Abstract
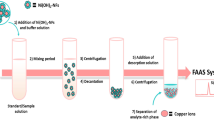
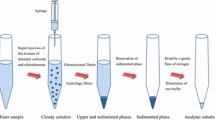
In the present work, a new microextraction technique, namely in situ-produced CO2-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction was introduced for the extraction and preconcentration of cobalt, nickel, and copper from aqueous samples followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection. The proposed method relies on the CO2 gas produced due to a chemical reaction as the disperser agent instead of the disperser solvent used in the conventional dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Initially, a solid mixture of tartaric acid and sodium bicarbonate was placed in the bottom of a dry conical glass test tube. Then µL level of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane as the extraction solvent was added into the tube. An aqueous solution of the analytes containing sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (as chelating agent) was transferred into the tube. The reaction between tartaric acid and sodium bicarbonate was immediately occurred, and the produced CO2 led to dispersion of the extraction solvent as tiny droplets into the sample which resulted in extraction of the analytes into the organic solvent. The cloudy solution was centrifuged, and the sedimented phase was analyzed by the instrumental analytical method. Under the optimum conditions, the calibration curves were linear in the ranges of 20–300, 20–200, and 15–250 ng L−1 for Co2+, Ni2+, and Cu2+, respectively. Repeatability of the proposed method, expressed as relative standard deviation, ranged from 2.3 to 4.6 and 4.5–5.6% for intra- and inter-day (n = 6, C = 50 ng L−1) precisions, respectively. Moreover, the detection limits and enrichment factors of the selected analytes were obtained in the ranges of 6.2–12 and 139–150 ng L−1, respectively. The accuracy of the developed procedure was checked by analyzing NRCC-SLRS4 Riverine water as a certified reference material. Finally, the proposed method was successfully applied for the simultaneous analysis of the selected analytes in environmental water and fruit juice samples. The relative recoveries obtained for the analytes in the spiked samples were within in the range of 84–107%.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AALLME:
-
Air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction
- 1,2-DBE:
-
1,2-Dibromoethane
- DLLME:
-
Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
- ER:
-
Extraction recovery
- GFAAS:
-
Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry
- LLE:
-
Liquid–liquid extraction
- LPME:
-
Liquid-phase microextraction
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- MSPD:
-
Matrix solid-phase dispersion
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SALLME:
-
Salt-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction
- SDDTC:
-
Sodium diethyldithiocarbamate
- SPE:
-
Solid-phase extraction
- SPME:
-
Solid-phase microextraction
- SBSE:
-
Stir bar sorptive extraction
- 1,1,2,2-TCE:
-
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
- 1,1,2-TCE:
-
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
- UDSA–DLLME:
-
Up-and-down shaker-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
References
Y. Wang, X. Ke, X. Zhou, J. Li, J. Ma, J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 20, S145 (2016)
C.E. Borba, R. Guirardello, E.A. Silva, M.T. Veit, C.R.G. Tavares, Biochem. Eng. J. 30, 184 (2006)
F. Fu, Q. Wang, J. Environ. Manag. 92, 407 (2011)
A.T. Paulino, F.A.S. Minasse, M.R. Guilherme, A.V. Reis, E.C. Muniz, J. Nozaki, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 301, 479 (2006)
A. Oliva, A. Molinari, F. Zuniga, P. Ponce, Microchim. Acta 140, 201 (2002)
T. Daşbaşı, Ş. Saçmacı, N. Çankaya, C. Soykan, Food Chem. 211, 68 (2016)
D. Citak, M. Tuzen, Food Chem. Toxicol. 48, 1399 (2010)
A.K. Malik, V. Kaur, N. Verma, Talanta 68, 842 (2006)
X.P. Yao, Z.J. Fu, Y.G. Zhao, L. Wang, L.Y. Fang, H.Y. Shen, Talanta 97, 124 (2012)
X. Huang, N. Qiu, D. Yuan, B. Huang, Talanta 78, 101 (2009)
M.A. Farajzadeh, S.M. Sorouraddin, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Microchim. Acta 181, 829 (2014)
P. Liang, R. Liu, J. Cao, Microchim. Acta 160, 135 (2008)
Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Hu, L. Ni, J. Han, T. Chen, H. Chen, Y. Liu, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 12, 371 (2015)
J. Abulhassani, J.L. Manzoori, M. Amjadi, J. Hazard. Mater. 176, 481 (2010)
M. Rezaee, Y. Assadi, M.R. Milani Hosseini, E. Aghaee, F. Ahmadi, S. Berijani, J. Chromatogr. A 1116, 1 (2006)
Y. Yamini, M. Rezaee, A. Khanchi, M. Faraji, A. Saleh, J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 2358 (2010)
H. Sereshti, V. Khojeh, S. Samadi, Talanta 83, 885 (2011)
M. Mirzaei, M. Behzadi, N.M. Abadi, A. Beizaei, J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 1739 (2011)
M. Shamsipur, N. Fattahi, M. Sadeghi, M. Pirsaheb, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 11, 249 (2014)
S.P. Chu, W.C. Tseng, P.H. Kong, C.K. Huang, J.H. Chen, P.S. Chen, S.D. Huang, Food Chem. 185, 377 (2015)
N. Wei, X.E. Zhao, S. Zhu, Y. He, L. Zheng, G. Chen, J. You, S. Liu, Z. Liu, Talanta 161, 253 (2016)
Naeemullah, M. Tuzen, T.G. Kazi, D. Citak, M. Soylak, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 28, 1441 (2013)
M.A. Farajzadeh, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Anal. Chim. Acta 728, 31 (2012)
M. Soylak, E. Kiranartligiller, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42, 175 (2017)
J. Xue, X. Chen, W. Jiang, F. Liu, H. Li, J. Chromatogr. B 975, 9 (2015)
G.L. Aragonés, R. Lucena, S. Cárdenas, M. Valcárcel, Anal. Chim. Acta 807, 61 (2014)
K. Medinskaia, C. Vakh, D. Aseeva, V. Andruch, L. Moskvin, A. Bulatov, Anal. Chim. Acta 902, 129 (2016)
M. Gupta, A. Jain, K.K. Verma, Talanta 80, 526 (2009)
H. Ma, Y. Li, H. Zhang, S.M. Shah, J. Chen, J. Chromatogr. A 1358, 14 (2014)
I. Rapp, Ch. Schlosser, D. Rusiecka, M. Gledhill, E.P. Achterberg, Anal. Chim. Acta 976, 1 (2017)
L. Hejazi, D.E. Mohammadi, Y. Yamini, R.G. Brereton, Talanta 62, 185 (2004)
S.M. Sorouraddin, M.A. Farajzadeh, T. Okhravi, Talanta 175, 359 (2017)
M. Niinae, T. Suzuki, Y. Inoue, H. Saito, J. Shibata, J. Min. Mater. Process. Inst. Jpn. 130, 16 (2014)
V.T. Nguyen, J.C. Lee, J. Jeong, B.S. Kim, B.D. Pandey, Met. Mater. Int. 20, 357 (2014)
P. Liang, J. Yu, E. Yang, Y. Mo, Food Anal. Methods 7, 1506 (2014)
H. Jiang, Y. Qin, B. Hu, Talanta 74, 1160 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Research Office at the University of Tabriz for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorouraddin, S.M., Farajzadeh, M.A. & Ghorbani, M. In situ-produced CO2-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for extraction and preconcentration of cobalt, nickel, and copper ions from aqueous samples followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry determination. J IRAN CHEM SOC 15, 201–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1224-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1224-8