Fe+3–TiO2/UV-C were identified as a promising technique for the removal of metronidazole with high efficiency from aqueous solutions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baghapour MA, Shamsedini N, Dehghani M, Nasseri S, Moghaddam MS (2016) Optimization of atrazine degradation in the aqueous phase using titanium catalyst doped with iron (Fe+3–TiO2). Health Scope 5:e33065. https://doi.org/10.17795/jhealthscope-33065
Bendesky A, Menéndez D, Ostrosky-Wegman P (2002) Is metronidazole carcinogenic? Mutat Res Rev 511:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5742(02)00007-8
Carrales-Alvarado DH, Ocampo-Pérez R, Leyva-Ramos R, Rivera-Utrilla J (2014) Removal of the antibiotic metronidazole by adsorption on various carbon materials from aqueous. phase Colloid. Interface Sci 436:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.08.023
Cheng W, Yang M, **e Y, Liang B, Fang Z, Tsang EP (2013) Enhancement of mineralization of metronidazole by the electro-Fenton process with a Ce/SnO2–Sb coated titanium anode. Chem Eng J 220:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.055
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Ka I, El Khakani MA (2012) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of chlortetracycline using Ti/TiO2 nanostructured electrodes deposited by means of a pulsed laser deposition process. J Hazard Mater 199–200:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.022
Dehghani fard E, Jonidi Jafari A, Rezae Kalantari R, Gholami M, Esrafili A (2012) Photocatalytic removal of aniline from synthetic wastewater using ZnO nanoparticle under ultraviolet irradiation. Iran J Health Environ 5:167–178
Dehghani M, Ahmadi M, Nasseri S (2013) Photodegradation of the antibiotic penicillin G in the aqueous solution using UV-A radiation. Iran J Health Sci 1:43–50. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.jhs.1.3.43
Dehghani M, Nasseri S, Ahmadi M, Samaei M, Anushiravani A (2014) Removal of penicillin G from aqueous phase by Fe+3–TiO2/UV-A process. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336x-12-56
Dimitrakopoulou D, Rethemiotaki I, Frontistis Z, Xekoukoulotakis NP, Venieri D, Mantzavinos D (2012) Degradation, mineralization and antibiotic inactivation of amoxicillin by UV-A/TiO2 photocatalysis. J Environ Manag 98:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.01.010
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2010a) Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for treatment of antibiotic aqueous solution. Desalination 256:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.02.019
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2010b) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution using UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2/TiO2 photocatalysis. Desalination 252:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.11.003
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2011) The feasibility of using combined TiO2 photocatalysis-SBR process for antibiotic wastewater treatment. Desalination 272:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.020
Fang Z, Chen J, Qiu X, Qiu X, Cheng W, Zhu L (2011) Effective removal of antibiotic metronidazole from water by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. Desalination 268:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.09.051
Farzadkia M, Bazrafshan E, Esrafili A, Jae-Kyu Y, Hirzad-Siboni M (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of Metronidazole with illuminated TiO2 nanoparticles. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0194-y
Gad-Allah TA, Ali MEM, Badawy MI (2011) Photocatalytic oxidation of ciprofloxacin under simulated sunlight. J Hazard Mater 186:751–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.066
Giraldo AL, Penuela GA, Torres-Palma RA, Pino NJ, Palominos RA, Mansilla HD (2010) Degradation of the antibiotic oxolinic acid by photocatalysis with TiO2 in suspension. Water Res 44:5158–5167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.011
Gonçalves AG, Órfao JJM, Pereira MFR (2012) Catalytic ozonation of sulphamethoxazole in the presence of carbon materials: catalytic performance and reaction pathways. J Hazard Mater 239–240:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.057
Hapeshi E, Achilleos A, Vasquez MI, Michael C, Xekoukoulotakis NP, Mantzavinos D, Kassinos D (2010) Drugs degrading photocatalytically: kinetics and mechanisms of ofloxacin and atenolol removal on titania suspensions. Water Res 44:1737–1746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.044
Haque MM, Muneer M (2007) Photodegradation of norfloxacin in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide. J Hazard Mater 145:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.086
Hashemi M, Okhovat N, Golpayegani AA (2015) Photocatalytic decomposition of Metronidazole in aqueous solutions using titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Mater Environ Sci 6:792–799
Hoseini M, Nabizadeh R, Nazmara S, Safari GH (2013) Influence of under pressure dissolved oxygen on trichloroethylene degradation by the H2O2/TiO2 process. J Environ Health Sci Eng 11:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336x-11-38
Hu L, Flanders PM, Miller PL, Strathmann TJ (2007) Oxidation of sulfamethoxazole and related antimicrobial agents by TiO2 photocatalysis. Water Res 41:2612–2626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.026
Klavarioti M, Mantzavinos D, Kassinos D (2009) Removal of residual pharmaceuticals from aqueous systems by advanced oxidation processes. Environ Int 35:402–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.009
Konstantinou I, Albanis T (2002) Photocatalytic transformation of pesticides in aqueous titanium dioxide suspensions using artificial and solar light: intermediates and degradation pathways. Appl Catal B 1310:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0926-3373(02)00266-7
Mahvi AH, Ghanbarian M, Nasseri S, Khairi A (2009) Mineralization and discoloration of textile wastewater by TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 239:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.002
Malakootian M, Mansuri F (2015) Hexavalent chromium removal By TiO2 photocatalytic reduction and the effect of phenol and humic acid on its removal efficiency. IJEHE 4:19. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9183.157720
Malakootian M, Yaghmaeian K, Mansoori F (2014) Effect of cations Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the removal efficiency of humic acid by UV/TiO2. J Shahrekord Univ Med Sci 16:9–20
Malakootian M, Bahraini S, Zarrabi M, Malakootian M (2016a) Removal of Tetracycline antibiotic from aqueous solutions using natural and modified pumice with magnesium chloride. JJHR 10:46–56. https://doi.org/10.17795/jjhr-37583
Malakootian M, Ehrampoush M, Hossaini H, Pourshaban Mazandarani M (2016b) Acetaminophen removal from aqueous solutions by TiO2-X photo catalyst. Tolooebehdasht 14:200–213
Malakootian M, Pourshaban-Mazandarani M, Hossaini H, Ehrampoush MH (2016c) Preparation and characterization of TiO2 incorporated 13X molecular sieves for photocatalytic removal of acetaminophen from aqueous solutions. Process Saf Environ Prot 104(Part A):334–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.09.018
Malakootian M, Bahraini S, Nuri Sepehr M (2017) Capacity of natural and modified zeolite with cationic surfactant in removal of antibiotic tetracycline from aqueous solutions. Koomesh 17:779–788
Mao W-J, Lv P-C, Shi L, Li H-Q, Zhu H-L (2009) Synthesis, molecular docking and biological evaluation of metronidazole derivatives as potent Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 17:7531–7536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2009.09.018
Martinez JL (2009) Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ Pollut 157:2893–2902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.051
Méndez-Arriaga F, Otsu T, Oyama T, Gimenez J, Esplugas S, Hidaka H, Serpone N (2011) Photooxidation of the antidepressant drug Fluoxetine (Prozac®) in aqueous media by hybrid catalytic/ozonation processes. Water Res 45:2782–2794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.030
Nasseri S, Hemmati Borji S, Mahvi AH, Nabizadeh R, Javadi AH (2011) Investigation of photocatalytic degradation of phenol by Fe(III)-doped TiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336x-12-101
Peterson JW, Petrasky LJ, Seymour MD, Burkhart RS, Schuiling AB (2012) Adsorption and breakdown of penicillin antibiotic in the presence of titanium oxide nanoparticles in water. Chemosphere 87:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.044
Salaices M, Serrano B, Lasa H (2001) Photo-catalytic conversion of organic pollutants Extinction coefficients and quantum efficiencies. Ind Eng Chem Res 40:5455–5464. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0102551
Saien J, Shahrezaei F (2012) Organic pollutants removal frompetroleum refinerywastewater with nanotitania photocatalyst and UV light emission. Int J Photoenergy 2012:5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/703074
Sood S, Umar A, Mehta SK, Kansal SK (2015) Highly effective Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles photocatalysts for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic compounds. J Colloid Interface Sci 450:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.018
Thakur RS, Chaudhary R, Singh C (2010) Fundamentals and applications of the photocatalytic treatment for the removal of industrial organic pollutants and effects of operational parameters: a review. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3467511
Yang L, Yu LE, Ray MB (2008) Degradation of paracetamol in aqueous solutions by TiO2 photocatalysis. Water Res 42:3480–3488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.04.023
Zhang X, Wu F, Wu X, Chen P, Deng N (2008) Photodegradation of acetaminophen in TiO2 suspended solution. J Hazard Mater 157:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.098
Zhou M, Yu J, Cheng B, Yu H (2005) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped mesoporous titanium dioxide nanocrystalline photocatalysts. Mater Chem Phys 93:159–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.03.007
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted at the Environmental Health Engineering Research Center and was sponsored by the Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology of Kerman University of Medical Sciences. The authors’ appreciation is expressed here to the Vice Chancellor and to all university staff who provided assistance to make this study possible. The authors also wish to acknowledge the cooperation of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences—Health and Nutrition Faculty, the assistance of Dr. Mohammad Reza Kazemi, Head of the Statistics Sector and Financial Deputy of Fasa University, Pars Daru Pharmaceutical Company, and Dana Pharmaceutical Company which greatly facilitated this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Abhishek RoyChowdhury.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malakootian, M., Olama, N., Malakootian, M. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of metronidazole from aquatic solution by TiO2-doped Fe3+ nano-photocatalyst. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 4275–4284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1836-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1836-2