Abstract
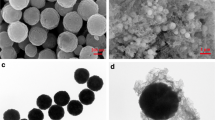
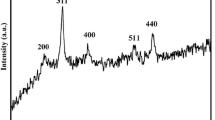
In this study, a simple approach was described for the fabrication of CaSO4/Fe0 composite used as a novel adsorbent for the reductive removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions. The magnetic CaSO4/Fe0 composite was prepared by a solid state reaction at 550 °C in the H2 atmosphere using CaSO4·2H2O/α-FeOOH as a precursor. The structure and morphology of the as-synthesized magnetic composite were characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy and a superconducting quantum interference device, respectively. Results showed that the CaSO4/Fe0 composite with a rod-like shape could be easily acquired from the CaSO4·2H2O/α-FeOOH precursor with the ratio of 1:0.5 at 550 °C in the H2 atmosphere for 1 h. The CaSO4/Fe0 composite exhibited enhanced performance relevant to the reductive removal of Cu2+. The removal amount of Cu2+ increased linearly with increasing of concentration of Cu2+ in wastewater. Possible removal mechanisms were proposed as follows: (1) the formation of Cu2O by fast reduction of Cu2+ with Fe0 nanoparticles on interface of CaSO4/Fe0 composite, (2) proper adsorption of Cu2+ on the surface of CaSO4/Fe0 composite, (3) the hydrous iron oxide (HIO) such as Fe (OH)3 and FeOOH in situ generated on the rest of CaSO4/Fe0 composite could further adsorb Cu2+ from wastewater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.H. Liou, S.-L. Lo, C.-J. Lin, W.H. Kuan, S.C. Weng, J. Hazard. Mater. 127, 102 (2005)
Q. Zhou, Y. Chen, M. Yang, W. Li, L. Deng, Bioresour. Technol. 136, 413 (2013)
J. Theron, J. Walker, T. Cloete, Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 34, 43 (2008)
M.-Q. Jiang, Q.-P. Wang, X.-Y. **, Z.-L. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater. 170, 332 (2009)
R. Crane, T. Scott, J. Hazard. Mater. 211, 112–125 (2012)
Ç. Üzüm, T. Shahwan, A.E. Eroğlu, I. Lieberwirth, T.B. Scott, K.R. Hallam, Chem. Eng. J. 144, 213 (2008)
C. Liu, X. Li, B. Ma, A. Qin, C. He, Appl. Surf. Sci. 321, 158 (2014)
Y.-F. Su, C.-Y. Hsu, Y.-H. Shih, Chemosphere 88, 1346 (2012)
L. Xu, J. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 256 (2011)
R. Singh, V. Misra, R.P. Singh, Environ. Monit. Assess. 184, 3643 (2012)
M.A. Ramos, W. Yan, X.-Q. Li, B.E. Koel, W.-X. Zhang, J. Phys. C 113, 14591 (2009)
Y. Li, J. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Hazard. Mater. 227, 211 (2012)
L.-N. Shi, X. Zhang, Z.-L. Chen, Water Res. 45, 886 (2011)
Y. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Li, G. Sheng, X. Zheng, Chemosphere 92, 368 (2013)
Z. Chen, T. Wang, X. **, Z. Chen, M. Megharaj, R. Naidu, J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 398, 59 (2013)
Ç. Üzüm, T. Shahwan, A.E. Eroğlu, K.R. Hallam, T.B. Scott, I. Lieberwirth, Appl. Clay Sci. 43, 172 (2009)
X. Cai, Y. Gao, Q. Sun, Z. Chen, M. Megharaj, R. Naidu, Chem. Eng. J. 244, 19 (2014)
L. Wu, L. Liao, G. Lv, F. Qin, J. Contam. Hydrol. 179, 1 (2015)
T. Liu, Z.-L. Wang, Y. Sun, Chem. Eng. J. 263, 55 (2015)
T. Liu, Z.-L. Wang, X. Yan, B. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J. 245, 34 (2014)
T. Liu, X. Yang, Z.-L. Wang, X. Yan, Water Res. 47, 6691 (2013)
N. Horzum, M.M. Demir, M. Nairat, T. Shahwan, RSC Adv. 3, 7828 (2013)
Y. Sun, C. Ding, W. Cheng, X. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater. 280, 399 (2014)
W. Wang, Y. Cheng, T. Kong, G. Cheng, J. Hazard. Mater. 299, 50 (2015)
Y. Kuang, J. Du, R. Zhou, Z. Chen, M. Megharaj, R. Naidu, J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 447, 85 (2015)
R. Justin Joseyphus, K. Shinoda, D. Kodama, B. Jeyadevan, Mater. Chem. Phys. 123, 487 (2010)
B. Kandapallil, R.E. Colborn, P.J. Bonitatibus, F. Johnson, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 535 (2015)
F. Liu, P. Cao, H. Zhang, J. Tian, C. **ao, C. Shen, J. Li, Hongjun Gao, Adv. Mater. 17, 1893 (2005)
C.-J. Jia, L.-D. Sun, F. Luo, X.-D. Han al, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16968 (2008)
M. Bhaumik, R.I. M, A. Maity, Chem. Eng. J. 260, 716 (2015)
K. Choi, W. Lee, J. Hazard. Mater. 211, 146 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge with thanks support of the Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Anhui Province (Grant No. KJ2015A170), the Natural Science Foundation of Hefei University (Grant No. 8ZR) and the National College Students Innovation Project (Grant No. 201411059019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Zhuang, L., Yao, Z. et al. High-yield preparation of rod-like CaSO4/Fe0 magnetic composite for effective removal of Cu2+ in wastewater. J IRAN CHEM SOC 13, 2185–2191 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0936-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-0936-5